Computer-Graphics
Question 1 |
Given below are different properties of 3D projections from A.D. Identify the correct order on the basis of property true of
(i) a perspective projection only
(ii) an orthographic projection only
(iii) both orthographic and projective transformations and
(iv) neither orthographic nor projective transformation, respectively.
(A) Straight lines are mapped to straight lines.
(B) Distance and angles are (in general) preserved.
(C) Far away objects appear the same size as closer ones.
(D) Requires homogeneous coordinates in order for it to be encoded into linear transformation.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
A | D, C, B, A |
B | B, C, D, A
|
C | D, C, A, B |
D | C, D, B, A |
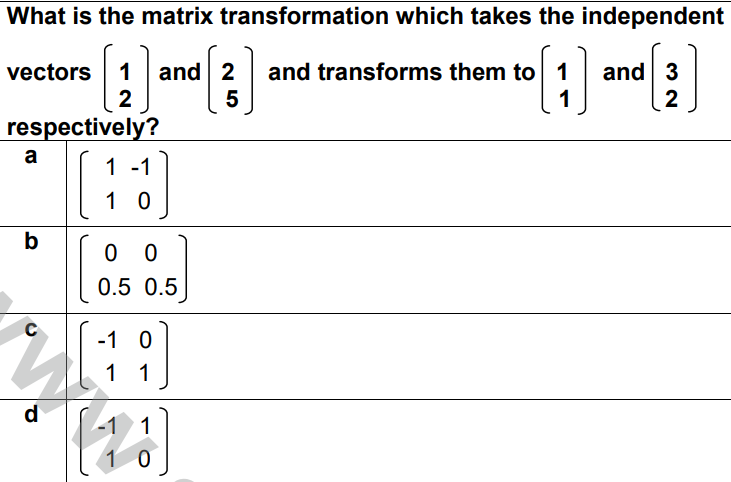
Question 2 |
Match List-I with List-II. List-I gives 33 matrices representing 2D transformations and List-II shows the corresponding transformation diagrams.
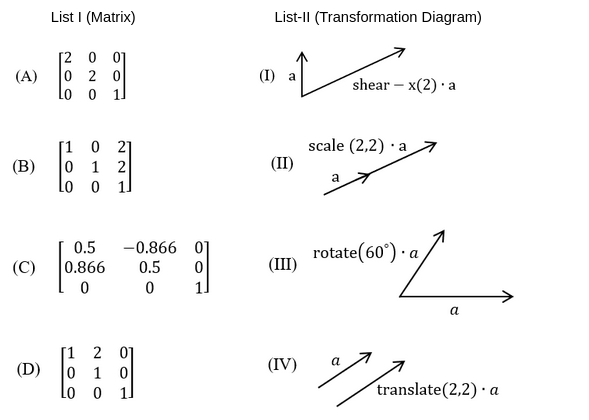
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:

Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
A | A-IV, B-II, C-III, D-I |
B | A-IV, B-III, C-II, D-I
|
C | A-III, B-II, C-IV, D-I |
D | A-II, B-IV, C-III, D-I |
Question 3 |
Given below are two statements:
Statement I: Bezier curves are curves that interpolate all of their control points
Statement II: A cubic bezier curve has four control points.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below
A | Both statement I and Statement II are true |
B | Both Statement I and Statement II are false |
C | Statement I is correct but Statement II is false |
D | Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is true |
Question 4 |
Concerning phong shading and gouraud shading in a 3D scene, which of the following statements are true?
(A) Gouraud shading requires more computation than phong shading
(B) Gouraud shading linearly interpolates the color of an interior pixel from the color at the vertices.
(C) Phong shading interpolates over the normal vectors specified at the vertices.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
A | (A) and (B) only |
B | (A) and (C) only |
C | (B) and (C) only |
D | (A), (B) and (C) |
Question 5 |
n the context of 3D Computer graphics, which of the following statements is/are correct?
A) Under perspective projection, each set of parallel lines in the object do not stay parallel in the image (except those that are parallel to the view plane to start with).
B) Applying a perspective transformation in the graphics pipeline to a vertex involves dividing by its ‘z’ coordinate.
C) Perspective transformation is a linear transformation.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
A | (A) and (B) only |
B | (A) and (C) only |
C | (B) and (C) only |
D | (A), (B) and (C) |
Question 6 |
Consider the Breshenham’s circle generation algorithm for plotting a circle with centre (0, 0) and radius ‘r’ units in first quadrant. If the current point is (xi , yi ) and decision parameter is pi then what will be the next point (xi + 1, yi + 1 + 1) and updated decision parameter pi + 1 for pi ≥ 0?
A | xi + 1 = xi+ 1 yi + 1 = yi pi + 1 = pi + 4xi + 6 |
B | xi + 1 = xi + 1 yi + 1 = yi - 1 pi + 1 = pi + 4(xi - yi) + 10 |
C | xi + 1 = xi yi + 1 = yi - 1 pi + 1 = pi + 4(xi - yi) + 6 |
D | xi + 1 = xi - 1 yi + 1 = yi pi + 1 = pi + 4(xi - yi) + 10 |
Question 6 Explanation:
Write the steps required to scan - convert a circle using Bresenham’s algorithm.
