artificial-intelligence
Question 1 |
What are the following sequence of steps taken in designing a fuzzy logic machine?
A | Fuzzi cation → Rule evaluation → Defuzzi cation |
B | Fuzzi cation → Defuzzi cation → Rule evaluation |
C | Rule evaluation → Fuzzi cation → Defuzzi cation |
D | Rule evaluation → Defuzzi cation → Fuzzi cation |
Question 1 Explanation:

Question 2 |
Let R and S be two fuzzy relations defined as
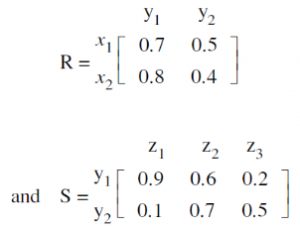
Then, the resulting relation, T, which relates elements of universe of X to elements of universe of Z using max-product composition is given by
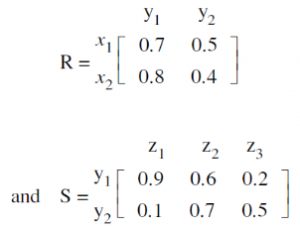
Then, the resulting relation, T, which relates elements of universe of X to elements of universe of Z using max-product composition is given by
A |  |
B |  |
C |  |
D | 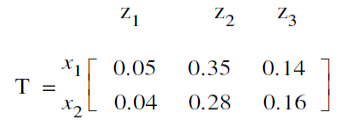 |
Question 2 Explanation:
Question 3 |
Match each Artificial Intelligence term in List-I that best describes a given situation in List-II


A | I-d, II-a, III-b, IV-c |
B | I-d, II-c, III-a, IV-b |
C | I-d, II-c, III-b, IV-a |
D | I-c, II-d, III-a, IV-b |
Question 3 Explanation:
Semantic network→ A method of knowledge representation that uses a graph
Frame→ A data structure representing stereotypical knowledge
Declarative knowledge→ Knowledge about what to do as opposed to how to do it
Primitive→ A premise of a rule that is not concluded by any rule
Frame→ A data structure representing stereotypical knowledge
Declarative knowledge→ Knowledge about what to do as opposed to how to do it
Primitive→ A premise of a rule that is not concluded by any rule
Question 4 |
In Artificial Intelligence , a semantic network
A | is a graph-based method of knowledge representation where nodes represent concepts and arcs represent relations between concepts. |
B | is a graph-based method of knowledge representation where nodes represent relations between concepts and arcs represent concepts. |
C | represents an entity as a set of slots and associated rules. |
D | is a subset of rst-order logic. |
Question 4 Explanation:
→ In Artificial Intelligence , a semantic network is a graph-based method of knowledge representation where nodes represent concepts and arcs represent relations between concepts.
→ Semantic networks are used in natural language processing applications such as semantic parsing and word-sense disambiguation.
→ Semantic networks are used in natural language processing applications such as semantic parsing and word-sense disambiguation.
Question 5 |
Which formal system provides the semantic foundation for Prolog?
A | Predicate calculus |
B | Lambda calculus |
C | Hoare logic |
D | Propositional logic |
Question 5 Explanation:
Predicate calculus provides the semantic foundation for Prolog.
Question 6 |
Consider the statement below.
A person who is radical (R) is electable (E) if he/she is conservative (C), but otherwise is not electable.
Few probable logical assertions of the above sentence are given below.,

Which of the above logical assertions are true?
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:

Which of the above logical assertions are true?
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
A | (B) only |
B | (C) only |
C | (A) and (C) only |
D | (B) and (D) only |
Question 6 Explanation:
1. (R ∧E) ↔C
This is not equivalent. It says that all (and only) conservatives are radical and electable.
2. R →(E ↔C)
This one is equivalent. if a person is a radical then they are electable if and only if they are conservative.
3. R →((C →E) ∨¬E)
This one is vacuous. It’s equivalent to ¬R ∨ (¬C ∨ E ∨ ¬E), which is true in all interpretations.
4.R ⇒ (E ⇐⇒ C) ≡ R ⇒ ((E ⇒ C) ∧ (C ⇒ E))
≡ ¬R ∨ ((¬E ∨ C) ∧ (¬C ∨ E))
≡ (¬R ∨ ¬E ∨ C) ∧ (¬R ∨ ¬C ∨ E))
This is not equivalent. It says that all (and only) conservatives are radical and electable.
2. R →(E ↔C)
This one is equivalent. if a person is a radical then they are electable if and only if they are conservative.
3. R →((C →E) ∨¬E)
This one is vacuous. It’s equivalent to ¬R ∨ (¬C ∨ E ∨ ¬E), which is true in all interpretations.
4.R ⇒ (E ⇐⇒ C) ≡ R ⇒ ((E ⇒ C) ∧ (C ⇒ E))
≡ ¬R ∨ ((¬E ∨ C) ∧ (¬C ∨ E))
≡ (¬R ∨ ¬E ∨ C) ∧ (¬R ∨ ¬C ∨ E))
Question 7 |
Consider the following argument with premise
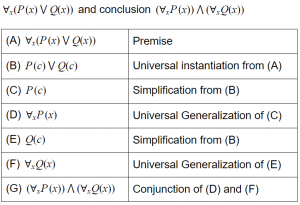

A | This is a valid argument. |
B | Steps (C) and (E) are not correct inferences |
C | Steps (D) and (F) are not correct inferences |
D | Step (G) is not a correct inference |
Question 8 |
Given below are two statements:
Statement I: A genetic algorithm is a stochastic hill climbing search in which a large population of states is maintained.
Statement II: In a nondeterministic environment, agents can apply AND-OR search to generate containing plans that reach the goal regardless of which outcomes occur during execution.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answers from the options given below
A | Both Statement I and Statement II are true |
B | Both Statement I and Statement II are false |
C | Statement I is correct but Statement II is false
|
D | Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is true |
Question 8 Explanation:
In a genetic algorithm, a population of candidate solutions (called individuals, creatures, or phenotypes) to an optimization problem is evolved toward better solutions. Each candidate solution has a set of properties (its chromosomes or genotype) which can be mutated and altered; traditionally, solutions are represented in binary as strings of 0s and 1s, but other encodings are also possible.
