Relational Schema
Question 1 |
Logical data independence is the ability to change________schema without having to change_____ Schema
internal; external | |
conceptual; internal | |
conceptual; external | |
internal; conceptual |
Question 1 Explanation:
The three-schema approach provides for three types of schemas with schema techniques based on formal language descriptions:
→External schema for user views
→Conceptual schema integrates external schemata
→Internal schema that defines physical storage structures
→External schema for user views
→Conceptual schema integrates external schemata
→Internal schema that defines physical storage structures
Question 2 |
Which of the following attributes can be considered as composite, single-valued and key attribute?
Age | |
Date of birth | |
Gender | |
Enrollment number |
Question 2 Explanation:
Types of Attributes
Simple attribute − Simple attributes are atomic values, which cannot be divided further. For example, a student's phone number is an atomic value of 10 digits.
Composite attribute − Composite attributes are made of more than one simple attribute. For example, a student's complete name may have first_name and last_name.
Derived attribute − Derived attributes are the attributes that do not exist in the physical database, but their values are derived from other attributes present in the database. For example, average_salary in a department should not be saved directly in the database, instead it can be derived. For another example, age can be derived from data_of_birth.
Single-value attribute − Single-value attributes contain single value. For example − Social_Security_Number.
Multi-value attribute − Multi-value attributes may contain more than one values. For example, a person can have more than one phone number, email_address, etc.
Key is an attribute or collection of attributes that uniquely identifies an entity among entity set.
Simple attribute − Simple attributes are atomic values, which cannot be divided further. For example, a student's phone number is an atomic value of 10 digits.
Composite attribute − Composite attributes are made of more than one simple attribute. For example, a student's complete name may have first_name and last_name.
Derived attribute − Derived attributes are the attributes that do not exist in the physical database, but their values are derived from other attributes present in the database. For example, average_salary in a department should not be saved directly in the database, instead it can be derived. For another example, age can be derived from data_of_birth.
Single-value attribute − Single-value attributes contain single value. For example − Social_Security_Number.
Multi-value attribute − Multi-value attributes may contain more than one values. For example, a person can have more than one phone number, email_address, etc.
Key is an attribute or collection of attributes that uniquely identifies an entity among entity set.
Question 3 |
Let R and S be two relations with the following schema
R (P, Q, R1, R2, R3)
S (P, Q, S1, S2)
Where (P, Q) is the key for both schemas. Which of the following queries are equivalent?
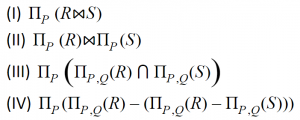
R (P, Q, R1, R2, R3)
S (P, Q, S1, S2)
Where (P, Q) is the key for both schemas. Which of the following queries are equivalent?
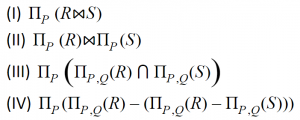
Only (I) and (II) | |
Only (I) and (III) | |
Only (I), (II) and (III) | |
Only (I), (III) and (IV) |
Question 3 Explanation:
Natural join is based on the common columns of the two tables.
We have two common columns in 'R' and 'S' which are 'P' and 'Q'.
(I) Both P and Q are used while doing the join, i.e., both P and Q are used to filter.
(II) Q is not used here for filtering. Natural join is done on all P's from R and all P's from S. So different from option (I).
(III) Through venn diagram it can be proved that A∩B = A - (A-B).
So through the above formula we can say that (III) and (IV) are equivalent.
So, finally (I), (III) and (IV) are equivalent.
We have two common columns in 'R' and 'S' which are 'P' and 'Q'.
(I) Both P and Q are used while doing the join, i.e., both P and Q are used to filter.
(II) Q is not used here for filtering. Natural join is done on all P's from R and all P's from S. So different from option (I).
(III) Through venn diagram it can be proved that A∩B = A - (A-B).
So through the above formula we can say that (III) and (IV) are equivalent.
So, finally (I), (III) and (IV) are equivalent.
Question 4 |
Anomalies are avoided by splitting the offending relation into multiple relations, also known as ________.
Acupressure | |
Decomposition | |
Precomposition | |
Both decomposition & precomposition |
Question 4 Explanation:
Anomalies are avoided by splitting the offending relation into multiple relations, also known as Decomposition.
There are 4 questions to complete.