Set the initial values of the variables: (h, k) = coordinates of circle center; x=0; y=circle radius r and d = 3 - 2r.
Test to determine whether the entire circle has been scan-converted. If x>y, stop.
Plot the eight points, found by symmetry with respect to the center (h, k), at the current (x, y) coordinates:
Plot(x+h, y+k) Plot(-x+h, -y+k)
Plot(y+h, x+k) Plot(-y+h, -x+k)
Plot(-y+h, x+k) Plot(y+h, -x+k)
Plot(-x+h, y+k) Plot(x+h, -y+k)
Compute the location of the next pixel. If d<0, then d=d+4x+6 and x=x+1. If d≥0, then d=d+4(x-y)+10, x=x+1 and y=y-1.
Go to step 2.
Set the initial values of the variables: (h, k) = coordinates of circle center; x=0; y=circle radius r and d = 3 - 2r.
Test to determine whether the entire circle has been scan-converted. If x>y, stop.
Plot the eight points, found by symmetry with respect to the center (h, k), at the current (x, y) coordinates:
Plot(x+h, y+k) Plot(-x+h, -y+k)
Plot(y+h, x+k) Plot(-y+h, -x+k)
Plot(-y+h, x+k) Plot(y+h, -x+k)
Plot(-x+h, y+k) Plot(x+h, -y+k)
Compute the location of the next pixel. If d<0, then d=d+4x+6 and x=x+1. If d≥0, then d=d+4(x-y)+10, x=x+1 and y=y-1.
Go to step 2.
Question 7 |
A point P(5, 1) is rotated by 90° about a pivot point (2, 2). What is the coordinate of new transformed point P′ ?
A | (3, 5) |
B | (5, 3) |
C | (2, 4) |
D | (1, 5) |
Question 7 Explanation:
Rotation around a pivot point (2, 2) can be represented as:
(h, k) = (2, 2)

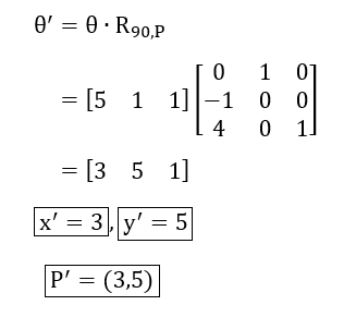
(h, k) = (2, 2)

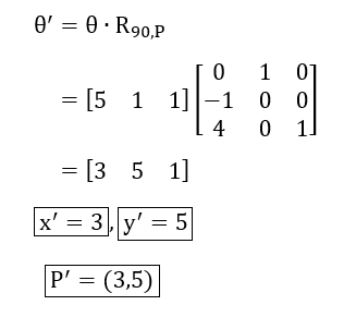
Question 8 |
Let R be the rectangular window against which the lines are to be clipped using 2D Sutherland-Cohen line clipping algorithm. The rectangular window has a lower left-hand corner at (– 5, 1) and upper right-hand corner at (3, 7). Consider the following three lines for clipping with the given endpoint coordinates:
Line AB : A (– 6, 2) and B (–1, 8)
Line CD : C (– 1, 5) and D (4, 8)
Line EF : E (–2, 3) and F (1, 2)
Which of the following line(s) is/are candidate for clipping?
Line AB : A (– 6, 2) and B (–1, 8)
Line CD : C (– 1, 5) and D (4, 8)
Line EF : E (–2, 3) and F (1, 2)
Which of the following line(s) is/are candidate for clipping?
A | AB |
B | CD |
C | EF |
D | AB and CD |
Question 9 |
In perspective projection, if a line segment joining a point which lies in front of the viewer to a point in back of the viewer is projected to a broken line of infinite extent. This is known as _______.
A | View confusion |
B | Vanishing point |
C | Topological distortion |
D | Perspective foreshortening |
Question 10 |
Let us consider that the original point is (x, y) and new transformed point is (x′, y′). Further, Shx and Shy are shearing factors in the x and y directions. If we perform the y-direction shear relative to x = xref then the transformed point is given by _______.
A | x′ = x + Shx ⋅ (y – yref) y′ = y |
B | x′ = x y′ = y ⋅ Shx |
C | x′ = x y′ = Shy (x – xref) + y |
D | x′ = Shy ⋅ y y′ = y ⋅ (x – xref) |
Question 10 Explanation:

Question 11 |
Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct with reference to curve generation?
I. Hermite curves are generated using the concepts of interpolation.
II. Bezier curves are generated using the concepts of approximation.
III. The Bezier curve lies entirely within the convex hull of its control points.
IV. The degree of Bezier curve does not depend on the number of control points.
I. Hermite curves are generated using the concepts of interpolation.
II. Bezier curves are generated using the concepts of approximation.
III. The Bezier curve lies entirely within the convex hull of its control points.
IV. The degree of Bezier curve does not depend on the number of control points.
A | I, II and IV only |
B | II and III only |
C | I and II only |
D | I, II and III only |
Question 12 |
A triangulation of a polygon is a set of T chords that divide the polygon into disjoint triangles. Every triangulation of n-vertex convex polygon has _____ chords and divides the polygon into _____ triangles.
A | n – 2, n – 1 |
B | n – 3, n – 2 |
C | n – 1, n |
D | n – 2, n – 2 |
Question 13 |
Which of the following techniques is used for Clipping?