In nondeterministic environments, percepts tell the agent which of the possible outcomes has actually occurred.Solutions for nondeterministic problems can contain nested if-then-else statements that create a tree rather than a sequence of actions
In nondeterministic environments, percepts tell the agent which of the possible outcomes has actually occurred.Solutions for nondeterministic problems can contain nested if-then-else statements that create a tree rather than a sequence of actions
Question 9 |
Which of the following statements are true?
A) Minimax search is breadth-first; it processes all the nodes at a level before moving to a node in the next level.
B) The effectiveness of the alpha-beta pruning is highly dependent on the order in which the states are examined.
C) The alpha-beta search algorithm computes the same optimal moves as the minimax algorithm.
D) Optimal play in games of imperfect information does not require reasoning about the current and future belief states of each player.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
A | (A) and (C) only |
B | (A) and (D) only |
C | (B) and (C) only |
D | (C) and (D) only |
Question 9 Explanation:
Minimax is a decision rule used in artificial intelligence, decision theory, game theory, statistics, and philosophy for minimizing the possible loss for a worst case (maximum loss) scenario.
Optimal decision in deterministic, perfect information games
Idea : choose the move resulting in the highest minimax value
Completeness: Yes if the tree is finite
Optimality: Yes, against an optimal opponent.
Time Complexity: O(bm)
Space Complexity: O(bm) – depth first exploration.
Hence Statement (A) is true.
Statement (B):
Alpha Bound of J:
→ The max current The max current val of all MAX ancestors of J of all MAX ancestors of J
→ Exploration of a min node, J, Exploration of a min node, J, is stopped when its value is stopped when its value equals or falls below alpha. equals or falls below alpha.
→ In a min node, we n node, we update beta update beta
Beta Bound of J:
→ The min current The min current val of all MIN ancestors of J of all MIN ancestors of J
→ Exploration of a Exploration of a max node, J ax node, J, is stopped when its stopped when its value equals or exceeds beta equals or exceeds beta
→ In a max node, we update a ax node, we update alpha
Pruning does not affect the final result
Does ordering affect the pruning process?
Best case O(bm/2)
Random (instead of best first search) - O(b3m/4)
Hence statement (B) is false.
Statement C: This statement is true.
Statement D: This statement is false because past exploration information is used from transposition tables.
Optimal decision in deterministic, perfect information games
Idea : choose the move resulting in the highest minimax value
Completeness: Yes if the tree is finite
Optimality: Yes, against an optimal opponent.
Time Complexity: O(bm)
Space Complexity: O(bm) – depth first exploration.
Hence Statement (A) is true.
Statement (B):
Alpha Bound of J:
→ The max current The max current val of all MAX ancestors of J of all MAX ancestors of J
→ Exploration of a min node, J, Exploration of a min node, J, is stopped when its value is stopped when its value equals or falls below alpha. equals or falls below alpha.
→ In a min node, we n node, we update beta update beta
Beta Bound of J:
→ The min current The min current val of all MIN ancestors of J of all MIN ancestors of J
→ Exploration of a Exploration of a max node, J ax node, J, is stopped when its stopped when its value equals or exceeds beta equals or exceeds beta
→ In a max node, we update a ax node, we update alpha
Pruning does not affect the final result
Does ordering affect the pruning process?
Best case O(bm/2)
Random (instead of best first search) - O(b3m/4)
Hence statement (B) is false.
Statement C: This statement is true.
Statement D: This statement is false because past exploration information is used from transposition tables.
Question 10 |
Given below are two statements:
If two variables V1and V2 are used for clustering, then consider the following statements for k means clustering with k=3:-
Statement I: If V1and V2 have correlation of 1 the cluster centroid will be in straight line.
Statement II: If V1and V2 have correlation of 0 the cluster centroid will be in straight line.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below
A | Both Statement I and Statement II are true |
B | Both Statement I and Statement II are false |
C | Statement I is correct but Statement II is false |
D | Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is true |
Question 10 Explanation:
If the correlation between the variables V1 and V2 is 1, then all the data points will be in a straight line. So, all the three cluster centroids will form a straight line as well.
Question 11 |
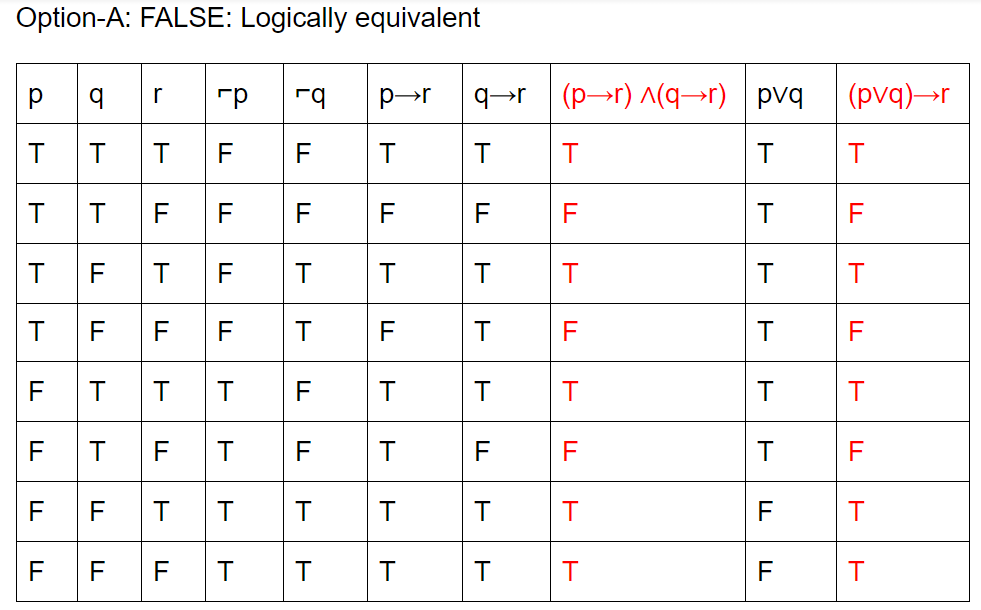
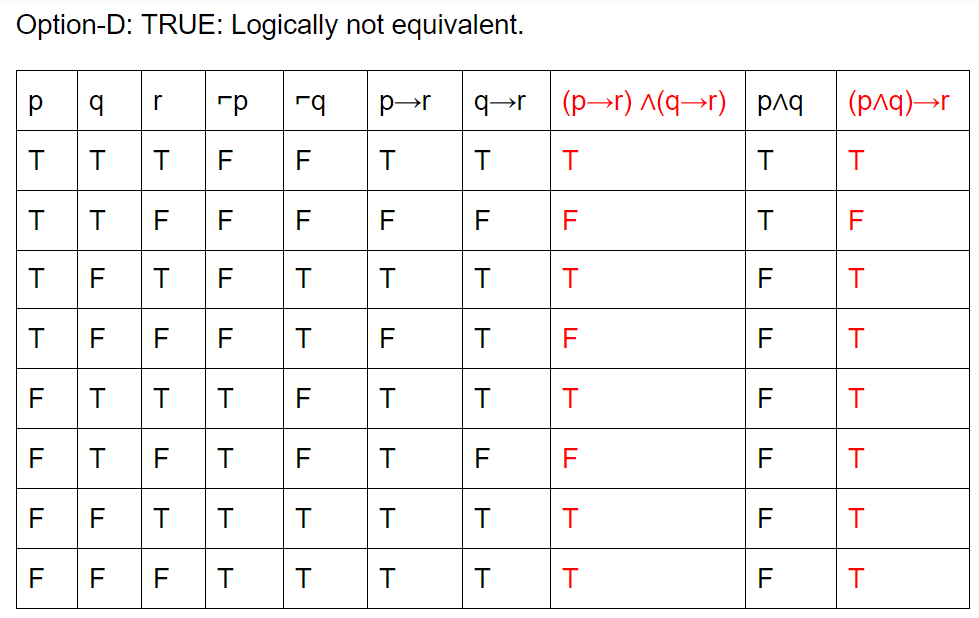
Which of the following pairs of propositions are not logically equivalent?
