Computer-Networks
Question 1 |
A | SYN bit = 1, SEQ number = X+1, ACK bit = 0, ACK number = Y, FIN bit = 0 |
B | SYN bit = 0, SEQ number = X+1, ACK bit = 0, ACK number = Y, FIN bit = 1 |
C | SYN bit = 1, SEQ number = Y, ACK bit = 1, ACK number = X+1, FIN bit = 0 |
D | SYN bit = 1, SEQ number = Y, ACK bit = 1, ACK number = X, FIN bit = 0 |
Q will send the SYN bit = 1 to the connection establishment.
Q Seq number will be Y different from X
ACK bit = 1 because sending the ACK
ACK number = X+1 (Next seq number id)
FIN bit = 0 (Because establishing the connection)
Question 2 |
A | 111 |
B | 100 |
C | 101 |
D | 110 |

Question 3 |
A | The next hop router for a packet from R to P is Y. |
B | The distance from R to Q will be stored as 7. |
C | The next hop router for a packet from R to Q is Z. |
D | The distance from R to P will be stored as 10. |
Given R gets the distance vector (3,2,5)
After the one iteration distance vector from X to P, Y to P, and Z to P is (7, 6, 5) respectively
The distance vector from R to P via X Y Z is (3+7, 2+6, 5+5) =(10, 8, 10)
So Take minimum distance from R to P which is 8 via Y
After the iteration distance vector from X to Q, Y to Q, Z to Q is ( 4, 6, 8) respectively
The distance vector from R to Q via X Y Z is (3+4, 2+6, 5+8) = (7, 8 13)
So Take minimum distance from R to Q which is 7 via X.
Question 4 |
A | 135 |
1 frames takes = Tt = L / B.w. => 1000 / 10^6 = 1 millisec
1000 frame Tt = 1000 x 1 millisec = 1 sec
In 1 sec, 1000 frames sends, which is 1 millisec per frame.
So, G = 1
Efficiency of Pure Aloha (η) = G x e-2G
where G = Number of requests per time slot willing to transmit.
e = Mathematical constant approximately equal to 2.718
So, η = 1 x 2.718(-2 x 1) = 0.1353
Therefore, In 1 sec1000 frames = 0.1353 x 1000 = 135.3(closest integer) =>135
Throughput => 135
Question 5 |
- For any two letters, the code assigned to one letter must not be a prefix of the code assigned to the other letter.
- For any two letters of the same frequency, the letter which occurs earlier in the dictionary order is assigned a code whose length is at most the length of the code assigned to the other letter.
A | 21 |
B | 30 |
C | 23 |
D | 25 |
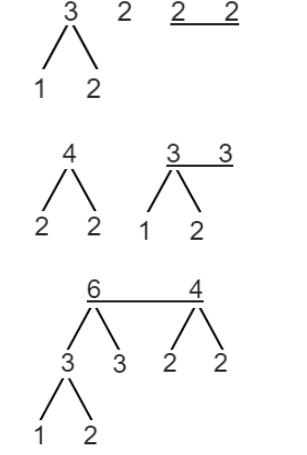
Input String : abbccddeee
The character frequencies are
|
Character |
a |
b |
c |
d |
e |
|
Frequency |
1 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
3 |
|
Binary Code |
? |
? |
? |
? |
? |

Question 6 |
What is the distance of the following code 000000, 010101, 000111, 011001, 111111?
A | 2 |
B | 3 |
C | 4 |
D | 1 |
010101 ⊕ 011001 = 001100
Question 7 |
Assume that you have made a request for a web page through your web browser to a web server. Initially the browser cache is empty. Further, the browser is configured to send HTTP requests in non-persistent mode. The web page contains text and five very small images. The minimum number of TCP connections required to display the web page completely in your browser is ______.
A | 6 |
Hence, 1 Text + 5 Image = 6 Objects
Question 8 |
Consider the following statements about the functionality of an IP based router.
- I. A router does not modify the IP packets during forwarding.
