Class-and-object
Question 1 |
It is possible to define a class within a class termed as nested class. There are _____ types of nested classes.
2 | |
3 | |
4 | |
5 |
Question 1 Explanation:
Nested classes are divided into two categories:
1. Static
2. Non static.
Nested classes that are declared static are simply called static nested classes.
Non static nested classes are called inner classes.
1. Static
2. Non static.
Nested classes that are declared static are simply called static nested classes.
Non static nested classes are called inner classes.
Question 2 |
When one object reference variable is assigned to another object reference variable then
a copy of the object is created. | |
a copy of the reference is created. | |
a copy of the reference is not created. | |
it is illegal to assign one object reference variable to another object reference variable. |
Question 2 Explanation:
• A reference variable is an alias, that is, another name for an already existing variable. Once a reference is initialized with a variable, either the variable name or the reference name may be used to refer to the variable.
• A reference variable must be initialized at the time of declaration.
• A reference variable must be initialized at the time of declaration.
Question 3 |
Which of the following C++ statements correctly declares an abstract class?
Class A {virtual void show() = 0; };
| |
Class A {void show() = 0;};
| |
Class A {void show() { } ; };
| |
Class A {show() = 0; }; |
Question 4 |
If a class C is derived from class B, which is derived from class A, all through public inheritance, then a class C member function can access
Protected and public data only in C and B | |
Protected and public data only in C | |
Private data in A and B | |
Protected data in A and B |
Question 4 Explanation:
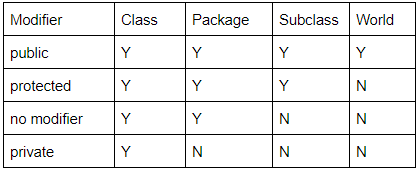
The following table shows the access to members permitted by each modifier.

Question 5 |
Members of class by default are
Public | |
Private | |
Protected | |
Mandatory to specify |
Question 5 Explanation:
→A class in C++ is a user defined type or data structure declared with keyword class that has data and functions (also called methods) as its members whose access is governed by the three access specifiers private, protected or public (by default access to members of a class is private).
→The private members are not accessible outside the class; they can be accessed only through methods of the class. The public members form an interface to the class and are accessible outside the class.
→The private members are not accessible outside the class; they can be accessed only through methods of the class. The public members form an interface to the class and are accessible outside the class.
There are 5 questions to complete.