A | 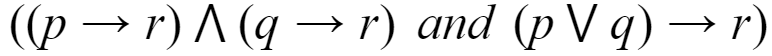 |
B | 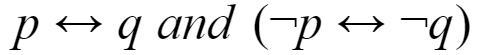 |
C | 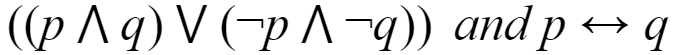 |
D | 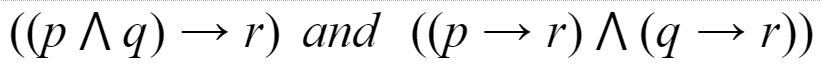 |
Question 11 Explanation:


Question 12 |
Match List I with List II

Choose the correct answer from the options given below

Choose the correct answer from the options given below
A | A-II, B-IV, C-I, D-III
|
B | A-II, B-III, C-I, D-IV |
C | A-III, B-II, C-IV, D-I |
D | A-III, B-IV, C-II, D-I |
Question 12 Explanation:
Greedy best-first search algorithm always selects the path which appears best at that moment. It is the combination of depth-first search and breadth-first search algorithms.
Time Complexity: The worst case time complexity of Greedy best first search is O(bm).
Space Complexity: The worst case space complexity of Greedy best first search is O(bm). Where, m is the maximum depth of the search space.
Complete: Greedy best-first search is also incomplete, even if the given state space is finite.
Optimal: Greedy best first search algorithm is not optimal.
Note:Refer the corresponding algorithms from standard sources.
Time Complexity: The worst case time complexity of Greedy best first search is O(bm).
Space Complexity: The worst case space complexity of Greedy best first search is O(bm). Where, m is the maximum depth of the search space.
Complete: Greedy best-first search is also incomplete, even if the given state space is finite.
Optimal: Greedy best first search algorithm is not optimal.
Note:Refer the corresponding algorithms from standard sources.
Question 13 |
If f(x)=x is my friend, and p(x) = x is perfect, then the correct logical translation of the statement "some of my friends are not perfect" is _____.
A | 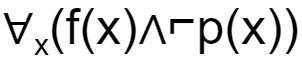 |
B |  |
C | 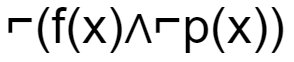 |
D |  |
Question 13 Explanation:
Input:
f(x)=x is my friend
p(x) = x is perfect
So, they are asking about SOME. Finally, outer most parentheses will get SOME.
So, based on this we will eliminate 2 options.
They are given conditions like NOT perfect. So, we get ⌐p(x).
The final condition is ∃x(f(x)∧⌐p(x))
f(x)=x is my friend
p(x) = x is perfect
So, they are asking about SOME. Finally, outer most parentheses will get SOME.
So, based on this we will eliminate 2 options.
They are given conditions like NOT perfect. So, we get ⌐p(x).
The final condition is ∃x(f(x)∧⌐p(x))
Question 14 |
Match List I with List II
List I List II
A) Branch-and-bound (I) Keeps track of all partial paths which can be can be a candidate for further exploration.
B) Steepest-ascent hill climbing (II) Detects difference between current state and goal state.
C) Constraint satisfaction (III) Discovers problem state(s) that satisfy a set of constraints.
D) Means-end-analysis (IV) Considers all moves from current state and selects the best move.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
A | A-I, B-IV, C-III, D-II |
B | A-I, B-II, C-III, D-IV
|
C | A-II, B-I, C-III, D-IV |
D | A-II, B-IV, C-III, D-I |
Question 14 Explanation:
Branch-and-bound→ Keep track of all partial paths which can be a candidate for further exploration.
Steepest-ascent hill climbing → Considers all moves from current state and selects the best move.
Constraint satisfaction → Discovers problem state(s) that satisfy a set of constraints.
Means-end-analysis → Detects difference between current state and goal state.
Steepest-ascent hill climbing → Considers all moves from current state and selects the best move.
Constraint satisfaction → Discovers problem state(s) that satisfy a set of constraints.
Means-end-analysis → Detects difference between current state and goal state.
Question 15 |
Which of the following is NOT true in problem solving in artificial intelligence?
A | Implements heuristic search techniques |
B | Solution steps are not explicit |
C | Knowledge is imprecise |
D | it works on or implements repetition mechanism |
Question 16 |
Which of the following is not a component of the classic Planning Definition?
A | Init
|
B | Domain
arti |
C | Action |
D | Goal |
Question 17 |
Which of the following are correct for the neural network?