II. It is not necessary for a router to implement any routing protocol.
III. A router should reassemble IP fragments if the MTU of the outgoing link is larger than the size of the incoming IP packet.
Which of the above statements is/are TRUE?
A | I and II only |
B | II only |
C | I only |
D | II and III only
|
II: Is True.
III: Reassemble is not necessary at the router.
Question 9 |
An organization requires a range of IP addresses to assign one to each of its 1500 computers. The organization has approached an Internet Service Provider (ISP) for this task. The ISP uses CIDR and serves the requests from the available IP address space 202.61.0.0/17. The ISP wants to assign an address space to the organization which will minimize the number of routing entries in the ISP’s router using route aggregation. Which of the following address spaces are potential candidates from which the ISP can allot any one to the organization?
I. 202.61.84.0/21 II. 202.61.104.0/21 III. 202.61.64.0/21 IV. 202.61.144.0/21
A | I and II only
|
B | III and IV only
|
C | II and III only
|
D | I and IV only
|
And to Assign an IP address for 1500 computer, we require 11 bit from HID part.
So NID + SID = 17 + 4 = 21 bits and HID = 11 bits
NID HID
202.61.0 0000 000.00000000
So, from the given option, possible IP Address is
I. 84 -> 0 1010 100 (Because in HID bit 1 is not possible)
II. 104 -> 0 1101 000
III. 64 -> 0 1000 000
IV. 144 -> 1 0010 000 (Because in NID bit 1 is not possible )
Question 10 |
Consider a TCP connection between a client and a server with the following specifications: the round trip time is 6 ms, the size of the receiver advertised window is 50 KB, slow start threshold at the client is 32 KB, and the maximum segment size is 2 KB. The connection is established at time t=0. Assume that there are no timeouts and errors during transmission. Then the size of the congestion window (in KB) at time t+60 ms after all acknowledgements are processed is ______.
A | 44 |
Here, t + 60 is nothing but at the 10 RTT (60/6 = 10), but here it’s asking after all acknowledgement are processed it means after the 10th RTT, i.e., at the 11RTT.
1st transmission: 2 KB
2nd transmission: 4 KB
3rd transmission: 8 KB
4th transmission: 16 KB
5th transmission: 32 KB (Threshold reached)
6th transmission: 34 KB
7th transmission: 36 KB
8th transmission: 38 KB
9th transmission: 40 KB
10th transmission: 42 KB
At the completion of 10th transmission RTT = 10*6 = 60 ms
For the 11th transmission, The congestion window size is 44 KB.
Question 11 |
Consider a long-lived TCP session with an end-to-end bandwidth of 1 Gbps (= 109 bits/second). The session starts with a sequence number of 1234. The minimum time (in seconds, rounded to the closest integer) before this sequence number can be used again is _________.
A | 33 |
B | 34 |
C | 35 |
D | 36 |
The process of using all the sequence number and repeating a previously used sequence number.
The time taken to wrap around is called wrap around time:
Minimum Time = Wrap around time = Total number of bits in sequence number / Bandwidth = 232 * 8 / 109 = 34.35 == 34 (closest integer)
Question 12 |
Match the following:
Field Length in bits P. UDP Header's Port Number I. 48 Q. Ethernet MAC Address II. 8 R. IPv6 Next Header III.32 S. TCP Header's Sequence Number IV. 16
A | P-III, Q-IV, R-II, S-I |
B | P-II, Q-I, R-IV, S-III |
C | P-IV, Q-I, R-II, S-III |
D | P-IV, Q-I, R-III, S-II |
Q. Ethernet MAC Address - 48 bits
R. IPV6 Next Header - 8 bits
S. TCP Header’s Sequence Number - 32 bits
Question 13 |
(i) The cwnd increase by 2 MSS on every successful acknowledgement.
(ii) The cwnd approximately doubles on every successful acknowledgement.
(iii) The cwnd increase by 1 MSS every round trip time.
(iv) The cwnd approximately doubles every round trip time.
Which one of the following is correct?
