Logical-Reasoning
Question 1 |
Given below are two statements: One if labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R):
Assertion (A): Substance is always the subject of all predicates.
Reason (R): Substance is self-existence and self-conceived.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the option given below:
Assertion (A): Substance is always the subject of all predicates.
Reason (R): Substance is self-existence and self-conceived.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the option given below:
A | Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
|
B | Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is NOT the correct explanation of (A) |
C | (A) is true but (R) is false |
D | (A) is false but (R) is true |
Question 2 |
Match List I with List II: List I consists of the Vedangas and List II contains subjects dealt in them.
List I List II
A) Nirukta (I) Phonetics
B) Chhandas (II) Ritual
C) Shiksha (III) Metrics
D) Kalpa (IV) Etymology
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
List I List II
A) Nirukta (I) Phonetics
B) Chhandas (II) Ritual
C) Shiksha (III) Metrics
D) Kalpa (IV) Etymology
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
A | (A)-(II), (B)-(IV), (C)-(III), (D)-(I)
|
B | (A)-(IV), (B)-(III), (C)-(I), (D)-(II)
|
C | (A)-(III), (B)-(I), (C)-(II), (D)-(IV)
|
D | (A)-(I), (B)-(II), (C)-(IV), (D)-(III) |
Question 3 |
Which one of the following schools has not accepted anumāna (inference) as a valid source of knowledge?
A | Advaita Vedānta
|
B | Visisādvaita
|
C | Chārvāka
|
D | Sānkhya |
Question 4 |
If some pens are pencils but no pencil is sharpener then
A) All pencils are pens
B) Some sharpeners are pencils
C) Some pens are not sharpener
D) Some pencils are not pens
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
A) All pencils are pens
B) Some sharpeners are pencils
C) Some pens are not sharpener
D) Some pencils are not pens
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
A | (A) and (C) only
|
B | (B) and (C) only
|
C | (A) and (D) only |
D | (B) and (D) only |
Question 4 Explanation:

→ All pencils are pens and Some pens are not sharpener
Note: Statement-B is definitely FALSE. So, Option-B and D are definitely wrong.
No pencil is sharpener
Then
some sharpeners are pencils ==> it is false
So we can eliminate Options consists of statement-B
Now answer is either A & C or A &D But most suitable is A &C
Question 5 |
Which one of the following pramānas has been accepted in Buddhism?
A | Arthāpatti |
B | Anupalabdhi |
C | S’abda |
D | Pratyaksha |
Question 6 |
Given below are two Statements:
The water of the pond is muddy. It must have rained last night.
What kind of Anumāna (inference) has been used in the above statements. Choose the correct option from the following:
A) S’esavat anumāna
B) Comparison
C) Pūrvovat anumāna
D) Both (A) and (B)
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
The water of the pond is muddy. It must have rained last night.
What kind of Anumāna (inference) has been used in the above statements. Choose the correct option from the following:
A) S’esavat anumāna
B) Comparison
C) Pūrvovat anumāna
D) Both (A) and (B)
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
A | (A) only |
B | (B) only
|
C | (C) only |
D | (D) only
|
Question 6 Explanation:
Yes, It may be challenging.
You can refer the below explanation
According to Causal relation anumāna is of three kinds:
(a) Purvavat: In Purvavat anumāna, we infer the unperceived effect from a perceived cause. For example, when from the presence of dark heavy clouds in the sky, we infer that there will be rainfall.
(b) Sesavat: Here, we infer the unperceived cause from a perceived effect. For example, when we see a river in flood and infer that there was heavy rain, we have a case of Sesavat inference.
Note: As per the official key they gave option-C is the correct answer but according to concept, Option-A is the correct answer.
You can refer the below explanation
According to Causal relation anumāna is of three kinds:
(a) Purvavat: In Purvavat anumāna, we infer the unperceived effect from a perceived cause. For example, when from the presence of dark heavy clouds in the sky, we infer that there will be rainfall.