A. The training time depends upon the size of network.
B. Neural network can be simulated on the conventional computer.
C. Neural network mimic the same way as that of the humans brain.
D. A neural network include feedback.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
A. The training time depends upon the size of network.
B. Neural network can be simulated on the conventional computer.
C. Neural network mimic the same way as that of the humans brain.
D. A neural network include feedback.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
A | A and B only |
B | A, C and D only |
C | A, B and C only |
D | A and C only |
Question 18 |
Match the LIST-I with LIST-II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
| LIST-I | LIST-II | ||
| A | Decision Tree | I | Delta Learning Rule |
| B | Supervised Learning | II | Self Organizing Map |
| C | Artificial Neural Network | III | C4.5 Algorithm |
| D | Instance base Learning | IV | Non-linear Regression Algorithm |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
A | A-I,B-II, C-III, D-IV
|
B | A-II, B-III, C-IV, D-I |
C | A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II |
D | A-IV, B-I, C-II, D-III |
Question 19 |
Which one of the following is not related to the feed forward networks on the Backpropagation
Algorithm ?
A | Boolean function |
B | Continuous function |
C | Arbitrary function |
D | Greedy function |
Question 20 |
Definition's of ____ organized into following four categories namely, Thinking Humanly, Thinking Rationally, Acting Humanly, Acting Rationally
A | Machine Learning |
B | Deep Learning |
C | Artificial Intelligence |
D | Neural Network |
Question 21 |
Match List -I with List - II
List - I List - II
(A) The activation function (I)is called the delta rule.
(B) The learning method of perceptron (II)is one of the key components of the perceptron as in the most common neural network architecture.
(C) Areas of application of artificial neural network include (III)is always boolean like a switch.
(D) The output of the perceptron (IV)system identification and control.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
List - I List - II
(A) The activation function (I)is called the delta rule.
(B) The learning method of perceptron (II)is one of the key components of the perceptron as in the most common neural network architecture.
(C) Areas of application of artificial neural network include (III)is always boolean like a switch.
(D) The output of the perceptron (IV)system identification and control.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
A | (A)-(II),(B)-(IV),(C)-(III),(D)-(I)
|
B | (A)-(IV),(B)-(III),(C)-(II),(D)-(I) |
C | (A)-(II),(B)-(I),(C)-(IV),(D)-(III)
|
D | (A)-(III),(B)-(IV),(C)-(II),(D)-(I)
|
Question 22 |
Match List - I with List - II
List - I
(A)Natural language processing
(B)Reinforcement learning
(C)Support vector machine
(D)Expert system
List - II
I) A method of training algorithm by rewarding desired behaviour and/or punishing undesired one.
II)System designed to emulate the making abilities of a human expert.
III) A branch of AI focused on understanding and generating human language.
IV) A machine learning technique that finds the hyper plane that best separates different class in a feature space.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
List - I
(A)Natural language processing
(B)Reinforcement learning
(C)Support vector machine
(D)Expert system
List - II
I) A method of training algorithm by rewarding desired behaviour and/or punishing undesired one.
II)System designed to emulate the making abilities of a human expert.
III) A branch of AI focused on understanding and generating human language.
IV) A machine learning technique that finds the hyper plane that best separates different class in a feature space.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
A | (A)-(I),(B)-(II),(C)-(IV),(D)-(III)
|
B | (A)-(III),(B)-(II),(C)-(I),(D)-(IV)
|
C | (A)-(III),(B)-(I),(C)-(IV),(D)-(II) |
D | (A)-(II),(B)-(IV),(C)-(III),(D)-(I)
|
Question 23 |
Arrange the following steps in a proper sequence for the process of training a neural network.
A)Weight initialization
B)Feed forward
C)Back Propagation
D)Loss Calculation
E)Weight Update
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
A)Weight initialization
B)Feed forward
C)Back Propagation
D)Loss Calculation
E)Weight Update
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
A | (A),(B),(D),(C),(E)
|
B | (D),(B),(A),(C),(E)
|
C | (A),(C),(D),(B),(E)
|
D | (E),(C),(B),(D),(A) |
Question 24 |
Arrange the following steps in the proper sequence involved in a Genetic Algorithm :
A)Selection
B)Initialization
C)Crossover
D)Mutation
E)Evaluation
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
A)Selection
B)Initialization
C)Crossover
D)Mutation
E)Evaluation
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
A | (A),(B),(C),(D),(E)
|
B | (E),(A),(B),(D),(C)
|
C | (B),(E),(C),(A),(D)
|
D | (A),(C),(B),(D),(E) |
Question 25 |
Read the below passage and answer the question.
Artificial Neutral Networks (ANNs) are computational models inspired by the human brain’s neural networks. They consist of inter-connected nodes, or neurons, organized into layers : an input layers, one or more hidden layers and an output layers. Each connection between neurons has a weight that adjusts as learning progress allowing the network to adopt and improve its performance. ANNs are particularly effective in recognizing patterns making them valuable for tasks such as image and speech recognition, Natural language processing and predictive analytics. Learning in ANNs typically involves training algorithms like back propagation, which minimize the error by adjusting the weights. As a subset of machine learning, ANNs have revolutionized the field of artificial intelligence by providing solutions to complex problems that traditional algorithms struggle with.
Artificial Neutral Networks (ANNs) are inspired by :
Artificial Neutral Networks (ANNs) are computational models inspired by the human brain’s neural networks. They consist of inter-connected nodes, or neurons, organized into layers : an input layers, one or more hidden layers and an output layers. Each connection between neurons has a weight that adjusts as learning progress allowing the network to adopt and improve its performance. ANNs are particularly effective in recognizing patterns making them valuable for tasks such as image and speech recognition, Natural language processing and predictive analytics. Learning in ANNs typically involves training algorithms like back propagation, which minimize the error by adjusting the weights. As a subset of machine learning, ANNs have revolutionized the field of artificial intelligence by providing solutions to complex problems that traditional algorithms struggle with.
Artificial Neutral Networks (ANNs) are inspired by :
A | Quantum mechanics
|
B | Human brain’s neural network
|
C | Computer Hardware architecture |
D | Genetic algorithm
|
Question 26 |
Read the below passage and answer the question.
Artificial Neutral Networks (ANNs) are computational models inspired by the human brain’s neural networks. They consist of inter-connected nodes, or neurons, organized into layers : an input layers, one or more hidden layers and an output layers. Each connection between neurons has a weight that adjusts as learning progress allowing the network to adopt and improve its performance. ANNs are particularly effective in recognizing patterns making them valuable for tasks such as image and speech recognition, Natural language processing and predictive analytics. Learning in ANNs typically involves training algorithms like back propagation, which minimize the error by adjusting the weights. As a subset of machine learning, ANNs have revolutionized the field of artificial intelligence by providing solutions to complex problems that traditional algorithms struggle with.
