Compilers
Question 1 |
Which one of the following statements is FALSE?
Context-free grammar can be used to specify both lexical and syntax rules. | |
Type checking is done before parsing. | |
High-level language programs can be translated to different Intermediate Representations. | |
Arguments to a function can be passed using the program stack. |
Question 2 |
1: a?(b∣c)*aT
2: b?(a∣c)*bT
3: c?(b∣a)*c
Note that ‘x?’ means 0 or 1 occurrence of the symbol x. Note also that the analyzer outputs the token that matches the longest possible prefix.
If the string bbaacabc is processes by the analyzer, which one of the following is the sequence of tokens it outputs?
T1T2T3 | |
T1T1T3 | |
T2T1T3 | |
T3T3 |
T1 : (b+c)*a + a(b+c)*a
T2 : (a+c)*b + b(a+c)*b
T3 : (b+a)*c + c(b+a)*c
Now the string is: bbaacabc
Please NOTE:
Token that matches the longest possible prefix
We can observe that the longest possible prefix in string is : bbaac which can be generated by T3.
After prefix we left with “abc” which is again generated by T3 (as longest possible prefix).
So, answer is T3T3.
Question 3 |
Type checking is normally done during
lexical analysis | |
syntax analysis | |
syntax directed translation | |
code optimization |
Question 4 |
The number of tokens in the Fortran statement DO 10 I = 1.25 is
3 | |
4 | |
5 | |
None of the above |
10 → 2
I → 3
= → 4
1.25 → 5
Question 5 |
The number of tokens in the following C statement.
printf("i = %d, &i = %x", i, &i);
is
3 | |
26 | |
10 | |
21 |
(i) Keyword
(ii) Identifier
(iii) Constant
(iv) Variable
(v) String
(vi) Operator
Print = Token 1
( = Token 2
"i=%d%x" = Token 3 [Anything inside " " is one Token]
, = Token 4
i = Token 5
, = Token 6
& = Token 7
i = Token 8
) = Token 9
; = Token 10
Here, totally 10 Tokens are present in the equation.
Question 6 |
Consider a program P that consists of two source modules M1 and M2 contained in two different files. If M1 contains a reference to a function defined in M2, the reference will be resolved at
Edit time | |
Compile time | |
Link time | |
Load time |
Question 7 |
Generation of intermediate code based on an abstract machine model is useful in compilers because
it makes implementation of lexical analysis and syntax analysis easier | |
syntax-directed translations can be written for intermediate code generation | |
it enhances the portability of the front end of the compiler | |
it is not possible to generate code for real machines directly from high level language programs |
Question 8 |
For the program segment given below, which of the following are true?
program main (output);
type link = ^data;
data = record
d : real;
n : link
end;
var ptr : link;
begin
new (ptr);
ptr:=nil;
.ptr^.d:=5.2;
write ln(ptr)
end.
The program leads to compile time error | |
The program leads to run time error | |
The program outputs 5.2 | |
The program produces error relating to nil pointer dereferencing | |
None of the above |
Question 9 |
In a compiler the module the checks every character of the source text is called:
The code generator. | |
The code optimizer. | |
The lexical analyser. | |
The syntax analyser. |
Question 10 |
Using longer identifiers in a program will necessarily lead to:
Somewhat slower compilation | |
A program that is easier to understand | |
An incorrect program | |
None of the above |
Question 11 |
Consider line number 3 of the following C-program.
int main ( ) { /* Line 1 */
int I, N; /* Line 2 */
fro (I = 0, I < N, I++); /* Line 3 */
}
Identify the compiler's response about this line while creating the object-module:
No compilation error
| |
Only a lexical error | |
Only syntactic errors | |
Both lexical and syntactic errors |
Question 12 |
Match the following according to input (from the left column) to the compiler phase (in the right column) that processes it:
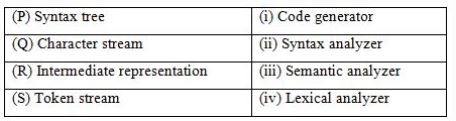
P→(ii), Q→(iii), R→(iv), S→(i) | |
P→(ii), Q→(i), R→(iii), S→(iv) | |
P→(iii), Q→(iv), R→(i), S→(ii) | |
P→(i), Q→(iv), R→(ii), S→(iii) |
Token stream is forwarded as input to Syntax analyzer which produces syntax tree as output. So, S → (ii).
Syntax tree is the input for the semantic analyzer, So P → (iii).
Intermediate representation is input for Code generator. So R → (i).