(b) Sesavat: Here, we infer the unperceived cause from a perceived effect. For example, when we see a river in flood and infer that there was heavy rain, we have a case of Sesavat inference.
Note: As per the official key they gave option-C is the correct answer but according to concept, Option-A is the correct answer.
Question 7 |
Match List I with List II:
List I List II
(Philosophical doctrines) (Philosophical schools)
A) Syādavāda (I) Nyāya
B) Anupalabdhi (II) Buddhism
C) Apoha (III) Vedānta
D) Abhāva (IV) Jainism
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
List I List II
(Philosophical doctrines) (Philosophical schools)
A) Syādavāda (I) Nyāya
B) Anupalabdhi (II) Buddhism
C) Apoha (III) Vedānta
D) Abhāva (IV) Jainism
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
A | (A)-(II), (B)-(IV), (C)-(III), (D)-(I)
|
B | (A)-(IV), (B)-(III), (C)-(II), (D)-(I)
|
C | (A)-(I), (B)-(II), (C)-(IV), (D)-(III)
|
D | (A)-(III), (B)-(I), (C)-(II), (D)-(IV) |
Question 8 |
Refer the statement and solve the question according to the conclusions.
Statement:
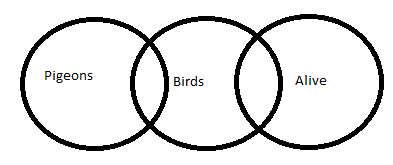
Some Pigeons are Bird;
Some Birds are Alive
Conclusion:
(I) Some Pigeons are Alive
(II) Some Birds are Pigeons
A | Only (I) follows |
B | Only (II) follows |
C | Both (I) & (II) follows |
D | None follows |
Question 8 Explanation:
Question 9 |
Directions - Question number 6 to 10 are based on following information:
There are twelve persons named O, P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, W, X, Y and Z who live in a multi-storey apartment. The apartment has three floors and each floor has four rooms. These 12 persons who live in a set of 12 Rooms can be represented by a Matrix of 3 rows and 4 columns.
→Q lives immediate left below diagonally of a person who lives immediate left below diagonally of T.
→S lives immediate left above diagonally of a person who lives immediate left above diagonally of Z.
→X lives immediate right above diagonally of a person who lives immediate right below diagonally of O.
→P lives immediate right above diagonally of a person who lives immediate right above diagonally of Y.
→T lives immediate left above diagonally of a person who lives third to the right of V.
→Q lives immediate left of a person who lives two rooms below W in the same column.
→R lives to the immediate right of a person who lives immediate right above diagonally of Q. Z is living to the immediate left of U who receives ₹46000 as salary.
→The person who live on one of the floors (left to right) receive salary in the same order ₹50000, ₹48000, ₹47000 and ₹46000.
→The person who live on one of the floors (right to left) receive salary in the same order ₹45000, ₹38000, ₹35000 and ₹40000.
→The person who live on one of the floors (left to right) receive salary in the same order ₹37000, ₹42000, ₹36000 and ₹43000.
What is the aggregate salary of people living at the right end of the apartment?
A | ₹ 137000 |
B | ₹ 134000 |
C | ₹ 125000 |
D | ₹ 131000
|
Question 10 |
Directions - Question number 6 to 10 are based on following information:
There are twelve persons named O, P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, W, X, Y and Z who live in a multi-storey apartment. The apartment has three floors and each floor has four rooms. These 12 persons who live in a set of 12 Rooms can be represented by a Matrix of 3 rows and 4 columns.
→Q lives immediate left below diagonally of a person who lives immediate left below diagonally of T.
→S lives immediate left above diagonally of a person who lives immediate left above diagonally of Z.
→X lives immediate right above diagonally of a person who lives immediate right below diagonally of O.
→P lives immediate right above diagonally of a person who lives immediate right above diagonally of Y.
→T lives immediate left above diagonally of a person who lives third to the right of V.
→Q lives immediate left of a person who lives two rooms below W in the same column.
→R lives to the immediate right of a person who lives immediate right above diagonally of Q. Z is living to the immediate left of U who receives ₹46000 as salary.
