Pointers
Question 1 |
Consider the following ANSI C program
#include<stdio.h>
int main() {
int arr[4][5];
int i, j;
for (i=0; i<4; i++){
for (j=0; j<5; j++){
arr[i][j] = 10*i + j;
}
}
printf (“%d”, *(arr[1] + 9));
return 0;
}
What is the output of the above program?
#include<stdio.h>
int main() {
int arr[4][5];
int i, j;
for (i=0; i<4; i++){
for (j=0; j<5; j++){
arr[i][j] = 10*i + j;
}
}
printf (“%d”, *(arr[1] + 9));
return 0;
}
What is the output of the above program?
14 | |
30 | |
24 | |
20 |
Question 1 Explanation:
arr[4][5]


Question 2 |
Faster access to non-local variables is achieved using an array of pointers to activation records called a
stack | |
heap | |
display | |
activation tree |
Question 2 Explanation:
Properties of displays:
→ Use a pointer array to store the activation records along the static chain.
→ Fast access for non-local variables but may be complicated to maintain.
→ Use a pointer array to store the activation records along the static chain.
→ Fast access for non-local variables but may be complicated to maintain.
Question 3 |
Consider the following three C functions:
[PI] int*g(void)
{
int x = 10;
return(&x);
}
[P2] int*g(void)
{
int*px;
*px = 10;
return px;
}
[P3] int*g(void)
{
int*px;
px = (int *) malloc(sizeof(int));
*px = 10;
return px;
}
Which of the above three functions are likely to cause problems with pointers?
Only P3 | |
Only P1 and P3 | |
Only P1 and P2 | |
P1, P2 and P3 |
Question 3 Explanation:
[P1] → May cause error because the function is returning the address of locally declared variable.
[P2] → It will cause problem because px is in int pointer that is not assigned with any address and we are doing dereferencing.
[P3] → It will work because memory will be stored in px that can be use further. Once function execution completes this will exist in Heap.
[P2] → It will cause problem because px is in int pointer that is not assigned with any address and we are doing dereferencing.
[P3] → It will work because memory will be stored in px that can be use further. Once function execution completes this will exist in Heap.
Question 4 |
What is printed by the following ANSI C program?
#include
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int x = 1, z[2] = {10, 11};
int *p = NULL;
p = &x;
*p = 10;
p = &z[1];
*(&z[0] + 1) += 3;
printf("%d, %d, %d\n", x, z[0], z[1]);
return 0;
}
#include
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int x = 1, z[2] = {10, 11};
int *p = NULL;
p = &x;
*p = 10;
p = &z[1];
*(&z[0] + 1) += 3;
printf("%d, %d, %d\n", x, z[0], z[1]);
return 0;
}
1, 10, 11 | |
1, 10, 14 | |
10, 14, 11 | |
10, 10, 14 |
Question 4 Explanation:
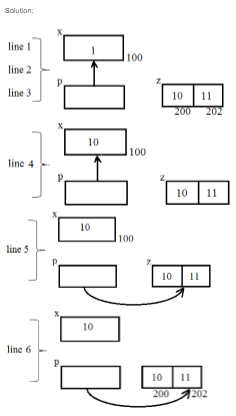

Question 5 |
Which of the following declares ‘pf’ as a pointer to a function, which returns an integer quantity and requires two integer arguments ?
int *pf(int, int); | |
int (*pf)(int, int); | |
(int *) pf(int, int); | |
int ( int *pf(int, int)); |
Question 5 Explanation:
int (*pf)(int, int) , Here ‘pf’ declares as a pointer to a function, which returns an integer quantity and requires two integer arguments
Question 6 |
Which of the following statements is TRUE for the function prototype declaration given below?
Int *(*P)(char *Q[]);
P is a function that accepts an argument which is a character array and returns a pointer to an integer quantity. | |
P is a function that accepts an argument which is a pointer to a character array and returns a pointer to an integer quantity. | |
P is a pointer to a function that accepts an argument which is an array of character pointers, and returns a pointer to an integer quantity. | |
P is a pointer to function that accepts an argument which is a character array and returns a pointer to an integer quantity . |
Question 6 Explanation:
P is a pointer to a function that accepts an argument which is an array of character pointers, and returns a pointer to an integer quantity.
Question 7 |
Only legal pointer operations:
A. pointer + number → pointer
B. pointer – number → number
C. pointer + pointer → pointer
D. pointer – pointer → pointer
E. pointer – pointer → number
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
A. pointer + number → pointer
B. pointer – number → number
C. pointer + pointer → pointer
D. pointer – pointer → pointer
E. pointer – pointer → number
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
A, B, C Only
| |
A, B, D Only | |
A, B Only
| |
A, E Only |
There are 7 questions to complete.