Which of the following layers may be more than one in numbers ?
Artificial Neutral Networks (ANNs) are computational models inspired by the human brain’s neural networks. They consist of inter-connected nodes, or neurons, organized into layers : an input layers, one or more hidden layers and an output layers. Each connection between neurons has a weight that adjusts as learning progress allowing the network to adopt and improve its performance. ANNs are particularly effective in recognizing patterns making them valuable for tasks such as image and speech recognition, Natural language processing and predictive analytics. Learning in ANNs typically involves training algorithms like back propagation, which minimize the error by adjusting the weights. As a subset of machine learning, ANNs have revolutionized the field of artificial intelligence by providing solutions to complex problems that traditional algorithms struggle with.
Which of the following layers may be more than one in numbers ?
A | Input layer |
B | Hidden layer |
C | Output layer |
D |
Physical layer
|
Question 27 |
Read the below passage and answer the question.
Artificial Neutral Networks (ANNs) are computational models inspired by the human brain’s neural networks. They consist of inter-connected nodes, or neurons, organized into layers : an input layers, one or more hidden layers and an output layers. Each connection between neurons has a weight that adjusts as learning progress allowing the network to adopt and improve its performance. ANNs are particularly effective in recognizing patterns making them valuable for tasks such as image and speech recognition, Natural language processing and predictive analytics. Learning in ANNs typically involves training algorithms like back propagation, which minimize the error by adjusting the weights. As a subset of machine learning, ANNs have revolutionized the field of artificial intelligence by providing solutions to complex problems that traditional algorithms struggle with.
Which of the following is/are the application area(s) of ANN ?
A)Natural Language Processing
B)Image Processing
C)Pattern Recognition
D)Speech Recognition
Choose the correct answer from the options given below
Artificial Neutral Networks (ANNs) are computational models inspired by the human brain’s neural networks. They consist of inter-connected nodes, or neurons, organized into layers : an input layers, one or more hidden layers and an output layers. Each connection between neurons has a weight that adjusts as learning progress allowing the network to adopt and improve its performance. ANNs are particularly effective in recognizing patterns making them valuable for tasks such as image and speech recognition, Natural language processing and predictive analytics. Learning in ANNs typically involves training algorithms like back propagation, which minimize the error by adjusting the weights. As a subset of machine learning, ANNs have revolutionized the field of artificial intelligence by providing solutions to complex problems that traditional algorithms struggle with.
Which of the following is/are the application area(s) of ANN ?
A)Natural Language Processing
B)Image Processing
C)Pattern Recognition
D)Speech Recognition
Choose the correct answer from the options given below
A | (A) and (B) only |
B | (B) and (C) only
|
C | (A),(B) and (C) only |
D | (A),(B),(C) and (D)
|
Question 28 |
Read the below passage and answer the question.
Artificial Neutral Networks (ANNs) are computational models inspired by the human brain’s neural networks. They consist of inter-connected nodes, or neurons, organized into layers : an input layers, one or more hidden layers and an output layers. Each connection between neurons has a weight that adjusts as learning progress allowing the network to adopt and improve its performance. ANNs are particularly effective in recognizing patterns making them valuable for tasks such as image and speech recognition, Natural language processing and predictive analytics. Learning in ANNs typically involves training algorithms like back propagation, which minimize the error by adjusting the weights. As a subset of machine learning, ANNs have revolutionized the field of artificial intelligence by providing solutions to complex problems that traditional algorithms struggle with.
What is the role of weights in an ANN ?
Artificial Neutral Networks (ANNs) are computational models inspired by the human brain’s neural networks. They consist of inter-connected nodes, or neurons, organized into layers : an input layers, one or more hidden layers and an output layers. Each connection between neurons has a weight that adjusts as learning progress allowing the network to adopt and improve its performance. ANNs are particularly effective in recognizing patterns making them valuable for tasks such as image and speech recognition, Natural language processing and predictive analytics. Learning in ANNs typically involves training algorithms like back propagation, which minimize the error by adjusting the weights. As a subset of machine learning, ANNs have revolutionized the field of artificial intelligence by providing solutions to complex problems that traditional algorithms struggle with.
What is the role of weights in an ANN ?
A | To store data |
B |
To adjust and improve network performance |
C | To control the speed |
D | To secure the network |
Question 29 |
Read the below passage and answer the question.
Artificial Neutral Networks (ANNs) are computational models inspired by the human brain’s neural networks. They consist of inter-connected nodes, or neurons, organized into layers : an input layers, one or more hidden layers and an output layers. Each connection between neurons has a weight that adjusts as learning progress allowing the network to adopt and improve its performance. ANNs are particularly effective in recognizing patterns making them valuable for tasks such as image and speech recognition, Natural language processing and predictive analytics. Learning in ANNs typically involves training algorithms like back propagation, which minimize the error by adjusting the weights. As a subset of machine learning, ANNs have revolutionized the field of artificial intelligence by providing solutions to complex problems that traditional algorithms struggle with.
What is the role of Back Propagation Algorithm ?
Artificial Neutral Networks (ANNs) are computational models inspired by the human brain’s neural networks. They consist of inter-connected nodes, or neurons, organized into layers : an input layers, one or more hidden layers and an output layers. Each connection between neurons has a weight that adjusts as learning progress allowing the network to adopt and improve its performance. ANNs are particularly effective in recognizing patterns making them valuable for tasks such as image and speech recognition, Natural language processing and predictive analytics. Learning in ANNs typically involves training algorithms like back propagation, which minimize the error by adjusting the weights. As a subset of machine learning, ANNs have revolutionized the field of artificial intelligence by providing solutions to complex problems that traditional algorithms struggle with.
What is the role of Back Propagation Algorithm ?
A | To reduce error
|
B | To secure network |
C | To control speed of data
|
D | To add different layers |
Question 30 |
Which of the following is not a solution representation in a genetic algorithm?
A | Binary valued
|
B | Real valued
|
C | Permutation
|
D | Combinations |
Question 30 Explanation:
"Combinations" is not typically a direct solution representation in a genetic algorithm. In genetic algorithms, the common solution representations include:
Binary Valued: Where each gene in an individual is represented as a binary value (0 or 1).
