Access-Control-Methods
Question 1 |
Let us consider a statistical time division multiplexing of packets. The number of sources is 10. In a time unit, a source transmits a packet of 1000 bits. The number of sources sending data for the first 20 time units is 6, 9, 3, 7, 2, 2, 2, 3, 4, 6, 1, 10, 7, 5, 8, 3, 6, 2, 9, 5 respectively. The output capacity of multiplexer is 5000 bits per time unit. Then the average number of backlogged of packets per time unit during the given period is
5 | |
4.45 | |
3.45 | |
0 |
If the no. of packets transmitted is larger than 5 then the extra packets are backlogged. This means gets added to the next number and further backlog is calculated.
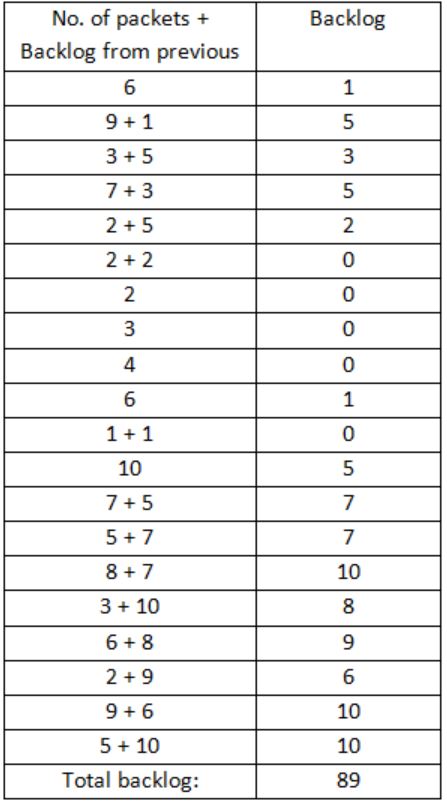
Average no. of backlogged packets = 89/20 = 4.45
Question 2 |
A broadcast channel has 10 nodes and total capacity of 10 Mbps. It uses polling for medium access. Once a node finishes transmission, there is a polling delay of 80 μs to poll the next node. Whenever a node is polled, it is allowed to transmit a maximum of 1000 bytes. The maximum throughput of the broadcast channel is
1 Mbps | |
100/11 Mbps | |
10 Mbps | |
100 Mbps |
(Tt) = 1000bytes/10×106bits/sec = 800μs
Polling delay = 80 μs
Efficiency = 800/800+80 = 800/880 = 10/11
Maximum throughput is
= 10/11 × 10 Mbps
= 100/11 Mbps
Question 3 |
64 Kbps | |
32 Mbps | |
32 Kbps | |
64 Mbps |
-- Link transmits frame per second= 4000 Frames per second
-- Each slot bits= 8 bits
-- Transmission rate of circuit of this TDM=?
Step-1: Transmission rate of circuit of this TDM= Link transmits frame per second * Each slot bits
= 4000 * 8
= 32000 bits (or 32Kbps)
Question 4 |
(A) Frequency Division Multiplexing(FDM) is a technique that can be applied when the bandwidth of a link is greater than combined bandwidth of signals to be transmitted.
(B) Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) is an analog multiplexing Technique to combine optical signals.
(C) WDM is a Digital Multiplexing Technique.
(D) TDM is a Digital Multiplexing Technique.
Which of the following is correct?
(A), (B), (C) and (D) are true. | |
(A), (B), (C) and (D) are false. | |
(A), (B) and (D) are false; (C) is true. | |
(A), (B) and (D) are True; (C) is false. |
If Statement-B is FALSE then definitely Statement-C should be TRUE.
Option-A: We can ruled out based on the above two constraints.
Option-B: We can ruled out based on the above two constraints.
Option-C: Statement-B is FALSE because Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) is an analog multiplexing Technique to combine optical signals.