A | Only (ii) and (iii) are true |
B | Only (i) and (iii) are true
|
C | Only (iv) is true |
D | Only (i) and (iv) are true |
Initially, TCP starts with cwnd of 1 MSS. On every ack, it increases cwnd by 1 MSS.
That is, cwnd doubles every RTT.
Initially sends 1 segment. On ack, sends 2 segments.
After these 2 acks come back, sends 4 segments etc.
TCP rate increases exponentially during slow start.
Slow start continues till cwnd reaches threshold.
After threshold is reached, cwnd increases more slowly, by one 1 MSS every RTT.
Question 14 |
Consider a simple communication system where multiple nodes are connected by a shared broadcast medium (like Ethernet or wireless). The nodes in the system use the following carrier-sense based medium access protocol. A node that receives a packet to transmit will carrier-sense the medium for 5 units of time. If the node does not detect any other transmission in this duration, it starts transmitting its packet in the next time unit. If the node detects another transmission, it waits until this other transmission finishes, and then begins to carrier-sense for 5 time units again. Once they start to transmit, nodes do not perform any collision detection and continue transmission even if a collision occurs. All transmissions last for 20 units of time. Assume that the transmission signal travels at the speed of 10 meters per unit time in the medium.
Assume that the system has two nodes P and Q, located at a distance d meters from each other. P starts transmitting a packet at time t=0 after successfully completing its carrier-sense phase. Node Q has a packet to transmit at time t=0 and begins to carrier-sense the medium.
The maximum distance d (in meters, rounded to the closest integer) that allows Q to successfully avoid a collision between its proposed transmission and P’s ongoing transmission is ___________.
A | 50 |
B | 51 |
C | 52 |
D | 53 |
Now signal travels at the speed of 10 meters per unit time.
Therefore, in 5 unit time, it can travel a maximum distance (d) of 50 m (5*10), which allows the receiver (Q) to sense that the channel is busy.
Question 15 |
Consider an IP packet with a length of 4,500 bytes that includes a 20-byte IPv4 header and a 40-byte TCP header. The packet is forwarded to an IPv4 router that supports a Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) of 600 bytes. Assume that the length of the IP header in all the outgoing fragments of this packet is 20 bytes. Assume that the fragmentation offset value stored in the first fragment is 0.
The fragmentation offset value stored in the third fragment is __________.
A | 144 |
B | 145 |
C | 146 |
D | 147 |
Therefore Payload = 600 - 20 = 580 bytes.
As we know fragment size should be multiple of 8 but 580 bytes is not a multiple of 8, therefore fragment size is 576 bytes.
Offset value of kth fragment = Fragment size *( kth fragment - 1) / scaling factor
Offset value of third fragment = 576 * (3-1) / 8 = 144
Question 16 |
Which of the following assertions is FALSE about the Internet Protocol (IP)?
A | It is possible for a computer to have multiple IP addresses
|
B | IP packets from the same source to the same destination can take different routes in the network
|
C | IP ensures that a packet is discarded if it is unable to reach its destination within a given number of hops
|
D | The packet source cannot set the route of an outgoing packets; the route is determined only by the routing tables in the routers on the way
|
Question 17 |
Which of the following functionalities must be implemented by a transport protocol over and above the network protocol?
A | Recovery from packet losses |
B | Detection of duplicate packets |
C | Packet delivery in the correct order |
D | End to end connectivity |
Question 18 |
The subnet mask for a particular network is 255.255.31.0. Which of the following pairs of IP addresses could belong to this network?
A | 172.57.88.62 and 172.56.87.233
|
B | 10.35.28.2 and 10.35.29.4 |
C | 191.203.31.87 and 191.234.31.88 |
D | 128.8.129.43 and 128.8.161.55 |
128.8.129.43 (Bitwise AND) 255.255.31.0 = 128.8.1.0
128.8.161.55 (Bitwise AND) 255.255.31.0 = 128.8.1.0
Question 19 |
A 2 km long broadcast LAN has 107 bps bandwidth and uses CSMA/CD. The signal travels along the wire at 2×108 m/s. What is the minimum packet size that can be used on this network?