→The person who live on one of the floors (left to right) receive salary in the same order ₹50000, ₹48000, ₹47000 and ₹46000.
→The person who live on one of the floors (right to left) receive salary in the same order ₹45000, ₹38000, ₹35000 and ₹40000.
→The person who live on one of the floors (left to right) receive salary in the same order ₹37000, ₹42000, ₹36000 and ₹43000.
What is the salary received by a person who lives second to the right of S?
A | ₹ 35000 |
B | ₹ 45000 |
C | ₹ 37000 |
D | ₹ 38000 |
Question 11 |
Directions - Question number 6 to 10 are based on following information:
There are twelve persons named O, P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, W, X, Y and Z who live in a multi-storey apartment. The apartment has three floors and each floor has four rooms. These 12 persons who live in a set of 12 Rooms can be represented by a Matrix of 3 rows and 4 columns.
→Q lives immediate left below diagonally of a person who lives immediate left below diagonally of T.
→S lives immediate left above diagonally of a person who lives immediate left above diagonally of Z.
→X lives immediate right above diagonally of a person who lives immediate right below diagonally of O.
→P lives immediate right above diagonally of a person who lives immediate right above diagonally of Y.
→T lives immediate left above diagonally of a person who lives third to the right of V.
→Q lives immediate left of a person who lives two rooms below W in the same column.
→R lives to the immediate right of a person who lives immediate right above diagonally of Q. Z is living to the immediate left of U who receives ₹46000 as salary.
→The person who live on one of the floors (left to right) receive salary in the same order ₹50000, ₹48000, ₹47000 and ₹46000.
→The person who live on one of the floors (right to left) receive salary in the same order ₹45000, ₹38000, ₹35000 and ₹40000.
→The person who live on one of the floors (left to right) receive salary in the same order ₹37000, ₹42000, ₹36000 and ₹43000.
What is the sum of salaries of Y and P?
A | ₹ 90000 |
B | ₹ 99000 |
C | ₹ 93000 |
D | ₹ 89000 |
Question 12 |
Directions - Question number 6 to 10 are based on following information:
There are twelve persons named O, P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, W, X, Y and Z who live in a multi-storey apartment. The apartment has three floors and each floor has four rooms. These 12 persons who live in a set of 12 Rooms can be represented by a Matrix of 3 rows and 4 columns.
→Q lives immediate left below diagonally of a person who lives immediate left below diagonally of T.
→S lives immediate left above diagonally of a person who lives immediate left above diagonally of Z.
→X lives immediate right above diagonally of a person who lives immediate right below diagonally of O.
→P lives immediate right above diagonally of a person who lives immediate right above diagonally of Y.
→T lives immediate left above diagonally of a person who lives third to the right of V.
→Q lives immediate left of a person who lives two rooms below W in the same column.
→R lives to the immediate right of a person who lives immediate right above diagonally of Q. Z is living to the immediate left of U who receives ₹46000 as salary.
→The person who live on one of the floors (left to right) receive salary in the same order ₹50000, ₹48000, ₹47000 and ₹46000.
→The person who live on one of the floors (right to left) receive salary in the same order ₹45000, ₹38000, ₹35000 and ₹40000.
→The person who live on one of the floors (left to right) receive salary in the same order ₹37000, ₹42000, ₹36000 and ₹43000.
Who among the following lives third to the left of U?
A | O |
B | Q |
C | T |
D | S |
Question 13 |
Directions - Question number 6 to 10 are based on following information:
There are twelve persons named O, P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, W, X, Y and Z who live in a multi-storey apartment. The apartment has three floors and each floor has four rooms. These 12 persons who live in a set of 12 Rooms can be represented by a Matrix of 3 rows and 4 columns.
→Q lives immediate left below diagonally of a person who lives immediate left below diagonally of T.
→S lives immediate left above diagonally of a person who lives immediate left above diagonally of Z.
→X lives immediate right above diagonally of a person who lives immediate right below diagonally of O.
→P lives immediate right above diagonally of a person who lives immediate right above diagonally of Y.