A | Stack based Seed |
B | Scan Line Seed |
C | Sutherland–Cohen |
D | Inverse Scaling
|
Question 13 Explanation:
The Sutherland–Cohen algorithm is a well-known method used in computer graphics to perform line clipping.
Clipping is the process of determining the portion of a geometric object (like a line segment, polygon, or text) that is visible within a rectangular area, called the clipping window. Any part of the object outside this window is discarded.
Clipping is the process of determining the portion of a geometric object (like a line segment, polygon, or text) that is visible within a rectangular area, called the clipping window. Any part of the object outside this window is discarded.
Question 14 |
Match List I with List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
| List I | List II |
| A. Oblique Projection | I. When the direction of projection is so chosen that the lines perpendicular to the plane of projection are foreshortened. |
| B. Cavelier Projection | II. When the direction of projection is so chosen that there is no foreshortening of lines perpendicular to the plane of projection. |
| C. Cabinet Projection | III. When the direction of projection is perpendicular to the plane of projection. |
| D. Orthographic Projection | IV. When the angle between the projectors and the plane of projection is not equal to 90°. |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
A | A-III, B-II, C-IV, D-I
|
B | A-IV, B-II, C-I, D-III
|
C | A-III, B-I, C-IV, D-II |
D |
A-IV, B-I, C-III, D-II
|
Question 15 |
Arrange the 2-D viewing transformation pipeline.
A. Convert to viewing coordinates
B. Map viewing coordinates to normalized viewing coordinates using window - viewpoint specifications
C. Construct world - coordinates scene using modeling - coordinates transformations
D. Map normalized viewpoint to device coordinates
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
A. Convert to viewing coordinates
B. Map viewing coordinates to normalized viewing coordinates using window - viewpoint specifications
C. Construct world - coordinates scene using modeling - coordinates transformations
D. Map normalized viewpoint to device coordinates
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
A | D,C,B,A
|
B | D,C,A,B
|
C | D,A,B,C |
D | B,C,A,D |
Question 16 |
The light given off by the phosphor during exposure to the electron beam is known as
A | Fluorescence |
B | Phosphorescence |
C | Persistence |
D | Retracing |
Question 17 |
The major adverse side effects of scan conversion are :-
A. Staircase appearance
B. Unequal brightness of slanted lines
C. Picket fence problem
D. Rasterization
E. Pre-filtering and Post-filtering
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
A. Staircase appearance
B. Unequal brightness of slanted lines
C. Picket fence problem
D. Rasterization
E. Pre-filtering and Post-filtering
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
A | A & B only |
B | A, B & C only |
C | B, C & D only |
D | C, D & E only
|
Question 18 |
Consider the rectangle with vertices (0,0),(0,2),(3,0),(3,2).There is a scaling of 2 towards the x-axis and 3 towards the y-axis. The new coordinates of the rectangle are
A | (0,0)(6,0)(0,4)(6,4)
|
B | (0,0)(6,0)(0,4)(3,2)
|
C | (0,0)(6,0)(0,6)(6,6)
|
D | (0,0)(4,0)(0,6)(4,6) |
Question 18 Explanation:
To scale a rectangle by a factor of 2 along the x-axis and 3 along the y-axis, you can apply the scaling factor to each vertex individually. The scaling operation multiplies the x-coordinate by 2 and the y-coordinate by 3 for each vertex.
Given the original vertices of the rectangle:
(0, 0)
(0, 2)
(3, 0)
(3, 2)
After scaling, the new coordinates are:
(0 * 2, 0 * 3) = (0, 0)
(0 * 2, 2 * 3) = (0, 6)
(3 * 2, 0 * 3) = (6, 0)
(3 * 2, 2 * 3) = (6, 6)
So, the correct new coordinates of the rectangle after scaling are:
(0, 0) (0, 6) (6, 0) (6, 6)
The option that matches these coordinates is:
(0, 0) (0, 6) (6, 0) (6, 6)
Question 19 |
The clipping process in computer graphics is used for
A | Adding graphics
|
B | copying
|
C | Zooming
|
D | removing objects and lines |
Question 19 Explanation:
The clipping process in computer graphics is used for removing objects and lines.
Clipping is a technique used to determine which portions of an object or line are visible and should be displayed within the boundaries of a given region or window.
Any part of an object or line that falls outside this region is "clipped" or removed, ensuring that only the visible portions are rendered on the screen.
This is a fundamental operation in computer graphics used to control what is displayed within a defined viewing area or viewport.
Question 20 |
Which of the following transforms in 2 dimension is used to resize a 2-dimensional object?
A | Translation
|
B | Rotation
|
C | Scaling
|
D | Shearing |
Question 21 |
This transformation is called
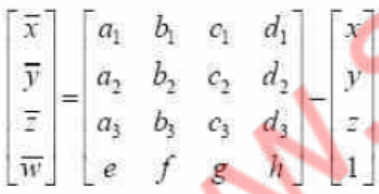
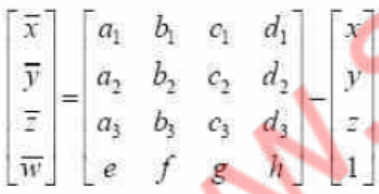
A | Scaling |
B | Shear |
C | Homography |
D | Steganography |
Question 22 |
Consider the following statements:
a) 3D Studio Max includes a number of high-level professional tools for character animation, game development, and visual effect production.
b) MAYA is a complete modeling package developed by Microsoft
c) RenderMan is a rendering package developed by Pixar
Which of the above statements are true?
a) 3D Studio Max includes a number of high-level professional tools for character animation, game development, and visual effect production.
b) MAYA is a complete modeling package developed by Microsoft
c) RenderMan is a rendering package developed by Pixar
Which of the above statements are true?