Real Valued: Where each gene in an individual is represented as a real number, often within a specific range.
Permutation: Where the genes represent a permutation or ordering of elements. This is often used for problems like the Traveling Salesman Problem.
"Combinations" as a direct representation is not commonly used in genetic algorithms. Instead, it might be implemented using other representations like binary, real-valued, or permutation depending on the specific problem being solved.
Question 31 |
Consider the following statements
A. C-fuzzy means cluster is supervised method of learning
B. PCA is used for dimension reduction
C. Apriori is not a supervised technique
D. When a machine learning model becomes so specially tuned to its exact input data that it fails to generalize to other similar data it is called underfitting
Choose the correct answer from the options given below
A. C-fuzzy means cluster is supervised method of learning
B. PCA is used for dimension reduction
C. Apriori is not a supervised technique
D. When a machine learning model becomes so specially tuned to its exact input data that it fails to generalize to other similar data it is called underfitting
Choose the correct answer from the options given below
A | A and B
|
B | B and C
|
C | C and D
|
D | D and A
|
Question 31 Explanation:
Statement B is correct. PCA (Principal Component Analysis) is indeed used for dimension reduction in machine learning and data analysis.
Statement C is also correct. Apriori is a frequent itemset mining algorithm used in association rule learning and is not a supervised technique in machine learning.
Statements A and D are not correct:
Statement A is incorrect. "C-fuzzy" is not a standard term in machine learning, and the statement doesn't accurately describe a supervised method of learning.
Statement D is also incorrect. "Underfitting" is when a model is too simple and fails to capture the underlying patterns in data. It is the opposite of overfitting, which is when a model becomes too specialized to its training data.
Question 32 |
Given below are two statements:
Statement I: Fuzzifier is a part of a fuzzy system
Statement Ii: Inference engine is a part of fuzzy system
In the ligt of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below
Statement I: Fuzzifier is a part of a fuzzy system
Statement Ii: Inference engine is a part of fuzzy system
In the ligt of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below
A | Both statement I and Statement II are correct
|
B | Both statement I and Statement II are incorrect
|
C | Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
|
D | Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct |
Question 32 Explanation:
Statement I correctly identifies that a "fuzzifier" is a component of a fuzzy system. A fuzzifier is responsible for converting crisp (non-fuzzy) inputs into fuzzy sets.
Statement II is also correct because an "inference engine" is a crucial component of a fuzzy system. It's responsible for making decisions and performing reasoning based on fuzzy logic rules and inputs.
Both statements are accurate, and there is no conflict between them.
Question 33 |
Which of the following is not a mutation operator in a genetic algorithm?
A.Random resetting
B.Scramble
C.Inversion
D.Difference
Choose the correct answer from the options given below
A.Random resetting
B.Scramble
C.Inversion
D.Difference
Choose the correct answer from the options given below
A | A and B only
|
B | B and D only
|
C | C and D only
|
D | D only |
Question 33 Explanation:
A genetic algorithm typically uses various mutation operators to introduce diversity into the population. Here's an explanation of each of the options:
A. Random Resetting: Random resetting is a mutation operator where one or more genes in an individual's chromosome are randomly changed or reset to new random values. It is a valid mutation operator in genetic algorithms.
B. Scramble: The scramble operator involves shuffling or permuting a subset of genes within a chromosome. It is a valid mutation operator in genetic algorithms.
C. Inversion: The inversion operator reverses the order of a subset of genes within a chromosome. It is a valid mutation operator in genetic algorithms.
D. Difference: "Difference" is not a standard mutation operator in genetic algorithms. While operators like "random resetting," "scramble," and "inversion" are commonly used, "difference" is not a recognized mutation operator in this context.
So, the correct answer is D only because "Difference" is not a mutation operator commonly used in genetic algorithms.
Question 34 |
Which of the following is not a property of a good system for representation of knowledge in a particular domain?
A | Presentation adequacy
|
B | Inferential adequacy
|
C | Inferential efficiency
|
D | Acquisitional efficiency |
Question 34 Explanation:
The property that is not typically considered a property of a good system for the representation of knowledge in a particular domain is "Presentation adequacy."
Presentation adequacy refers to how well the system's knowledge representation can be presented and understood by humans. While it's important to have a representation that can be comprehended by humans, the primary properties often associated with a good knowledge representation system are:
Inferential Adequacy: The system's ability to support reasoning and inference within the domain. It should be able to draw meaningful conclusions and make inferences based on the represented knowledge.
Inferential Efficiency: How efficiently the system can perform reasoning and inference. A good system should allow for efficient processing and deduction of new knowledge from the existing representation.
Acquisitional Efficiency: How efficiently the system can acquire or learn new knowledge and integrate it into the existing representation. This relates to the ease of updating and expanding the knowledge base.
While presentation adequacy is important for human understanding, it's not traditionally considered one of the core properties of a knowledge representation system. Instead, it's often viewed as an interface or display issue, focusing on how well the representation can be communicated to users.
Question 35 |
Which is not a component of the natural language understanding process?
A | Morphological analysis
|
B | Semantic analysis
|
C | Pragmatic analysis
|
D | Meaning analysis |
Question 35 Explanation:
Meaning analysis is not typically considered a distinct component of the natural language understanding (NLU) process. Instead, it is often encompassed within the broader category of semantic analysis.
The key components of the NLU process include:
Morphological Analysis: This component deals with the analysis of word structure, including breaking words into meaningful units (morphemes), inflections, and word forms.
Semantic Analysis: This is the component responsible for understanding the meaning of words, phrases, and sentences. It involves determining the relationships between words and extracting the intended meaning.
Pragmatic Analysis: Pragmatics focuses on the interpretation of language in context, including factors like speech acts, implicatures, and understanding the intentions and presuppositions of the speaker.
So, "Meaning analysis" is usually encompassed within "Semantic analysis," and all the other components listed are integral parts of the natural language understanding process.
Question 36 |
Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R.
Assertion A: Dendral is an expert system
Reason R: The rationality of an agent is not related to its reaction to the environment.
In the light of the above statements. choose the correct answer from the options given below.
Assertion A: Dendral is an expert system
Reason R: The rationality of an agent is not related to its reaction to the environment.
In the light of the above statements. choose the correct answer from the options given below.
A | Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
|
B | Both A and R are true, but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
|
C | A is true but R is false
|
D | A is false but R is true |
Question 37 |
Overfitting is expected when we observe that?