→T lives immediate left above diagonally of a person who lives third to the right of V.
→Q lives immediate left of a person who lives two rooms below W in the same column.
→R lives to the immediate right of a person who lives immediate right above diagonally of Q. Z is living to the immediate left of U who receives ₹46000 as salary.
→The person who live on one of the floors (left to right) receive salary in the same order ₹50000, ₹48000, ₹47000 and ₹46000.
→The person who live on one of the floors (right to left) receive salary in the same order ₹45000, ₹38000, ₹35000 and ₹40000.
→The person who live on one of the floors (left to right) receive salary in the same order ₹37000, ₹42000, ₹36000 and ₹43000.
What is the sum of the salaries received by the persons living on the top floor of the apartment?
A | ₹ 158000 |
B | ₹ 193000 |
C | ₹ 157000 |
D | ₹ 161000
|
Question 14 |
Directions for question number 11 and 12:
Study the following information carefully and answer the question:
Group of girl’s gossip with each other. All are sitting surrounding a round table. The names of the girls are Shiksha, Radha, Chinu, Snigdha and Rani. It is not necessary that they are sitting in the order of the name as mentioned here. Radha is second to the right of Shiksha. Shiksha doesn’t sit with Chinu. Rani is second to the right of Radha. Radha sits near Snigdha.
Q11. If Radha and Snigdha change their places then who will be second to the left of Rani?
A | Radha |
B | Snigdha |
C | Shiksha |
D | None of the options |
Question 14 Explanation:
According to the given passage the seating order is
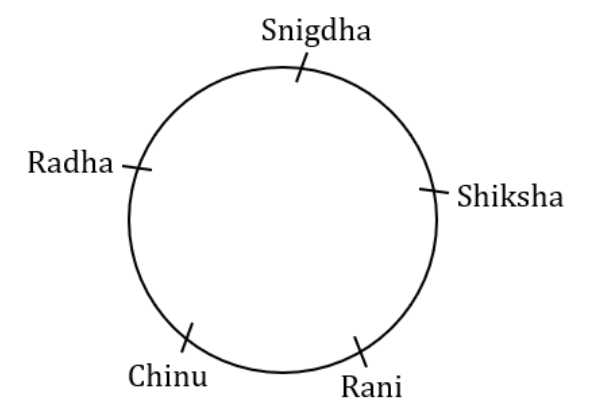
If Radha and Snigdha change their places then Snigdha will be second to the left of Rani

If Radha and Snigdha change their places then Snigdha will be second to the left of Rani
Question 15 |
Directions for question number 11 and 12:
Study the following information carefully and answer the question:
Group of girl’s gossip with each other. All are sitting surrounding a round table. The names of the girls are Shiksha, Radha, Chinu, Snigdha and Rani. It is not necessary that they are sitting in the order of the name as mentioned here. Radha is second to the right of Shiksha. Shiksha doesn’t sit with Chinu. Rani is second to the right of Radha. Radha sits near Snigdha.
Q12. Who sits to the left of Shiksha?
A | Rani |
B | Radha |
C | Chinu |
D | Snigdha |
Question 15 Explanation:

Question 16 |
Directions for question number 13 to 15:
Relationship between different elements is provided in the statements. The statements are followed by conclusions. Study the conclusions based on the given statement and choose the correct answer.
Q13: T >= U = V <= W < X; V >= Y
Conclusions:
(I) Y <= T
(II) U >= X
A | if only conclusion (I) follows |
B | if only conclusion (II) follows |
C | if neither (I) nor (II) conclusion follows |
D | if both (I) and (II) conclusions follow |
Question 16 Explanation:
T >= U = V <= W < X; V >= Y
T>= U= V>= Y
Y <= T
T>= U= V>= Y
Y <= T
Question 17 |
Directions for question number 13 to 15:
Relationship between different elements is provided in the statements. The statements are followed by conclusions. Study the conclusions based on the given statement and choose the correct answer.