A | Only a and b |
B | Only a and c |
C | Only b and c |
D | a,b and c |
Question 22 Explanation:
MAYA 3D animation software offers a comprehensive creative feature set for 3D computer animation, modeling, simulation, rendering, and compositing on a highly extensible production platform. Maya has next-generation display technology, accelerated modeling workflows, and tools for handling complex data.
Question 23 |
The ____ file format allows storing an animation sequence
A | PNG |
B | GIF |
C | JPG |
D | PDF |
Question 23 Explanation:
→PDF means portable document format.
→Portable Network Graphics is a raster-graphics file-format that supports lossless data compression.
→JPG/JPEG: Joint Photographic Experts Group. JPEG is usually known as JPG. It stands for Joint Photographic Expert Group, a joint working group of International Standardization Organization (ISO) and International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). It is a standard method of compressing graphic images.
→A GIF is a computer file that is used on the internet for sending images, especially moving images. GIF is an abbreviation for 'Graphic Interchange Format'.
→Portable Network Graphics is a raster-graphics file-format that supports lossless data compression.
→JPG/JPEG: Joint Photographic Experts Group. JPEG is usually known as JPG. It stands for Joint Photographic Expert Group, a joint working group of International Standardization Organization (ISO) and International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). It is a standard method of compressing graphic images.
→A GIF is a computer file that is used on the internet for sending images, especially moving images. GIF is an abbreviation for 'Graphic Interchange Format'.
Question 24 |
Transformation that moves objects without deformation is called:
A | Rotation |
B | Scaling |
C | Translation |
D | Morphism |
Question 24 Explanation:
→ A translation process moves every point a constant distance in a specified direction. It can be described as a rigid motion.
→ A translation can also be interpreted as the addition of a constant vector to every point, or as shifting the origin of the coordinate system.
→ A translation can also be interpreted as the addition of a constant vector to every point, or as shifting the origin of the coordinate system.
Question 25 |
Using Mid Point algorithm, the new coordinates of the point P(x,y) having slope ‘m’ and constant and ‘b’ is calculated using:
A | F(x,y)=mx+b-y |
B | F(x,y)=mx-y+b |
C | F(x,y)=mx+b |
D | F(x,y)=mx-y+b-y |
Question 25 Explanation:
In order to check this, we need to consider the implicit equation:
F(x,y) = mx + b - y
For positive m at any given X,
If y is on the line, then F(x, y) = 0
If y is above the line, then F(x, y) < 0
If y is below the line, then F(x, y) > 0
F(x,y) = mx + b - y
For positive m at any given X,
If y is on the line, then F(x, y) = 0
If y is above the line, then F(x, y) < 0
If y is below the line, then F(x, y) > 0
Question 26 |
The process of rotating the image by 1800 without changing its size is called:
A | Translation |
B | Rotation |
C | Scaling |
D | Reflection |
Question 26 Explanation:
The process of rotating the image by 1800 without changing its size is called Rotation
Question 27 |
In 3D Graphics, which of the following statements about perspective and parallel projection is/are true?
-
P: In a perspective projection, the farthest an object is from the center of projection, the smaller it appears.
Q: Parallel projection is equivalent to a perspective projection where the viewer is standing infinitely far away
R: Perspective projections do not preserve straight lines.
Choose the correct answer from the code given below:
Code:A | P and R only |
B | P, Q and R |
C | Q and R only |
D | P and Q only
|
Question 27 Explanation:
Perspective Projection :
Perspective projection is representing or drawing objects which resemble the real thing.
Perspective projection preserves the straight line.
In perspective projection, objects that are far away appear smaller, and objects that are near appear bigger.
Parallel lines do not remain parallel.
Distance and angles are not preserved.
Parallel Projection :
In this projection drawing objects looks less realistic.
In this projection parallel lines remains parallel.
Angles are not preserved in this projection.
It is good for exact measurements.
Perspective projection is representing or drawing objects which resemble the real thing.
Perspective projection preserves the straight line.
In perspective projection, objects that are far away appear smaller, and objects that are near appear bigger.
Parallel lines do not remain parallel.
Distance and angles are not preserved.
Parallel Projection :
In this projection drawing objects looks less realistic.
In this projection parallel lines remains parallel.
Angles are not preserved in this projection.
It is good for exact measurements.
Question 28 |
In 3D Graphics, which of the following statement/s is/are true ?
-
P: Back-face culling is an example of an image-precision visible-surface determination.
Q: Z-Buffer is a 16-bit, 32-bit, or 64-bit field associated with each pixel in a frame buffer
that can be used to determine the visible surface at each pixel.