A | With training iterations error on training set as well as test set decreases |
B | With training iterations error on training set decreases but test set increases |
C | With training iterations error on training set as well as test set increases |
D | With training iterations training set as well as test error remains constant |
Question 38 |
The A* algorithm is optimal when,
A | It always finds the solution with the lowest total cost if the heuristic 'h' is admissible. |
B | Always finds the solution with the highest total cost if the heuristic 'h' is admissible. |
C | Finds the solution with the lowest total cost if the heuristic 'h' is not admissible. |
D | It always finds the solution with the highest total cost if the heuristic 'h' is not admissible. |
Question 39 |
Which Artificial intelligence technique enables the computers to understand the associations and relationships between objects & Events?
A | Heuristic Processing |
B | Cognitive Science |
C | Relative Symbolism |
D | Pattern matching |
Question 40 |
What does the values of alpha-beta search get updated?
A | Along the path of search |
B | Initial state itself |
C | At the end |
D | None of these |
Question 41 |
A 4-input neuron has weights 1,2,3,4. The transfer function is linear with the constant of proportionality being equal to 3. The inputs are 5,7,10,30, respectively, Then the output will be,
A | 120 |
B | 213 |
C | 410 |
D | 507 |
Question 42 |
In a game playing search tree, up to which depth α-β pruning can be applied?
(A) Root (0) level
(B) 6 level
(C) 8 level
(D) Depends on utility value in a breadth first order
(A) Root (0) level
(B) 6 level
(C) 8 level
(D) Depends on utility value in a breadth first order
A | (B) and (C) only |
B | (A) and (B) only |
C | (A),(B) and (C) only |
D | (A) and (D) only |
Question 42 Explanation:
Alpha-beta pruning is a modified version of the minimax algorithm. It is an optimization technique for the minimax algorithm.
Alpha-beta Algorithm:
- Uses Depth first search
- only considers nodes along a single path from root at any time
α = highest-value choice found at any choice point of path for MAX (initially, α = −infinity)
β = lowest-value choice found at any choice point of path for MIN (initially, β = +infinity)
- Pass current values of α and β down to child nodes during search.
- Update values of α and β during search:
- MAX updates α at MAX nodes
- MIN updates β at MIN nodes
When to Prune:
- Prune whenever α ≥ β.
- Prune below a Max node whose alpha value becomes greater than or equal to the beta value of its ancestors.
- Max nodes update alpha based on children’s returned values. - Prune below a Min node whose beta value becomes less than or equal to the alpha value of its ancestors.
- Min nodes update beta based on children’s returned values.
Effectiveness of Alpha-Beta Search:
- Alpha/beta best case is O(b(d/2)) rather than O(bd)
- This is the same as having a branching factor of sqrt(b),
- (sqrt(b))d/ = b(d/2) (i.e., we have effectively gone from b to square root of b)
- In chess go from b ~ 35 to b ~ 6
- permitting much deeper search in the same amount of time
- In practice it is often b(2d/3)
Alpha-beta Algorithm:
- Uses Depth first search
- only considers nodes along a single path from root at any time
α = highest-value choice found at any choice point of path for MAX (initially, α = −infinity)
β = lowest-value choice found at any choice point of path for MIN (initially, β = +infinity)
- Pass current values of α and β down to child nodes during search.
- Update values of α and β during search:
- MAX updates α at MAX nodes
- MIN updates β at MIN nodes
When to Prune:
- Prune whenever α ≥ β.
- Prune below a Max node whose alpha value becomes greater than or equal to the beta value of its ancestors.
- Max nodes update alpha based on children’s returned values. - Prune below a Min node whose beta value becomes less than or equal to the alpha value of its ancestors.
- Min nodes update beta based on children’s returned values.
Effectiveness of Alpha-Beta Search:
- Alpha/beta best case is O(b(d/2)) rather than O(bd)
- This is the same as having a branching factor of sqrt(b),
- (sqrt(b))d/ = b(d/2) (i.e., we have effectively gone from b to square root of b)
- In chess go from b ~ 35 to b ~ 6
- permitting much deeper search in the same amount of time
- In practice it is often b(2d/3)
Question 43 |
In a database, a rule is defined as (P1 and P2) or P3? R1(0.8) and R2(0.3),where P1,P2,P3 are premises and R1,R2 are conclusions of rules with certainty factors(CF) 0.8 and 0.3 respectively. If any running program has produced P1,P2,P3 with CF as 0.5,0.8,0.2 respectively, find the CF of results on the basis of premises.
A | CF(R1=0.8),CF(R2=0.3)
|
B | CF(R1=0.40),CF(R2=0.15)
|
C | CF(R1=0.15),CF(R2=0.35)
|
D | CF(R1=0.8),CF(R2=0.35) |
Question 44 |
Match the following :


A | a-i, b-ii, c-iii, d-iv |
B | a-i, b-iii, c-iv, d-ii |
C | a-ii, b-iii, c-iv, d-i |
D | a-ii, b-ii, c-iii, d-iv |
Question 44 Explanation:
Absurd→ Clearly impossible being contrary to some evident truth.
Ambiguous→ Capable of more than one interpretation or meaning.
Axiom→ An assertion that is accepted and used without a proof.
Conjecture→ An opinion preferably based on some experience or wisdom
Ambiguous→ Capable of more than one interpretation or meaning.
Axiom→ An assertion that is accepted and used without a proof.
Conjecture→ An opinion preferably based on some experience or wisdom
Question 45 |
Match the following:


A | a-i, b-ii, c-iii, d-iv |
B | a-i, b-iii, c-ii, d-iv |
C | a-iii, b-ii, c-iv, d-i |
D | a-ii, b-iii, c-i, d-iv |
Question 45 Explanation:
Affiliate Marketing: Vendors ask partners to place logos on partner’s site. If customers click, come to vendors and buy.
Viral Marketing: Spread your brand on the net by word-of-mouth. Receivers will send your information to their friends.
Group Purchasing: Aggregating the demands of small buyers to get a large volume. Then negotiate a price.
Bartering Online: Exchanging surplus products and services with the process administered completely online by an intermediary. Company receives “points” for its contribution.
Viral Marketing: Spread your brand on the net by word-of-mouth. Receivers will send your information to their friends.
Group Purchasing: Aggregating the demands of small buyers to get a large volume. Then negotiate a price.