Q13: T >= U = V <= W < X; V >= Y
Q14. P <= Q <= R > S; T >= R; S >= U
Conclusions:
(I) T > S
(II) U < R
A | if only conclusion (I) follows |
B | if only conclusion (II) follows |
C | if neither (I) nor (II) conclusion follows |
D | if both (I) and (II) conclusions follow |
Question 17 Explanation:
P <= Q <= R > S; T >= R; S >= U
T >= R > S R > S>=U
T>S U
T >= R > S R > S>=U
T>S U
Question 18 |
Directions for question number 13 to 15:
Relationship between different elements is provided in the statements. The statements are followed by conclusions. Study the conclusions based on the given statement and choose the correct answer.
Q13: T >= U = V <= W < X; V >= Y
Q15: A <= B < C >= D; C <= E <= F
Conclusions:
(I) F >= D
(II) A > E
A | if only conclusion (I) follows |
B | if only conclusion (II) follows |
C | if neither (I) nor (II) conclusion follows |
D | if both (I) and (II) conclusions follow |
Question 18 Explanation:
A <= B < C >= D; C <= E <= F
D <= C <= E < F
F >= D
Question 19 |
Five people are standing in a row. Aman is standing next to Karan but not adjacent to Tanuj. Radhika is standing next to Priyanka who is standing on the extreme left and Tanuj is not standing next to Radhika. Who are Standing adjacent to Aman?
A | Radhika and Karan |
B | Karan and Tanuj |
C | Karan and Priyanka |
D | Radhika and Tanuj |
Question 19 Explanation:

Question 20 |
Ramesh’s father is a paediatrician. Ram’s father is a trader. Krishan’s father is a school teacher. Krishan falls ill. Where should his father take him?
A | to home
|
B | to school |
C | to Ramesh’s father |
D | to Ram’s father |
Question 20 Explanation:
Ramesh’s father is a paediatrician
Ram’s father is a trader
Krishan’s father is a school teacher
Krishan falls ill
According to the given input Ramesh's father is a paediatrician. So, they went to Ramesh’s father.
Ram’s father is a trader
Krishan’s father is a school teacher
Krishan falls ill
According to the given input Ramesh's father is a paediatrician. So, they went to Ramesh’s father.
Question 21 |
What is the total number of ways to reach A to B in the network given?

A | 12 |
B | 16 |
C | 20 |
D | 22 |
Question 22 |
Directions for question number 30 to 31:
Two statements followed by four conclusions numbered from (I) to (IV) are given. You have to take the two statements to be true even if these seem to be at variance from the commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and decide which of the given conclusions logically follow from the two given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
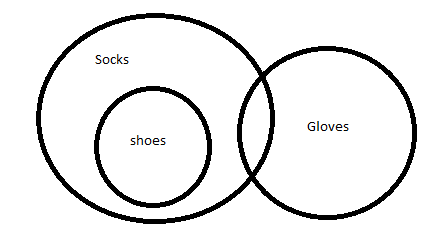
Q30. All Shoes are Socks
Some Socks are Gloves
Conclusions:
(I) Some Shoes are Gloves
(II) Some Socks are Shoes
(III) All Gloves are Shoes
(IV) No Shoes are Gloves
A | Only (I) follows |
B | Only (II) follows |
C | Only (III) follows
|
D | Only (IV) follows |
Question 22 Explanation:
Question 23 |
Directions for question number 30 to 31:
Two statements followed by four conclusions numbered from (I) to (IV) are given. You have to take the two statements to be true even if these seem to be at variance from the commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and decide which of the given conclusions logically follow from the two given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
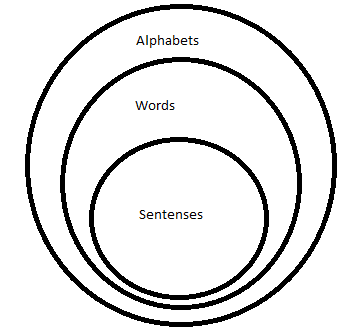
Q31: All Sentences are Words
All Words are Alphabets
Conclusions:
(I) All words are sentences
(II) All sentences are alphabets
(III) All alphabets are words
(IV) Some alphabets are words
A | Only (I) and (III) follows |
B | Only (II), (III) and (IV) follows |
C | Only (II) and (IV) follows |
D | All follows |
Question 23 Explanation:
Question 24 |
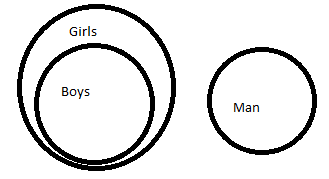
All Boys are Girls
No Girl is a Man
Conclusions:
(I) No Boy is a Man
(II) Some Boys are Man
(III) All Girls are Boys
(IV) Some Man are Boys
A | Only (III) follows |
B | Only (I) follows |
C | All follows |
D | None follows
|
Question 24 Explanation:
Question 25 |
A Class has 100 students with roll number from 101 to 200. All the even numbered students study Physics, whose roll number are divisible by 5 study Chemistry & students with roll numbers divisible by 7 study Biology. How many students do not study any of the given subject Physics, Chemistry or Biology?