A | 50 bytes |
B | 100 bytes |
C | 200 bytes |
D | None of the above |
d= 2 km = 2 x 103 m, v = 2 x 108 m/s, B= 107
Tp = d / v = 2 x 103 /(2 x 108 ) seconds = 10-5 seconds
Let L bits be minimum size of frame, then Tt = t L / B = L / 107 seconds
Now, Tt = 2Tp
L/107 = 2 x 10-5 = 200 bits = (200 / 8) bytes = 25 bytes
Question 20 |
Host A is sending data to host B over a full duplex link. A and B are using the sliding window protocol for flow control. The send and receive window sizes are 5 packets each. Data packets (sent only from A to B) are all 1000 bytes long and the transmission time for such a packet is 50 µs. Acknowledgement packets (sent only from B to A) are very small and require negligible transmission time. The propagation delay over the link is 200 µs. What is the maximum achievable throughput in this communication?
A | 7.69 × 106 bps
|
B | 11.11 × 106 bps |
C | 12.33 × 106 bps |
D | 15.00 × 106 bps |
Transmission rate , Tt = L / B.W
Therefore, B.W. = L / Tt = 1000 bytes/ 50 μs = 8000 bits / 50 μs=160 Mbps
Efficiency = N / 1 + 2a, where a = Tp / Tt
Efficiency = 5 * 50 / (50+400) = 250/450 = 5/9
Maximum achievable throughput = Efficiency * B.W = (5/9)*160 Mbps = 88.88 Mbps = = 11.11 x 106 bytes per second
*Actual option should be in bytes per second.
Question 21 |
Choose the best matching between Group 1 and Group 2.
Group-1 Group-2
P. Data link 1. Ensures reliable transport of data
over a physical point-to-point link
Q. Network layer 2. Encoder/decodes data for physical
transmission
R. Transport layer 3. Allows end-to-end communication
between two processes
4. Routes data from one network
node to the nextA | P - 1, Q - 4, R - 3 |
B | P - 2, Q - 4, R - 1
|
C | P - 2, Q - 3, R - 1 |
D | P - 1, Q - 3, R - 2 |
Transport Layer :: Fourth layer of the OSI Model, Responsible for Service point addressing/Socket to socket connection or end to end connection with full reliability.
Network Layer :: Third layer of the OSI Model, Responsible for Host to Host.
Question 22 |
Which of the following is NOT true with respect to a transparent bridge and a router?
A | Both bridge and router selectively forward data packets
|
B | A bridge uses IP addresses while a router uses MAC addresses
|
C | A bridge builds up its routing table by inspecting incoming packets |
D | A router can connect between a LAN and a WAN |
Question 23 |
How many 8-bit characters can be transmitted per second over a 9600 baud serial communication link using asynchronous mode of transmission with one start bit, eight data bits, two stop bits, and one parity bit?
A | 600 |
B | 800 |
C | 876 |
D | 1200 |
So bit rate is 9600 bps.
To send one char we need to send (1 + 8 + 2 +1) = 12
So total char send = 9600 / 12 = 800
Question 24 |
A and B are the only two stations on an Ethernet. Each has a steady queue of frames to send. Both A and B attempt to transmit a frame, collide, and A wins the first backoff race. At the end of this successful transmission by A, both A and B attempt to transmit and collide. The probability that A wins the second backoff race is:
A | 0.5 |
B | 0.625 |
C | 0.75 |
D | 1.0 |
The probability that A wins the second back-off race = 5/8 = 0.625
More explanation in the video.
Question 25 |
The routing table of a router is shown below:
Destination Sub net mask Interface 128.75.43.0 255.255.255.0 Eth0 128.75.43.0 255.255.255.128 Eth1 192.12.17.5 255.255.255.255 Eth3 Default Eth2
On which interfaces will the router forward packets addressed to destinations 128.75.43.16 and 192.12.17.10 respectively?
A | Eth1 and Eth2 |
B | Eth0 and Eth2 |
C | Eth0 and Eth3 |
D | Eth1 and Eth3 |
If results of ANDing subnet masks and IP address are same then subnet mask with higher number of 1s is preferred.
