System-Calls
Question 1 |
Which of the following standard C library functions will always invoke a system call when executed from a single-threaded process in a UNIX/linux operating system?
sleep | |
strlen | |
malloc | |
exit |
Question 1 Explanation:
- A sleep system call takes a time value as a parameter, specifying the minimum amount of time that the process is to sleep before resuming execution. The parameter typically specifies seconds, although some operating systems provide finer resolution, such as milliseconds or microseconds.
- strlen() is not system call.
- The function call malloc() is a library function call that further uses the brk() or sbrk() system call for memory allocation
- Exit also system call
Question 2 |
The following C program is executed on a Unix/Linux system:
#include <unistd.h>
int main ()
{
int i ;
for (i=0; i<10; i++)
if (i%2 == 0) fork ( ) ;
return 0 ;
}
The total number of child processes created is _____.
26 | |
33 | |
31 | |
28 |
Question 2 Explanation:
Fork( ) statement is executed when 'i' is even. Thus the above code is equivalent to
#include
int main( )
{
int i;
fork( );
fork( );
fork( );
fork( );
fork( );
}
n - fork statements will have 2n-1 child.
Hence, n = 5 ⇒ We have 31 child processes.
#include
int main( )
{
int i;
fork( );
fork( );
fork( );
fork( );
fork( );
}
n - fork statements will have 2n-1 child.
Hence, n = 5 ⇒ We have 31 child processes.
Question 3 |
System calls are usually invoked by using
a software interrupt | |
polling | |
an indirect jump | |
a privileged instruction |
Question 3 Explanation:
Software interrupts are implementing device drivers (or) transitions between protected mode of operations, such as system calls.
Question 4 |
A process executes the following code
for(i=0; i<n; i++) for();
The total number of child processes created is
n | |
(2n) - 1 | |
2n | |
(2n+1) - 1 |
Question 4 Explanation:
Fork is a system call, implements in kernel.
It is a operation where process creates a copy of itself.
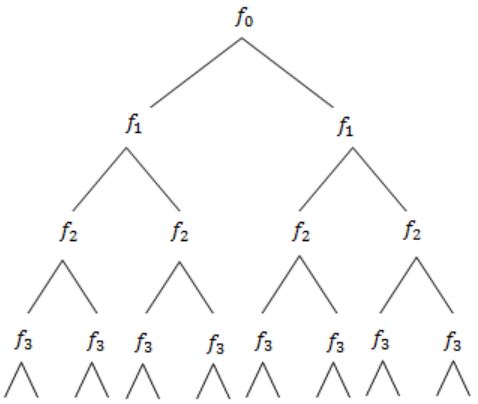
1,3,7,15,31,... ⇒ 2n-1
It is a operation where process creates a copy of itself.

1,3,7,15,31,... ⇒ 2n-1
Question 5 |
A process executes the code
fork(); fork(); fork();
The total number of child processes created is
3 | |
4 | |
7 | |
8 |
Question 5 Explanation:
The no. of child process created = 2n - 1 = 23 - 1 = 7 (where n is number of fork() statements)
7 are child processes.
7 are child processes.
Question 6 |
Consider the following code fragment:
if (fork() == 0)
{ a = a + 5; printf(“%d, %d\n”, a, &a); }
else { a = a – 5; printf(“%d, %d\n”, a, &a); }
Let u, v be the values printed by the parent process, and x, y be the values printed by the child process. Which one of the following is TRUE?
u = x + 10 and v = y
| |
u = x + 10 and v is ≠ y | |
u + 10 = x and v = y | |
u + 10 = x and v ≠ y |
Question 6 Explanation:
u, v values printed by parent process.
u = a - 5; v be address of a
a = u + 5;
x, y values printed by child process.
x = a + 5; y be the address of a
x = u + 5 + 5; v = y
x = u + 10
u = a - 5; v be address of a
a = u + 5;
x, y values printed by child process.
x = a + 5; y be the address of a
x = u + 5 + 5; v = y
x = u + 10
Question 7 |
Consider the following segment of codes related to process creation. How many times the message “ child process created” will be printed?
#include
Void main(){
fork();fork();fork();
printf(“child process created”);
}
9 | |
7 | |
8 | |
3 |
Question 7 Explanation:
System call fork() is used to create processes. It takes no arguments and returns a process ID. The purpose of fork() is to create a new process, which becomes the child process of the caller. After a new child process is created, both processes will execute the next instruction following the fork() system call.
Number process created are 2number of fork() calls= 23=8
Number process created are 2number of fork() calls= 23=8
There are 7 questions to complete.