Choose the correct answer from the code given below :;
Code :A | P only |
B | Q only
|
C | Neither P nor Q
|
D | P and Q
|
Question 28 Explanation:
Back Face Culling:
→ Back-face culling (an object space algorithm) works on 'solid' objects which you are looking at from the outside. That is, the polygons of the surface of the object completely enclose the object.
→ Back-face culling is not an example of an image-precision visible-surface determination.
→ Back-face culling can very quickly remove unnecessary polygons. Unfortunately there are often times when back-face culling can not be used. For example if you wish to make an open-topped box - the inside and the outside of the box both need to be visible, so either two sets of polygons must be generated, one set facing out and another facing in, or back-face culling must be turned off to draw that object.
1. Back faces: faces of opaque object which are “pointing away” from viewer.
2. Back face culling – remove back faces (supported by OpenGL).
→ TRUE: Z-Buffer is a 16-bit, 32-bit, or 64-bit field associated with each pixel in a frame buffer that can be used to determine the visible surface at each pixel.
→ Back-face culling (an object space algorithm) works on 'solid' objects which you are looking at from the outside. That is, the polygons of the surface of the object completely enclose the object.
→ Back-face culling is not an example of an image-precision visible-surface determination.
→ Back-face culling can very quickly remove unnecessary polygons. Unfortunately there are often times when back-face culling can not be used. For example if you wish to make an open-topped box - the inside and the outside of the box both need to be visible, so either two sets of polygons must be generated, one set facing out and another facing in, or back-face culling must be turned off to draw that object.
1. Back faces: faces of opaque object which are “pointing away” from viewer.
2. Back face culling – remove back faces (supported by OpenGL).
→ TRUE: Z-Buffer is a 16-bit, 32-bit, or 64-bit field associated with each pixel in a frame buffer that can be used to determine the visible surface at each pixel.
Question 29 |
Memory mapped displays
A | are utilized for high resolution graphics such as maps |
B | uses ordinary memory to store the display data in character form |
C | stores the display data as individual bits |
D | are associated with electromechanical teleprinters |
Question 29 Explanation:
● Graphs can be displayed on a screen by writing character values into a special area of RAM within the video controller.
● Prior to cheap RAM that enabled bit-mapped displays, this character cell method was a popular technique for computer video displays.
Question 30 |
Which of the following statements is/are True regarding the solution to the visibility problem in 3D graphics ?
S1 : The Painter’s algorithm sorts polygons by depth and then paints (scan - converts) each Polygon onto the screen starting with the most nearest polygon. S2 : Backface Culling refers to eliminating geometry with back facing normals. Code :A | S1 only |
B | S2 only
|
C | Both S1 and S2 |
D | Neither S1 Nor S2 |
Question 30 Explanation:
Visibility problem in 3D graphics
1. Painter's algorithm
- A depth sorting method
- Surfaces are sorted in the order of decreasing depth
- Surfaces are drawn in the sorted order, and overwrite the pixels in the frame buffer - Subtle difference from depth buffer approach: entire face drawn
- Two problems:
• It can be nontrivial to sort the surfaces
• There can be no solution for the sorting order
2. Back Face Culling
- Back faces: faces of opaque object which are “pointing away” from viewer
- Back face culling – remove back faces (supported by OpenGL)
How to detect back faces
- If we find backface, do not draw, save rendering resources
- There must be other forward face(s) closer to eye
- F is face of object we want to test if backface
- P is a point on F
- Form view vector, V as (eye – P)
- N is normal to face F
3. View-Frustum Culling
- Remove objects that are outside the viewing frustum
- Done by 3D clipping algorithm (e.g. Liang-Barsky)
4. Ray Tracing
- Ray tracing is another example of image space method
- Ray tracing: Cast a ray from eye through each pixel to the world
5. Z(Depth buffer algorithm)
Reference: https://web.cs.wpi.edu/~emmanuel/courses/cs543/slides/lecture08_p2.pdf
1. Painter's algorithm
- A depth sorting method
- Surfaces are sorted in the order of decreasing depth
- Surfaces are drawn in the sorted order, and overwrite the pixels in the frame buffer - Subtle difference from depth buffer approach: entire face drawn
- Two problems:
• It can be nontrivial to sort the surfaces
• There can be no solution for the sorting order
2. Back Face Culling
- Back faces: faces of opaque object which are “pointing away” from viewer
- Back face culling – remove back faces (supported by OpenGL)
How to detect back faces
- If we find backface, do not draw, save rendering resources
- There must be other forward face(s) closer to eye
- F is face of object we want to test if backface
- P is a point on F
- Form view vector, V as (eye – P)
- N is normal to face F
3. View-Frustum Culling
- Remove objects that are outside the viewing frustum
- Done by 3D clipping algorithm (e.g. Liang-Barsky)
4. Ray Tracing
- Ray tracing is another example of image space method
- Ray tracing: Cast a ray from eye through each pixel to the world
5. Z(Depth buffer algorithm)
Reference: https://web.cs.wpi.edu/~emmanuel/courses/cs543/slides/lecture08_p2.pdf
Question 31 |
How much memory is required to implement the z-buffer algorithm for a 512 x 512 x 24 bit-plane image?