Bartering Online: Exchanging surplus products and services with the process administered completely online by an intermediary. Company receives “points” for its contribution.
Question 46 |
Let P(m, n) be the statement “m divides n” where the Universe of discourse for both the variables is the set of positive integers. Determine the truth values of the following propositions.
(a)∃m ∀n P(m, n)
(b)∀n P(1, n)
(c) ∀m ∀n P(m, n)
(a)∃m ∀n P(m, n)
(b)∀n P(1, n)
(c) ∀m ∀n P(m, n)
A | (a) - True; (b) - True; (c) - False |
B | (a) - True; (b) - False; (c) - False |
C | (a) - False; (b) - False; (c) - False |
D | (a) - True; (b) - True; (c) - True |
Question 46 Explanation:
Given P(m,n) ="m divides n"
Statement-A is ∃m ∀n P(m, n). Here, there exists some positive integer which divides every positive integer. It is true because there is positive integer 1 which divides every positive integer.
Statement-B is ∀n P(1, n). Here, 1 divided every positive integer. It is true.
Statement-C is ∀m ∀n P(m, n). Here, every positive integer divided every positive integer. It is false.
Statement-A is ∃m ∀n P(m, n). Here, there exists some positive integer which divides every positive integer. It is true because there is positive integer 1 which divides every positive integer.
Statement-B is ∀n P(1, n). Here, 1 divided every positive integer. It is true.
Statement-C is ∀m ∀n P(m, n). Here, every positive integer divided every positive integer. It is false.
Question 47 |
An agent can improve its performance by
A | Learning
|
B | Responding
|
C | Observing
|
D | Perceiving
|
Question 47 Explanation:
→ An intelligent agent (IA) is an autonomous entity which observes through sensors and acts upon an environment using actuators (i.e. it is an agent) and directs its activity towards achieving goals (i.e. it is "rational", as defined in economics).
→ Intelligent agents may also learn or use knowledge to achieve their goals. They may be very simple or very complex. A reflex machine, such as a thermostat, is considered an example of an intelligent agent.

→ Intelligent agents may also learn or use knowledge to achieve their goals. They may be very simple or very complex. A reflex machine, such as a thermostat, is considered an example of an intelligent agent.

Question 48 |
In Challenge-Response authentication the claimant
A | Proves that she knows the secret without revealing it |
B | Proves that she doesn’t know the secret |
C | Reveals the secret
|
D | Gives a challenge |
Question 48 Explanation:
→ Challenge-Response authentication is a family of protocols in which one party presents a question ("challenge") and another party must provide a valid answer ("response") to be authenticated.
→ The simplest example of a challenge–response protocol is password authentication, where the challenge is asking for the password and the valid response is the correct password.
→ A more interesting challenge–response technique works as follows. Say, Bob is controlling access to some resource. Alice comes along seeking entry. Bob issues a challenge, perhaps "52w72y". Alice must respond with the one string of characters which "fits" the challenge Bob issued. The "fit" is determined by an algorithm "known" to Bob and Alice. (The correct response might be as simple as "63x83z" (each character of response one more than that of challenge), but in the real world, the "rules" would be much more complex.) Bob issues a different challenge each time, and thus knowing a previous correct response (even if it isn't "hidden" by the means of communication used between Alice and Bob) is of no use.
→ The simplest example of a challenge–response protocol is password authentication, where the challenge is asking for the password and the valid response is the correct password.
→ A more interesting challenge–response technique works as follows. Say, Bob is controlling access to some resource. Alice comes along seeking entry. Bob issues a challenge, perhaps "52w72y". Alice must respond with the one string of characters which "fits" the challenge Bob issued. The "fit" is determined by an algorithm "known" to Bob and Alice. (The correct response might be as simple as "63x83z" (each character of response one more than that of challenge), but in the real world, the "rules" would be much more complex.) Bob issues a different challenge each time, and thus knowing a previous correct response (even if it isn't "hidden" by the means of communication used between Alice and Bob) is of no use.
Question 49 |
In Artificial Intelligence (AI), an environment is uncertain if it is
A | Not fully observable and not deterministic |
B | Not fully observable or not deterministic |
C | Fully observable but not deterministic
|
D | Not fully observable but deterministic
|
Question 49 Explanation:
→ Deterministic AI environments are those on which the outcome can be determined based on a specific state. In other words, deterministic environments ignore uncertainty.
→ Most real world AI environments are not deterministic. Instead, they can be classified as stochastic. Self-driving vehicles are a classic example of stochastic AI processes.
→ Most real world AI environments are not deterministic. Instead, they can be classified as stochastic. Self-driving vehicles are a classic example of stochastic AI processes.
Question 50 |
In Artificial Intelligence (AI), a simple reflex agent selects actions on the basis of
A | current percept, completely ignoring rest of the percept history. |
B | rest of the percept history, completely ignoring current percept. |
C | both current percept and complete percept history.
|
D | both current percept and just previous percept.
|
Question 50 Explanation:
→ Simple reflex agents act only on the basis of the current percept, ignoring the rest of the percept history. The agent function is based on the condition-action rule: "if condition, then action".
→ This agent function only succeeds when the environment is fully observable. Some reflex agents can also contain information on their current state which allows them to disregard conditions whose actuators are already triggered.
→ Infinite loops are often unavoidable for simple reflex agents operating in partially observable environments. Note: If the agent can randomize its actions, it may be possible to escape from infinite loops.

→ This agent function only succeeds when the environment is fully observable. Some reflex agents can also contain information on their current state which allows them to disregard conditions whose actuators are already triggered.
→ Infinite loops are often unavoidable for simple reflex agents operating in partially observable environments. Note: If the agent can randomize its actions, it may be possible to escape from infinite loops.

Access subject wise (1000+) question and answers by becoming as a solutions adda PRO SUBSCRIBER with Ad-Free content
Register Now
You have completed
questions
question
Your score is
Correct
Wrong
Partial-Credit
You have not finished your quiz. If you leave this page, your progress will be lost.
Correct Answer
You Selected
Not Attempted
Final Score on Quiz
Attempted Questions Correct
Attempted Questions Wrong
Questions Not Attempted
Total Questions on Quiz
Question Details
Results
Date
Score
Hint
Time allowed
minutes
seconds
Time used
Answer Choice(s) Selected
Question Text
Need more practice!
Keep trying!
Not bad!
Good work!
Perfect!