A | 35 |
B | 45 |
C | 51 |
D | 62 |
Question 25 Explanation:

Question 26 |
Choose the alternative to decide whether the data given in the statements is/are sufficient to answer the question based on the following information.
Five persons A, B, C, D and E are sitting in a row. Who is sitting in the middle?
Statements:
(I) E is to the left of B.
(II) B is in-between C and E.
(III) D is in-between E and A.
Choose which of the following will be sufficient to find out who is sitting in the middle?
A | Only (I) and (II) |
B | Only (II) and (III) |
C | Only (I) and (III) |
D | All (I), (II) and (III) |
Question 26 Explanation:
Here the question is only asking to find who is in the middle not for the exact pattern, so using only B we will get E in the middle and using D we will get only one pattern.
Question 27 |
What number would replace question mark (?) in the series given below?
1, 4, 11, 26, 57, 120, 247, ?
1, 4, 11, 26, 57, 120, 247, ?
A | 424 |
B | 367 |
C | 255 |
D | 502 |
Question 28 |
"If I were, a heavy smoker, smoking would shorten my life. That's why I do not smoke. And I except to live a long and healthy life". Which fallacy is committed in the above argument?
A | Existential fallacy |
B | Undistributed middle |
C | Affirming the consequent |
D | Denying the antecedent |
Question 29 |
Identify the fallacy committed in the following argument: "My opponent cheated on his taxes. He hired an illegal migrant as a nanny. His views on tax reforms simply cannot be trusted".
A | Inappropriate authority |
B | Ad hominem |
C | Appeal to ignorance |
D | Begging the question |
Question 30 |
Which of the following statement is logically equivalent to the statement "All tigers are hunting animals"?
A | Some hunting animals are tigers. |
B | No tigers are non-hunting animals. |
C | No hunting animals are tigers. |
D | Some hunting animals are not tigers. |
Question 31 |
Which of the following statements are contradictory to each other?
A. All human beings are mortal.
B. No human beings are mortal.
C. Some human beings are mortal.
D. Some human beings are not mortal.
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
A. All human beings are mortal.
B. No human beings are mortal.
C. Some human beings are mortal.
D. Some human beings are not mortal.
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
A | A and B only |
B | B and C only |
C | C and D only |
D | B and D only |
Question 32 |
According to Classical Indian school of logic knowledge derived from comparison and which roughly corresponds to analogy is:
A | Arthapati |
B | Anumana |
C | Upamana |
D | Anuplabdhi |
Question 33 |
Which of the following statements contradict each other?
A. All ducks are birds.
B. Some ducks are birds.
C. Some ducks are not birds.
D. No ducks are birds.
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below :
A. All ducks are birds.
B. Some ducks are birds.
C. Some ducks are not birds.
D. No ducks are birds.
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below :
A | A and D only
|
B | B and C only
|
C | B and D only |
D |
C and D only
|
Question 34 |
If the statement “No birds are animals” is given as false, which of the following statements can be inferred to be true?