IP address 128.75.43.16 is AND with 255.255.255.0 results 128.75.43.0 Net ID which is similar to destination of this mask, but ANDing 128.75.43.16 with 255.255.255.128 also results same destination. So, here, mask with higher number of one is considered and router will forward packet to Eth1.
ANDing 192.12.17.10 with three subnet mask in table does not result in destination Net ID so router will forward this packet to default network via Eth2.
Question 26 |
Consider three IP networks A, B and C. Host HA in network A sends messages each containing 180 bytes of application data to a host HC in network C. The TCP layer prefixes a 20 byte header to the message. This passes through an intermediate network B. The maximum packet size, including 20 byte IP header, in each network is:
A : 1000 bytes
B : 100 bytes
C : 1000 bytes
The network A and B are connected through a 1 Mbps link, while B and C are connected by a 512 Kbps link (bps = bits per second).

Assuming that the packets are correctly delivered, how many bytes, including headers, are delivered to the IP layer at the destination for one application message, in the best case? Consider only data packets.
A | 200 |
B | 220 |
C | 240 |
D | 260 |
Data will be divided in three packets as:
First packet: 80 bytes + 20 byte of header
Second packet: 80 bytes + 20 byte of header
Third packet: 40 bytes + 20 byte of header
Note: Defragmentation (grouping of fragments) is done only at destination.
HC will receive total 260 bytes including header.
Question 27 |
Consider three IP networks A, B and C. Host HA in network A sends messages each containing 180 bytes of application data to a host HC in network C. The TCP layer prefixes a 20 byte header to the message. This passes through an intermediate network B. The maximum packet size, including 20 byte IP header, in each network is:
A : 1000 bytes
B : 100 bytes
C : 1000 bytes
The network A and B are connected through a 1 Mbps link, while B and C are connected by a 512 Kbps link (bps = bits per second).

What is the rate at which application data is transferred to host HC? Ignore errors, acknowledgements, and other overheads.
A | 325.5 Kbps
|
B | 354.5 Kbps |
C | 409.6 Kbps |
D | 512.0 Kbps |
Application data is transferred at rate of (180/260) x 512 Kbps = 354.46 Kbps
Question 28 |
A simple and reliable data transfer can be accomplished by using the ‘handshake protocol’. It accomplishes reliable data transfer because for every data item sent by the transmitter __________.
A | in this case receiver has to respond that receiver can be able to receive the data item. |
Question 29 |
Start and stop bits do not contain an ‘information’ but are used in serial communication for
A | Error detection |
B | Error correction |
C | Synchronization |
D | Slowing down the communications |
Question 30 |
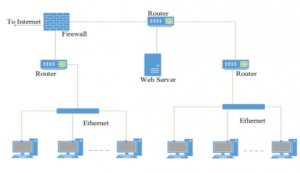
What is the number of subnets inside the enterprise network?
A | 3 |
B | 12 |
C | 6 |
D | 8 |
Where router 2 (via Firewall) has the half of the addresses.
Router 1 (via web server) has other half which is further divided into two subnets which is web server and router 3. So total of 3 subnets possible.
Question 31 |
A | 3 |
1.root server, 2. TLD DNS server, 3. authoritative server.
So there will be three pairs of request and response here.
Question 32 |

Which of the following prefixes in CIDR notation can be collectively used to correctly aggregate all of the subnets in the routing table?
A | 12.20.164.0/20 |
B | 12.20.164.0/22 |
C | 12.20.164.0/21 |
D | 12.20.168.0/22 |
Question 33 |
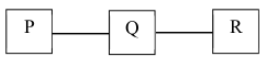
The routers exchange distance vector routing information and have converged on the routing tables, after which the link Q−R fails. Assume that P and Q send out routing updates at random times, each at the same average rate. The probability of a routing loop formation (rounded off to one decimal place) between P and Q, leading to count-to-infinity problem, is___________.
