IPv4-and-Fragmentation
Question 1 |
Consider an IP packet with a length of 4,500 bytes that includes a 20-byte IPv4 header and a 40-byte TCP header. The packet is forwarded to an IPv4 router that supports a Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) of 600 bytes. Assume that the length of the IP header in all the outgoing fragments of this packet is 20 bytes. Assume that the fragmentation offset value stored in the first fragment is 0.
The fragmentation offset value stored in the third fragment is __________.
144 | |
145 | |
146 | |
147 |
Therefore Payload = 600 - 20 = 580 bytes.
As we know fragment size should be multiple of 8 but 580 bytes is not a multiple of 8, therefore fragment size is 576 bytes.
Offset value of kth fragment = Fragment size *( kth fragment - 1) / scaling factor
Offset value of third fragment = 576 * (3-1) / 8 = 144
Question 2 |
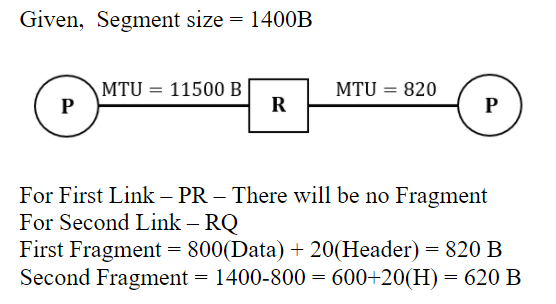
If the second fragment is lost, R will resend the fragment with the IP identification value 0x1234. | |
If the second fragment is lost, P is required to resend the whole TCP segment. | |
Two fragments are created at R and the IP datagram size carrying the second fragment is 620 bytes. | |
TCP destination port can be determined by analysing only the second fragment. |
Question 3 |
Host A sends a UDP datagram containing 8880 bytes of user data to host B over an Ethernet LAN. Ethernet frames may carry data up to 1500 bytes (i.e. MTU = 1500 bytes). Size of UDP header is 8 bytes and size of IP heard is 20 bytes. There is no option field in IP header. How many total number of IP fragments will be transmitted and what will be the contents of offset field in the last fragment?
6 and 925 | |
6 and 7400 | |
7 and 1110 | |
7 and 8880 |
Total Size excluding IP Header = 8888 bytes.
Number of fragments = ceil(8880+ UDP or TCP header /1500-IP header)
= ceil(8880+8 /1500-20)
= ceil(8888/1480)
= 7
Offset of last fragment = (MTU-IP header ) *( number of fragments -1) / scaling factor = 1110 (scaling factor of 8 is used in offset field).
= (1500-20)* (7-1)/8
= 1110
Question 4 |
An IP datagram of size 1000 bytes arrives at a router. The router has to forward this packet on a link whose MTU (maximum transmission unit) is 100 bytes. Assume that the size of the IP header is 20 bytes.
The number of fragments that the IP datagram will be divided into for transmission is _________.
13 | |
14 | |
15 | |
16 |
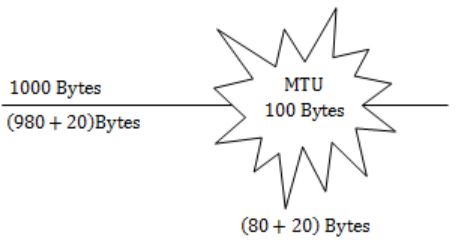
Size of Datagram (L) = 1000 bytes
MTU = 100 bytes
Size of IP header = 20 bytes
Size of Data that can be transmitted in one fragment (payload) = 100 – 20 = 80 bytes
Size of Data to be transmitted = Size of Datagram – size of header = 1000 – 20 = 980 bytes
No. of fragments required = ⌈980/80⌉ = 13
Question 5 |
Flag | |
Offset | |
TOS | |
Identifier |