A. Some animals are not birds.
B. Some birds are not animals.
C. Some animals are birds.
D. Some birds are animals.
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below :
A. Some animals are not birds.
B. Some birds are not animals.
C. Some animals are birds.
D. Some birds are animals.
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below :
A | A and B only |
B |
C and D only |
C | B only
|
D | A, B, C and D
|
Question 35 |
“This is the richest fraternity on the campus; therefore, Mr. X who is a member of this fraternity must be one of the richest young men on the campus.”
Which fallacy is involved in this argument?
Which fallacy is involved in this argument?
A | Fallacy of division
|
B | Fallacy of irrelevant conclusion
|
C | Red Herring |
D | Slippery slope |
Question 36 |
According to the classical Indian school of logic, which of the following instruments of knowledge is defined as the knowledge of the relation between a word and its denotation and is produced by the knowledge of resemblance or similarity?
A | Pratyakṣa (perception)
|
B | Anumāna (inference)
|
C | Upamāna (comparison) |
D | Śabda (verbal testimony) |
Question 37 |
Which among the following are contrary propositions?
A. All poets are dreamers
B. Some poets are dreamers,br> C. Some poets are not dreamers
D. No squares are circles
E. No poets are dreamers
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
A. All poets are dreamers
B. Some poets are dreamers,br> C. Some poets are not dreamers
D. No squares are circles
E. No poets are dreamers
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
A | D and E Only |
B | C and D only |
C | B and D Only |
D | A and E only |
Question 38 |
Match the LIST-I with LIST-II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
| LIST-I(Definition) | LIST-II(Characteristic) | ||
| A | Stipulative | I | They are used to eliminate ambiguity |
| B | Lexical | II | They encapsulate larger understanding of theory |
| C | Precising | III | It is neither accurate nor inaccurate |
| D | Theoretical | IV | It reports the meaning of the definiendum |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
A | A-II, B-IV, C-III, D-I |
B | A-I, B-III, c-IV, D-II
|
C | A-IV, B-II, C-III, D-I |
D | A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II |
Question 38 Explanation:
Question 39 |
According to Naiyäyikas, we perceive one pot we perceive the universal potness' as
its defining property due to
A | Yogaja |
B | Anumäna |
C | Jnäna Laksana |
D | Sämänya Laksana
|
Question 40 |
Which among the following is correct in the context of syllogistic rules
A | With two negative premises; a negative conclusion is drawn. |
B | Any Term distributed in the premises must be distributed in the conclusion. |
C | Middle term must be distributed in both the premises |
D | Syllogistic argument must contain only three terms |
Question 41 |
Among the following which is correct in the context of Sabda Pramana ?
A | For Samkhya, a word signifies universal
|
B | For Jainas, a word signifies a particular |
C | For old Nyaya, a word symbolizes universal only
|
D | For Vedantins,a word primarily means the class character of individuals
|
Question 42 |
What can be inferred correctly from the following ? “No musicians are Greeks. All traders are Musicians. Therefore, no traders are Greeks”
A)It represents figure II of the syllogistic argument
B)It is an EAE mood
C)The term ‘Greeks’ is the major word
D)The minor term of the conclusion is distributed
E)The middle term is undistributed
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
A)It represents figure II of the syllogistic argument
B)It is an EAE mood
C)The term ‘Greeks’ is the major word
D)The minor term of the conclusion is distributed
E)The middle term is undistributed
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
A | (A), (B) and (C) only |
B | (B), (C) and (D) only |
C | (D) and (E) only |
D | (A), (C) and (E) only
|
Question 43 |
Identify the pattern of the Argument in the following “Habits are like a cable. We weave a strand of it every day and soon it cannot be broken. ”
A | Causal Argument
|
B | Argument from Analogy |
C | Argument from Authority |
D | Argument from Definition
|
Question 44 |
If the statement “All women are honest is given as true; which of the following propositions can be inferred from it?
