Switching
Question 1 |
Consider a source computer (S) transmitting a file of size 106 bits to a destination computer (D) over a network of two routers (R1 and R2) and three links (L1, L2 and L3). L1 connects S to R1; L2 connects R1 to R2; and L3 connects R2 to D. Let each link be of length 100 km. Assume signals travel over each link at a speed of 108 meters per second. Assume that the link bandwidth on each link is 1Mbps. Let the file be broken down into 1000 packets each of size 1000 bits. Find the total sum of transmission and propagation delays in transmitting the file from S to D?
1005 ms | |
1010 ms | |
3000 ms | |
3003 ms |
Question 1 Explanation:
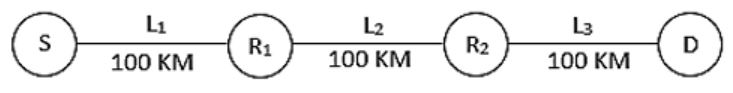
Propagation delay = (Distance) / (Velocity) = 3*105/108 = 3ms
Total transmission delay for 1 packet = 3 * L / B = 3*(1000/106) = 3ms. Because at source and 2 routers, we need to transmit the bits.
The first packet will reach destination = Tt + Tp = 6ms.
While the first packet was reaching to D, other packets must have been processing in parallel. So D will receive remaining packets 1 packet per 1 ms from R2. So remaining 999 packets will take 999 ms.
And total time will be 999 + 6 = 1005 ms
Question 2 |
The cost of the network is usually determined by :
Time complexity | |
Switching complexity | |
Circuit complexity | |
None of these |
Question 2 Explanation:
→ The cost of the network is usually determined by switching complexity. Switching complexity include, but not limited to, the number of switching components, the delay time of signal
propagating through the network, the complexity of path selection algorithms, and the complexity of physically designing the network.
Question 3 |
Virtual circuit is associated with a __________ service.
Connectionless | |
Error-free | |
Segmentation | |
Connection-oriented |
Question 3 Explanation:
Virtual circuit communication resembles circuit switching, since both are connection oriented, meaning that in both cases data is delivered in correct order, and signalling overhead is required during a connection establishment phase.
There are 3 questions to complete.
