CPU-Scheduling
Question 1 |
12 |
Question 2 |
- The fastest computer gets the toughest job and the slowest computer gets the easiest job.
- Every computer gets at least one job.
65 |
Let the levels be 1,2,3,4,5,6. (1 is the least difficult, 6 is the most difficult level)
Let the computers be F,M,S( fast, medium, slow).
As per the given constraint, 1 must be given to F and 6 must be given to S.
Now we are left with 2,3,4,5 and F being assigned 1, S being assigned 6 and M being assigned none.
Another constraint is that, every computer must be assigned atleast one.
So compute with assigning one job to M, two jobs to M, three jobs to M and four jobs to M.
Assigning one job to M: we can assign 1 out of 4 jobs in (4C1 ways) and remaining 3 jobs to F,S in 2*2*2 = 8 ways. (each job has two options, either F or S),
Assigning two jobs to M: we can select two jobs from 4 in 4C2 ways and remaining 2 can be distributed to F and S in 2*2 ways ( each job has two options either F or S)
Assigning three jobs to M: we can select 3 out of 4 in 4C3 ways remaining can be distributed to F,M in 2 ways.
Assigning 4 jobs to M: it can be done in only one way.
Total : 4c1*8 + 4C2* 4 + 4C3*2 + 1
= 32+24+8+1
=65
Question 3 |
Which scheduling policy is most suitable for a time shared operating system?
Shortest Job First | |
Round Robin | |
First Come First Serve | |
Elevator |
Question 4 |
The sequence …………… is an optimal non-preemptive scheduling sequence for the following jobs which leaves the CPU idle for …………… unit(s) of time.

{3,2,1),1 | |
(2,1,3},0 | |
{3,2,1),0 | |
{1,2,3},5 |
So, (B) and (C) will be eliminated.
Now in (A) and (D):
For r(A),
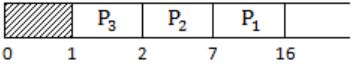
So, idle time is between 0 to 1 which in case of option (A).
For option(D),
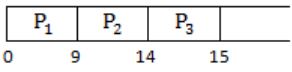
We can see there is no idle time at all, but in option given idle time is 5, which is not matching with our chart. So option (D) is eliminated.
Therefore, the correct sequence is option (A).
Question 5 |
Implementing preemptive scheduling needed hardware support. | |
Turnaround time includes waiting time | |
Round-robin policy can be used even when the CPU time required by each of the processes is not known apriori. | |
The goal is to only maximize CPU utilization and minimize throughput. |
- True. Preemptive scheduling needs hardware support such as a timer
- True. Turnaround time = Burst time + Waiting time
- True, RR assigns qunatume to each process equally. Hence, it is not required to know burst size apriori
- False. Maximize CPU utilization and throughput, and minimize waiting time etc.
Question 6 |
First-in First-Out | |
Round Robin | |
Priority Scheduling | |
Shortest Job First |
Question 7 |
A scheduling algorithm assigns priority proportional to the waiting time of a process. Every process starts with priority zero (the lowest priority). The scheduler re-evaluates the process priorities every T time units and decides the next process to schedule. Which one of the following is TRUE if the processes have no I/O operations and all arrive at time zero?
This algorithm is equivalent to the first-come-first-serve algorithm. | |
This algorithm is equivalent to the round-robin algorithm. | |
This algorithm is equivalent to the shortest-job-first algorithm. | |
This algorithm is equivalent to the shortest-remaining-time-first algorithm. |
Question 8 |
Consider a disk system with 100 cylinders. The requests to access the cylinders occur in following sequence:
4, 34, 10, 7, 19, 73, 2, 15, 6, 20
Assuming that the head is currently at cylinder 50, what is the time taken to satisfy all requests if it takes 1ms to move from one cylinder to adjacent one and shortest seek time first policy is used?
95 ms | |
119 ms | |
233 ms | |
276 ms |
4, 34, 10,7, 19, 73, 2, 15, 6, 20
Arrange the sequence in order
2, 4, 6, 10, 15, 19, 20, 34, 73
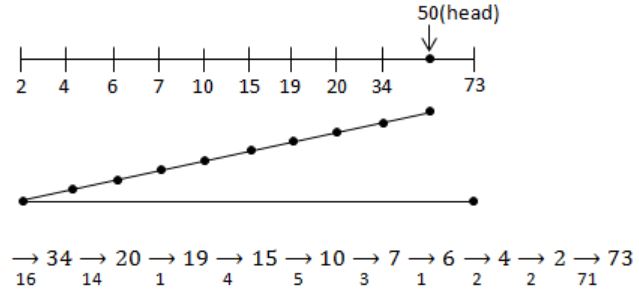
⇒ 1 ms to move from one cylinder to adjacent one
⇒ (16*1)+(14*1)+(1*1)+(4*1)+(5*1)+(3*1)+(1*1)+(2*1)+(2*1)+(71*1)
⇒ 16+14+1+4+5+3+1+2+2+71
⇒ 119 ms
Question 9 |
An operating system uses shortest remaining time first scheduling algorithm for pre-emptive scheduling of processes. Consider the following set of processes with their arrival times and CPU burst times (in milliseconds):

The average waiting time (in milliseconds) of the processes is
5.5 | |
5.6 | |
5.7 | |
5.8 |
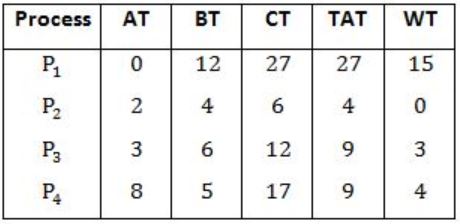
WT - Waiting Time
CT - Completion Time
TAT - Turn Around Time
TAT = CT - AT < br> WT = TAT - BT
Gantt chart using Shortest remaining time first,

Avg. WT = 15+0+3+4/4 = 22/4 = 5.5
Question 10 |

8 | |
16 | |
32 | |
48 |
Question 11 |
3 | |
2 | |
4 | |
5 |
 P 1 → P 2 is one switch
P 1 → P 2 is one switchP 2 → P 1 is 2nd switch
P 3 → P 3 is 3rd switch
Question 12 |
Priority scheduling | |
Round Robin Scheduling | |
Shortest Job First | |
FCFS |
Round Robin Scheduling: → To schedule processes fairly, a round-robin scheduler generally employs time-sharing, giving each job a time slot or quantum(its allowance of CPU time), and interrupting the job if it is not completed by then. The job is resumed next time a time slot is assigned to that process. If the process terminates or changes its state to waiting during its attributed time quantum, the scheduler selects the first process in the ready queue to execute.
→ Round-robin algorithm is a pre-emptive algorithm as the scheduler forces the process out of the CPU once the time quota expires.
Question 13 |
Consider the following set of processes and the length of CPU burst time given in milliseconds:

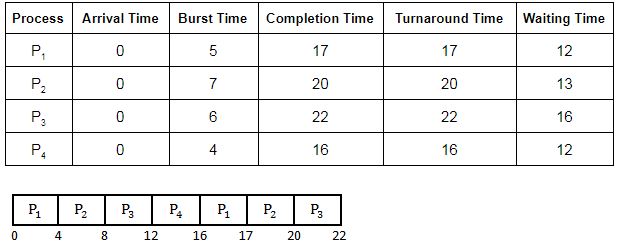
Assume that processes being scheduled with Round-Robin Scheduling Algorithm with Time Quantum 4ms. Then The waiting time for P4 is _________ ms.
0 | |
4 | |
12 | |
6 |
= Completion time - Arrival time
Since in question Arrival time is not given so consider it as “0” for all the processes.