A)No women is honest' is false
B)Some Women are honest' is true
C)No women is honest' is undetermined
D)Some women are not honest' is false
Choose the correct answer from the options given below
A)No women is honest' is false
B)Some Women are honest' is true
C)No women is honest' is undetermined
D)Some women are not honest' is false
Choose the correct answer from the options given below
A | A,B and D only
|
B | B and D Only |
C | B,C and D only |
D | C and D only |
Question 45 |
Given below are two statements:
Statement I: Aristotelian syllogism regards deduction and induction as inseparably related
Statement II: The Nyaya School of classical Indian philosophy regards deduction and induction as two aspects of the same process
In the light of the above statements. choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below
Statement I: Aristotelian syllogism regards deduction and induction as inseparably related
Statement II: The Nyaya School of classical Indian philosophy regards deduction and induction as two aspects of the same process
In the light of the above statements. choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below
A | Both Statement I and Statement II are true |
B | Both Statement I and Statement II are false |
C | Statement I is true but Statement II is false |
D | Statement I is false but Statement is true
|
Question 46 |
In Nyaya syllogism all the three terms stand synthesized in which of the following steps of the inferential process ?
A | Example(Udaharana) |
B | Conclusion(Nigamana) |
C | Application(Upanaya) |
D | Reason(hetu) |
Question 47 |
Which of the logical informal fallacy is committed in the following argument
“Mr X is used abusive language toward the child who threw a stone at his car. Since child abuse is a crime. he should be reported to the authorities"?
A | Appeal to Emotion
|
B | Hasty generalization
|
C | Equivocation
|
D | Appeal to force
|
Question 48 |
Given below are two statements :
Statement I : To form the contrapositive of a given proposition, we replace its subject term with the complement of its predicate term. and we replace its predicate term with the complement of its subject term.
Statement II: All contra positions are valid.
In the light of the above statements. choose the correct answer from the options given below
Statement I : To form the contrapositive of a given proposition, we replace its subject term with the complement of its predicate term. and we replace its predicate term with the complement of its subject term.
Statement II: All contra positions are valid.
In the light of the above statements. choose the correct answer from the options given below
A | Both Statement I and Statement II are true
|
B | Both Statement I and Statement II are false
|
C | Statement I is true but Statement II is false
|
D | Statement I is false but Statement II is true |
Question 49 |
Statements :
I All students are ambitious
II All ambitious persons are hard working
Conclusions :
(i) All students are hard-working
(ii) All hardly working people are not ambitious
Which of the following is correct ?
I All students are ambitious
II All ambitious persons are hard working
Conclusions :
(i) All students are hard-working
(ii) All hardly working people are not ambitious
Which of the following is correct ?
A | Only (i) is correct |
B | Only (ii) is correct |
C | Both (i) and (ii) are correct |
D | Neither (i) nor (ii) is correct |
Question 49 Explanation:
Question 50 |
Statement :
Most students are intelligent
Conclusions :
(i) Some students are intelligent
(ii) All students are not intelligent
Which of the following is implied ?
Most students are intelligent
Conclusions :
(i) Some students are intelligent
(ii) All students are not intelligent
Which of the following is implied ?
A | Only (i) is implied |
B | Only (ii) is implied |
C | Both (i) and (ii) are implied |
D | Neither (i) nor (ii) is implied |
Question 50 Explanation:
Most students are intelligent means that not all students are intelligent.
Only (ii) is implied.
Access subject wise (1000+) question and answers by becoming as a solutions adda PRO SUBSCRIBER with Ad-Free content
Register Now
You have completed
questions
question
Your score is
Correct
Wrong
Partial-Credit
You have not finished your quiz. If you leave this page, your progress will be lost.
Correct Answer
You Selected
Not Attempted
Final Score on Quiz
Attempted Questions Correct
Attempted Questions Wrong
Questions Not Attempted
Total Questions on Quiz
Question Details
Results
Date
Score
Hint
Time allowed
minutes
seconds
Time used
Answer Choice(s) Selected
Question Text
Need more practice!
Keep trying!
Not bad!
Good work!
Perfect!