A | 768 KB |
B | 1 MB |
C | 1.5 MB |
D | 2 MB |
Question 31 Explanation:
In computer graphics, z-buffering, also known as depth buffering, is the management of image depth coordinates in 3D graphics, usually done in hardware, sometimes in software
In a 3d-rendering engine, when an object is projected on the screen, the depth (z-value) of a generated pixel in the projected screen image is stored in a buffer (the z-buffer or depth buffer).
A z-value is the measure of the perpendicular distance from a pixel on the projection plane to its corresponding 3d-coordinate on a polygon in world-space.
Z-buffer requires 2 type of buffers to be filled: Depth buffer and Frame buffer
The amount of memory required by depth buffer in terms of bits is 512 x 512 x 24 = 6291456
The amount of memory required by frame buffer in terms of bits is 512 x 512 x 24 = 6291456
Total memory is required is sum of both depth and frame buffer memories = 6291456 + 6291456 = 12582912 bits which is equivalent to 1.5 MB(1.5x1024x1024x8)
In a 3d-rendering engine, when an object is projected on the screen, the depth (z-value) of a generated pixel in the projected screen image is stored in a buffer (the z-buffer or depth buffer).
A z-value is the measure of the perpendicular distance from a pixel on the projection plane to its corresponding 3d-coordinate on a polygon in world-space.
Z-buffer requires 2 type of buffers to be filled: Depth buffer and Frame buffer
The amount of memory required by depth buffer in terms of bits is 512 x 512 x 24 = 6291456
The amount of memory required by frame buffer in terms of bits is 512 x 512 x 24 = 6291456
Total memory is required is sum of both depth and frame buffer memories = 6291456 + 6291456 = 12582912 bits which is equivalent to 1.5 MB(1.5x1024x1024x8)
Question 32 |
A frame buffer array is addressed in row major order for a monitor with pixel locations starting from (0,0) and ending with (100,100). What is address of the pixel(6,10)? Assume one bit storage per pixel and starting pixel location is at 0.
A | 1016 |
B | 1006 |
C | 610 |
D | 616 |
Question 32 Explanation:
Given data,
Pixel location starts from =(0,0)
Pixel location ends from =(100,100)
Address of the pixel= ?
Hint: Frame buffer array is addressed in row major order
. Step-1: Row major order is= 0+1((6-0)+101(10-0))
= 0+6+1010
= 1016
Pixel location starts from =(0,0)
Pixel location ends from =(100,100)
Address of the pixel= ?
Hint: Frame buffer array is addressed in row major order
. Step-1: Row major order is= 0+1((6-0)+101(10-0))
= 0+6+1010
= 1016
Question 33 |
In graphics, the number of vanishing points depends on
A | the number of axes cut by the projection plane |
B | the centre of projection |
C | the number of axes which are parallel to the projection plane |
D | the perspective projections of any set of parallel lines that are not parallel to the projection plane |
Question 33 Explanation:
→Projections of lines that are not parallel to the view plane (i.e. lines that are not perpendicular to the view plane normal) appear to meet at some point on the view plane.
→This point is called the vanishing point. A vanishing point corresponds to every set of parallel lines.
→This point is called the vanishing point. A vanishing point corresponds to every set of parallel lines.
Question 34 |
In which of the following shading models of polygons, the interpolation of intensity values is done along the scan line?
A | Gourard shading |
B | Phong shading |
C | Constant shading |
D | Flat shading |
Question 34 Explanation:
→Gouraud shading is an interpolation method used in computer graphics to produce continuous shading of surfaces represented by polygon meshes.
→In practice, Gouraud shading is most often used to achieve continuous lighting on triangle surfaces by computing the lighting at the corners of each triangle and linearly interpolating the resulting colours for each pixel covered by the triangle.
→Phong shading refers to an interpolation technique for surface shading in 3D computer graphics.
→'Constant shading','faceted shading' or 'flat shading' is the approach applies an illumination model once to determine a single intensity value that is then used to shade an entire polygon, and holding the value across the polygon to reconstruct the polygon's shade.
→In practice, Gouraud shading is most often used to achieve continuous lighting on triangle surfaces by computing the lighting at the corners of each triangle and linearly interpolating the resulting colours for each pixel covered by the triangle.
→Phong shading refers to an interpolation technique for surface shading in 3D computer graphics.
→'Constant shading','faceted shading' or 'flat shading' is the approach applies an illumination model once to determine a single intensity value that is then used to shade an entire polygon, and holding the value across the polygon to reconstruct the polygon's shade.
Question 36 |
Which of the following is true about the z-buffer algorithm?
A | It is a depth sort algorithm |
B | No limitation on total number of objects |
C | Comparisons of objects is done |
D | z-buffer is initialized to background colour at start of algorithm |
Question 36 Explanation:
The Z-buffer algorithm is a convenient algorithm for rendering images properly according to depth.
To begin with, a buffer containing the closest depth at each pixel location is created parallel to the image buffer. Each location in this depth buffer is initialized to negative infinity.
Since the algorithm processes objects one at a time, the total number of polygons in a picture can be arbitrarily large.
To begin with, a buffer containing the closest depth at each pixel location is created parallel to the image buffer. Each location in this depth buffer is initialized to negative infinity.
Since the algorithm processes objects one at a time, the total number of polygons in a picture can be arbitrarily large.