A | 1 |
If asked for R, from among P, Q, R
Probability = 1 /3
Question 34 |
A | 7.08 ms |
Tt = L / B => 1000 x 8 bits / 10^8 bps = 0.08 ms
Tp = D / V => 2100 x 1000 m / 3 x10^8 ms = 7 ms
Therefore, Total time = 7.08 ms
Question 35 |
A | 33 |
1 sec = 20^30 / 8 bytes
=> 1 sec = 20^30 / 8 sequence number
=> 60 sec =20^30 x 60 / 8 bytes
Number of sequence bits required = log (20^30 x 60 / 8) => 33
Question 36 |
A | If the client was waiting to receive a packet, it may wait indefinitely. |
B | If the client sends a packet after the server reboot, it will receive a RST segment. |
C | The TCP server application on S can listen on P after reboot. |
D | If the client sends a packet after the server reboot, it will receive a FIN segment. |
- True
Since broken connections can only be detected by sending data, the receiving side will wait forever. This scenario is called a “half-open connection” because one side realizes the connection was lost but the other side believes it is still active. - True
The situation resolves itself when client tries to send data to server over the dead connection, and server replies with an RST packet (not FIN). - True
Yes, a TCP Server can listen to the same port number even after reboot. For example, the SMTP service application usually listens on TCP port 25 for incoming requests. So, even after reboot the port 25 is assigned to SMTP. - False
The situation resolves itself when client tries to send data to server over the dead connection, and server replies with an RST packet (not FIN), causing client to finally to close the connection forcibly.
FIN is used to close TCP connections gracefully in each direction (normal close of connection), while TCP RST is used in a scenario where TCP connections cannot recover from errors and the connection needs to reset forcibly.
Question 37 |
- The time taken for processing the data frame by the receiver is negligible.
- The time taken for processing the acknowledgement frame by the sender is negligible.
- The sender has an infinite number of frames available for transmission.
- The size of the data frame is 2,000 bits and the size of the acknowledgment frame is 10 bits.
- The link data rate in each direction is 1 Mbps (=106bits per second).
- One way propagation delay of the link is 100 milliseconds.
A | 51 |
Tt(packet) = L / B.W => 2000 bits / 10^6 bps = 2 x 10^-3 sec = 2 millisec
Tt(Ack) = L / B.W. => 10 bits / 10^6 bps = 10^-5 sec = 10^-2 millisec = 0.01 millisec
Tp = 100 millisec
Total time = Tt(packet) + 2 x Tp + Tt(Ack)
=> 2 + 2 x 100 + 0.01 = 202.01 millisec
Efficiency = 50 % = ½
Efficiency = Useful Time / Total time
½ = n x Tt / Total time
=> 2 x n x Tt = Total time
=>2 x n x 2 = 202.01
=> n = 202.01 / 4 => 50.50
For minimum, we have to take ceil, Hence size of window = 51
Question 38 |
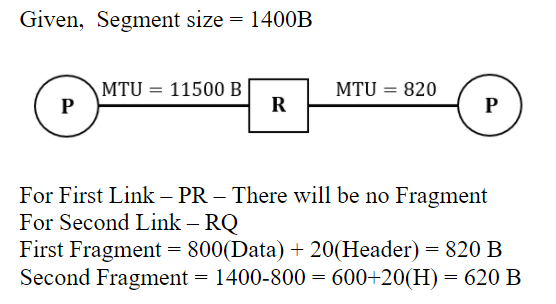
A | If the second fragment is lost, R will resend the fragment with the IP identification value 0x1234. |
B | If the second fragment is lost, P is required to resend the whole TCP segment. |
C | Two fragments are created at R and the IP datagram size carrying the second fragment is 620 bytes. |
D | TCP destination port can be determined by analysing only the second fragment. |
Question 39 |
S1: Destination MAC address of an ARP reply is a broadcast address.
S2: Destination MAC address of an ARP request is a broadcast address.
Which of the following choices is correct?
A | Both S1and S2are true. |
B | S1is true and S2is false. |
C | S1is false and S2is true. |
D | Both S1and S2are false. |
Question 40 |
Which one of the following statements is FALSE?
