Combinational-Circuit
Question 1 |
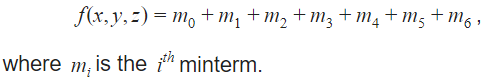
 | |
 | |
 | |
 | |

Question 2 |
A multiplexer is placed between a group of 32 registers and an accumulator to regulate data movement such that at any given point in time the content of only one register will move to the accumulator. The minimum number of select lines needed for the multiplexer is _____.
5 |
A 25x1 Multiplexer with 5 select lines selects one of the 32(= 25) registers at a time depending on the selection input.
The content from the selected register will be transferred through the output line to the Accumulator.
Question 3 |
If there are m input lines and n output lines for a decoder that is used to uniquely address a byte addressable 1 KB RAM, then the minimum value of m + n is ____.
1034 |
Each output line of the decoder is connected to one of the 1K(= 1024) rows of RAM.
Each row stores 1 Byte.
m=10 and n=1024
Question 4 |
A circuit outputs a digit in the form of 4 bits. 0 is represented by 0000, 1 by 0001, ..., 9 by 1001. A combinational circuit is to be designed which takes these 4 bits as input and outputs 1 if the digit ≥ 5, and 0 otherwise. If only AND, OR and NOT gates may be used, what is the minimum number of gates required?
2 | |
3 | |
4 | |
5 |

= A + BD + BC
= A + B (D + C)
So minimum two OR gates and 1 AND gate is required. Hence, in total minimum 3 gates is required.
Question 5 |

P is 10:1 multiplexer; Q is 5:1 multiplexer; T is 2:1 multiplexer | |
P is 10:2 ^10 decoder; Q is 5:2^ 5 decoder; T is 2:1 encoder | |
P is 10:2^ 10 decoder; Q is 5:2^ 5 decoder; T is 2:1 multiplexer | |
P is 1:10 de-multiplexer; Q is 1:5 de-multiplexer; T is 2:1 multiplexer |
Q is a 5:2^5 decoder that takes a 5-bit address from R-address as input and enable one of the 32 words of the R memory.
T is a 2x1 Multiplexer that select one of the 2 inputs and transmit it as output.
Question 6 |
State whether the following statements are TRUE or FALSE with reason:
RAM is a combinational circuit and PLA is a sequential circuit.True | |
False |
2) PLA is a combination circuit as ROM. PLA is a programmable AND array and a programmable OR array. A PLA with n inputs has fewer than 2n AND gates (otherwise there would be no advantage over a ROM implementation of the same size). A PLA only needs to have enough AND gates to decode as many unique terms as there are in the functions it will implement it.
Question 7 |
The amount of ROM needed to implement a 4 bit multiplier is
64 bits | |
128 bits | |
1 Kbits | |
2 Kbits |
Hence option D is the answer.
Question 8 |
In the following truth table, V = 1 if and only if the input is valid.
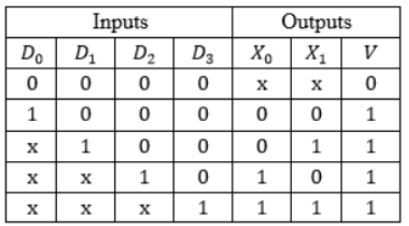
What function does the truth table represent?
Priority encoder | |
Decoder | |
Multiplexer | |
Demultiplexer |
Question 9 |

a | |
b | |
c | |
d | |
None of the above |
Question 10 |

Consider circuits composed only of clamp gates, possibly parametrized by different pairs (a, b) of real numbers. How many clamp gates are needed to construct a circuit that on input non-negative reals x and y outputs the maximum of x and y?
1 | |
2 | |
3 | |
4 | |
No circuit composed only of clamp gates can compute the max function. |
Question 11 |
Y= A+ B | |
Y = A | B | |
Y = A & B | |
Y = S ? A : B |
A multiplexer can be used to implement if-else statements.
Question 12 |
16 address lines, 7 data lines | |
7 address lines, 16 data lines | |
17 address lines, 16 data lines | |
16 address lines, 17 data lines |
96 is greater than 64 and less than 128 ,So we need to consider 128.
96= 2x2x2x2x2x3 which is equivalent to 2 ^ 7
96K which is 2^7 x 2^10 =2^17
So address lines are 17
Word size is 16
So data lines are 2 ^16.
So option C is correct .
Question 13 |
AND | |
OR | |
NAND | |
XOR |
Encoder may also be designed by using 3 NAND gates. Thus both option B,C are correct.
Question 14 |

Under what condition Z will be 1?
X > Y | |
X < Y | |
X = Y | |
X! = Y |
Case 1: X1=1 and Y1=0 which implies X > Y.
or Case 2: X1=Y1 and (X0=1 and Y0=0) which implies X > Y.
Z=1 in both of the above cases which implies X > Y.