Question 37 |
A system is having 8 M bytes of video memory for bit-mapped graphics with 64-bit colour. What is the maximum resolution it can support?
A | 800 x 600 |
B | 1024 x 768 |
C | 1280 x 1024 |
D | 1920 x 1440 |
Question 37 Explanation:
Explanation:
Given file size is 8M bytes= 8*1024**1024*8=83,88,608
From the options,
⦁ 800*600*8=34,80,000
⦁ 1024*768*8=62,91,456
⦁ 1280*1024*8=13,10,720
⦁ 1920*1440*8=22,118,400
From the above , option A and B are less than file size.
From that two , maximum one is option B.
Given file size is 8M bytes= 8*1024**1024*8=83,88,608
From the options,
⦁ 800*600*8=34,80,000
⦁ 1024*768*8=62,91,456
⦁ 1280*1024*8=13,10,720
⦁ 1920*1440*8=22,118,400
From the above , option A and B are less than file size.
From that two , maximum one is option B.
Question 38 |
The term Phong associated with
A | Ray tracing |
B | shading |
C | Hidden line removal |
D | a game |
Question 38 Explanation:
Phong shading is a per-fragment color computation. The vertex shader provides the normal and position data as out variables to the fragment shader. The fragment shader then interpolates these variables and computes the color
Question 39 |
A Steiner patch is
A | Biquadratic Bezier patch |
B | Bicubic patch |
C | Circular patch only |
D | Bilinear Bezier patch |
Question 39 Explanation:
Steiner patches are triangular surface patches for which the Cartesian coordinates of points on the patch are defined parametrically by quadratic polynomial functions of two variables. So these surfaces are formed from biquadratic Bezier patches.
Question 40 |
Anti aliasing is important to improve readability of text. It deals with the
A | Elimination of "jaggies" |
B | Spacing between two individual characters |
C | Underlining letters |
D | Spacing of a group of characters |
Question 40 Explanation:
● Antialiasing removes jagged edges by adding subtle color changes around the lines, tricking the human eye into thinking that the lines are not jagged.
● The slight changes in color around the edges of an image help the line blend around curves, giving the impression that the line is true.
● These color changes are made on a very small scale that the human eye cannot detect under normal circumstances. In order to be able to see that an image has been antialiased, it would have to be magnified.
● The slight changes in color around the edges of an image help the line blend around curves, giving the impression that the line is true.
● These color changes are made on a very small scale that the human eye cannot detect under normal circumstances. In order to be able to see that an image has been antialiased, it would have to be magnified.
Question 41 |
What is the bitrate for transmitting uncompressed 800x600 pixel color frame with 8 bits/pixel at 40 frames/Second?
A | 1536 Mbps |
B | 2.4 Mbps |
C | 15.36 Mbps |
D | 153.6 Mbps |
Question 41 Explanation:
Step-1: Given data, Uncompressed pixel = 800*600
Step-2: Each of 8 bit = 800*600 *8
Step-3: Bit rate for transmitting = 800*600 *8 *40 =153600000 bits
Step-4: Here, they are given in Mbps. 153600000 bits =153.6Mbps
Step-2: Each of 8 bit = 800*600 *8
Step-3: Bit rate for transmitting = 800*600 *8 *40 =153600000 bits
Step-4: Here, they are given in Mbps. 153600000 bits =153.6Mbps
Question 42 |
The easiest method in flash to draw a heptagon, is to use the___
A | Polystar tool with the "Polygon" style |
B | Polygon Tool |
C | Lasso Tool with the "create star" option |
D | Polystar Tool with the "star" style |
Question 42 Explanation:
There are 3 tools for drawing geometric shapes
1. Rectangle(Rectangle tool)
2. Oval(Oval tool)
3. Polygon(Polystar tool)
Note: We are not using Option A,C and D for drawing heptagon.
1. Rectangle(Rectangle tool)
2. Oval(Oval tool)
3. Polygon(Polystar tool)
Note: We are not using Option A,C and D for drawing heptagon.
Question 43 |
___ is a special effect in motion pictures and animations that changes one image or sharp into another through a seamless transition
A | Tweening |
B | Inverse kinematics |
C | Morphing |
D | Tweaking |
Question 43 Explanation:
Morphing is a special effect in motion pictures and animations that changes (or morphs) one image or shape into another through a seamless transition. morphing means stretching or as part of a fantasy or surreal sequence. Traditionally such a depiction would be achieved through cross-fading techniques on film.
Question 44 |
Given that a 22 inch monitor with an aspect ratio of 16:9 has a monitor of 1920x1080, what is the width of the monitor?
A | 22 inches |
B | 8:53 inches |
C | 10:79 inches |
D | 19:17 inches |
Question 44 Explanation:
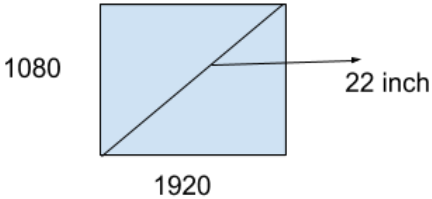
Step-1: To check the ratio [width/height= 1920 /1080 ]
Step-2: Ratio: 16/9.