A | Packet switching leads to better utilization of bandwidth resources than circuit switching. |
B | Packet switching results in less variation in delay than circuit switching. |
C | Packet switching requires more per packet processing than circuit switching. |
D | Packet switching can lead to reordering unlike in circuit switching. |
Question 41 |
Which one of the following statements is FALSE?
A | TCP guarantees a minimum communication rate |
B | TCP ensures in-order delivery |
C | TCP reacts to congestion by reducing sender window size |
D | TCP employs retransmission to compensate for packet loss
|
Sequence numbers can allow receivers to discard duplicate packets and properly sequence reordered packets.
Option C:
If the congestion is deleted, the transmitter decreases the transmission rate by a multiplicative factor.
Option D:
Acknowledgement allows the sender to determine when to retransmit lost packets.
Question 42 |
Which one of the following statements is FALSE?
A | HTTP runs over TCP |
B | HTTP describes the structure of web pages |
C | HTTP allows information to be stored in a URL |
D | HTTP can be used to test the validity of a hypertext link |
Question 43 |
A sender is employing public key cryptography to send a secret message to a receiver. Which one of the following statements is TRUE?
A | Sender encrypts using receiver’s public key |
B | Sender encrypts using his own public key |
C | Receiver decrypts using sender’s public key |
D | Receiver decrypts using his own public key |
Question 44 |
A subnet has been assigned a subnet mask of 255.255.255.192. What is the maximum number of hosts that can belong to this subnet?
A | 14 |
B | 30 |
C | 62 |
D | 126 |
= 26- 2
= 64 - 2
= 62
Question 45 |
A host is connected to a Department network which is part of a University network. The University network, in turn, is part of the Internet. The largest network in which the Ethernet address of the host is unique is:
A | the subnet to which the host belongs |
B | the Department network |
C | the University network |
D | the Internet |
Question 46 |
In TCP, a unique sequence number is assigned to each
A | byte |
B | word |
C | segment |
D | message |
Question 47 |
Which of the following objects can be used in expressions and scriplets in JSP (Java Server Pages) without explicitly declaring them?
A | session and request only |
B | request and response only |
C | response and session only |
D | session, request and response |
Question 48 |
Consider the following statements:
I. telnet, ftp and http are application layer protocols.
II.l EJB (Enterprise Java Beans) components can be deployed in a J2EE (Java2 Enterprise Edition) application server.
III. If two languages conform to the Common Language Specification (CLS) of the Microsoft.NET framework, then a class defined in any one of them may be inherited in the other.
Which statements are true?
A | l and II only |
B | II and III only |
C | l and III only |
D | I, II and III |
Then there are certain compliance rules which may be used for inheritance. So other statement (I) and (II) are True.
Question 49 |
A serial transmission T1 uses 8 information bits, 2 start bits, 1 stop bit and 1 parity bit for each character. A synchronous transmission T2 uses 3 eight bit sync characters followed by 30 eight bit information characters. If the bit rate is 1200 bits/second in both cases, what are the transfer rates of T1 and T2?
A | 100 characters/sec, 153 characters/sec |
B | 80 characters/sec, 136 characters/sec |
C | 100 characters/sec, 136 characters/sec |
D | 80 characters/sec, 153 characters/sec |
Transfer rate = 1200/12 = 100 char/sec
T2: Transfer character in bits = 24 + 240 = 264 bits
In 264 = 30 characters
Then in 1200 = ? 264/30 = 1200/x
x = 136.3 char/sec
So, correct option is (C).
Question 50 |
In a data link protocol, the frame delimiter flag is given by 0111. Assuming that bit stuffing is employed, the transmitter sends the data sequence 01110110 as
A | 01101011 |
B | 011010110 |
C | 011101100 |
D | 0110101100 |
Thus using the above logic,
Delimiter flag: 0111
Data sequence: 01110110
So, for a flag of 4 bits we will compare data sequence with a pattern of 3 bits, i.e., 011.
0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0
In the above pattern the underlined bits are found matched. Hence, 0 in italics is stuffed. Thus resulting in the data sequence as 0110101100 which is option (D).