Step-3: Using Pythagoras theorem (9x) 2 +(16x) 2 =(22) 2
x=19.17 inch
Question 45 |
Even when the screen is completely dark while the film is in motion, commercial motion pictures use
A | 32 frames per second or 101 screen illuminations per second |
B | 72 frames per second or 234 screen illuminations per second |
C | 8 frames per second or 32 screen illuminations per second |
D | 24 frames per second or 72 screen illuminations per second |
Question 45 Explanation:
→ Motion picture, also called film or movie, series of still photographs on film, projected in rapid succession onto a screen by means of light.
→ When a motion picture film is projected on a screen at the rate of at least 16 illuminations per second but the commercial motion pictures uses 24 frames per second or 72 screen illuminations per second.
→ Film Technology standard is 24 frames per second, a three bladed shutter and some dreamy motion blur, all projected as shadow and light on the side of a wall.
→ When a motion picture film is projected on a screen at the rate of at least 16 illuminations per second but the commercial motion pictures uses 24 frames per second or 72 screen illuminations per second.
→ Film Technology standard is 24 frames per second, a three bladed shutter and some dreamy motion blur, all projected as shadow and light on the side of a wall.
Question 46 |
The file size of a 640 by 480 pictures of 256 colours in a 8-bit resolution is
A | 300KB |
B | 900KB |
C | 128KB |
D | 1024KB |
Question 46 Explanation:
●Give picture size with 640 by 480 resolution with 256 colors per pixel.
●This implies 640 * 480 = 307,200 pixels. Recall that 256 values requires 8 bits of computer storage.
●Hence (307,200 pixels) * (8 bits per pixel) = 2,457,600 bits of storage.
●A common method for selling computer storage is in 8 bit groupings called bytes.
●Hence the picture would require (2,457,600 bits) / (8 bits per byte) = 307,200 bytes of computer storage.
●This implies 640 * 480 = 307,200 pixels. Recall that 256 values requires 8 bits of computer storage.
●Hence (307,200 pixels) * (8 bits per pixel) = 2,457,600 bits of storage.
●A common method for selling computer storage is in 8 bit groupings called bytes.
●Hence the picture would require (2,457,600 bits) / (8 bits per byte) = 307,200 bytes of computer storage.
Question 47 |
The process of producing bitmapped images from a view of 3-D models in a 3-D scene is called
A | Rendering |
B | Looping |
C | Cross dissolving |
D | Imaging |
Question 47 Explanation:
Rendering or image synthesis is the automatic process of generating a photorealistic or non-photorealistic image from a 2D or 3D model (or models in what collectively could be called a scene file) by means of computer programs.
Question 48 |
Which of the following is interactive?
A | A radio broadcast |
B | A talk show on TV |
C | A newspaper |
D | A computer game |
Question 48 Explanation:
Options A,B and C are not interactive , it will provide only information to the people. Where as Computer game in which computer user should interact with the computer in order to play the game
Question 49 |
While making bubbled lists, which of the following options are available?
A | Square,disc,tringle |
B | Triangle,disc,circle |
C | Triangle,square,circle |
D | Disc,square,circle |
Question 49 Explanation:
→ Disc: A filled circle
→ Circle : An unfilled circle
→ square : A filled square
→ Circle : An unfilled circle
→ square : A filled square
Question 50 |
MPEG involves both spatial compression and temporal compression. The spatial compression is similar to JPEG and temporal compression removes_____frames.
A | Voice |
B | Spatial |
C | Temporal |
D | Redundant |
Question 50 Explanation:
MPEG: The MPEG codec can only be used when the final video file will be in MPEG format (it is not compatible with other file types). It uses a lossy compression scheme (although it may be lossless at high-quality settings) and spatial and temporal compression. MPEG offers the best compression possible, but MPEGs are not yet as widely supported on the Web as other video formats.
Spatial compression:
Spatial (or intraframe) compression takes place on each individual frame of the video, compressing the pixel information as though it were a still image. JPEG, PNG and PICT files are an example of spatial compression.
It is known as the intraframe method.
Temporal compression:
It happens over a series of frames of the video. Temporal (or interframe) compression happens over a series of frames and takes advantage of areas of the image that remain unchanged from frame to frame, throwing out data for repeated pixels.
It is also called the interframe method.
Spatial compression:
Spatial (or intraframe) compression takes place on each individual frame of the video, compressing the pixel information as though it were a still image. JPEG, PNG and PICT files are an example of spatial compression.
It is known as the intraframe method.
Temporal compression:
It happens over a series of frames of the video. Temporal (or interframe) compression happens over a series of frames and takes advantage of areas of the image that remain unchanged from frame to frame, throwing out data for repeated pixels.
It is also called the interframe method.
Access subject wise (1000+) question and answers by becoming as a solutions adda PRO SUBSCRIBER with Ad-Free content
Register Now
You have completed
questions
question
Your score is
Correct
Wrong
Partial-Credit
You have not finished your quiz. If you leave this page, your progress will be lost.
Correct Answer
You Selected
Not Attempted
Final Score on Quiz
Attempted Questions Correct
Attempted Questions Wrong
Questions Not Attempted
Total Questions on Quiz
Question Details
Results
Date
Score
Hint
Time allowed
minutes
seconds
Time used
Answer Choice(s) Selected
Question Text
Need more practice!
Keep trying!
Not bad!
Good work!
Perfect!