Recursion
Question 1 |
Consider the following ANSI C program.
#include <stdio.h>
int foo(intx, int y, int q)
{
if ((x <= 0) && (y <= 0))
return q;
if (x <= 0)
return foo(x, y-q, q);
if (y <= 0)
return foo(x-q, y, q);
return foo(x, y-q, q) + foo(x-q, y, q);
}
int main()
{
int r = foo(15, 15, 10);
printf(“%d”, r);
return 0;
}
The output of the program upon execution is ______
#include <stdio.h>
int foo(intx, int y, int q)
{
if ((x <= 0) && (y <= 0))
return q;
if (x <= 0)
return foo(x, y-q, q);
if (y <= 0)
return foo(x-q, y, q);
return foo(x, y-q, q) + foo(x-q, y, q);
}
int main()
{
int r = foo(15, 15, 10);
printf(“%d”, r);
return 0;
}
The output of the program upon execution is ______
60 |
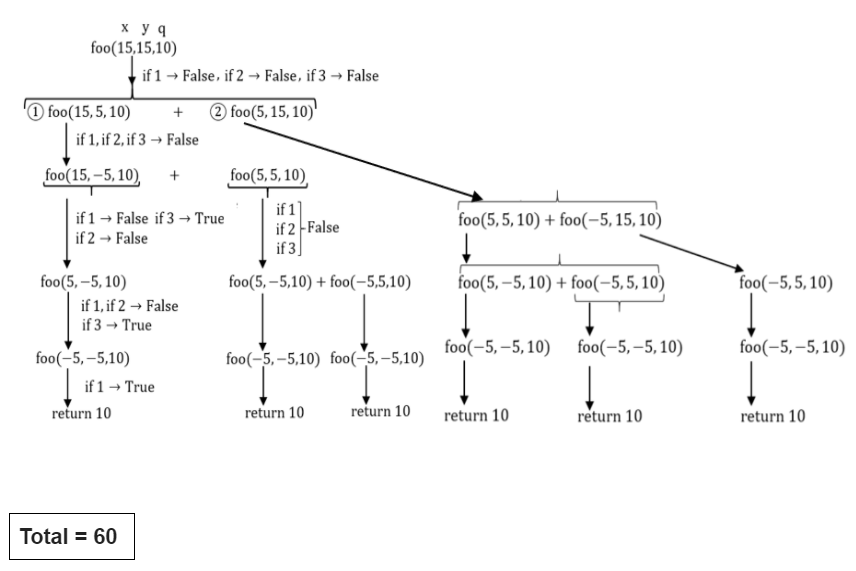
Question 1 Explanation:
int foo(intx, int y, int q)
{
if ((x <= 0) && (y <= 0)) //if 1
return q;
if (x <= 0) //if 2
return foo(x, y-q, q);
if (y <= 0) //if 3
return foo(x-q, y, q);
return foo(x, y-q, q) + foo(x-q, y, q);
}
int main()
{
int r = foo(15, 15, 10);
printf(“%d”, r);
return 0;
}
Question 2 |
Consider the following ANSI C function:
int SomeFunction (int x, int y)
{
if ((x == 1) || (y == 1)) return 1;
if (x == y) return x;
if (x > y) return SomeFunction (x-y, y);
if (y > x) return SomeFunction (x, y-x);
}
The value returned by SomeFunction (15, 255) is _______.
int SomeFunction (int x, int y)
{
if ((x == 1) || (y == 1)) return 1;
if (x == y) return x;
if (x > y) return SomeFunction (x-y, y);
if (y > x) return SomeFunction (x, y-x);
}
The value returned by SomeFunction (15, 255) is _______.
15 |
Question 2 Explanation:

Question 3 |
The following recursive function in C is a solution to the Towers of Hanoi problem.
Void move (int n, char A, char B, char C)
{
if (…………………………………) {
move (…………………………………);
printf(“Move disk %d from pole %c to pole %c\n”, n,A,C);
move (………………………………….);
Fill in the dotted parts of the solution.
Theory Explanation is given below. |
Question 3 Explanation:
move (disk-1, source, aux, dest) //Step-1
move disk from source to dest //Step-2
move (disk-1, aux, dest, source) //Step-3
Recurrence: 2T(n - 1) + 1
T(n) = 2T (n - 1) + 1
= 2[2T(n - 2) + 1] + 1
= 22T(n - 2) + 3
⁞
2k T(n - k) + (2k - 1)
= 2n-1T(1) + (2n-1 - 1)
= 2n-1 + 2n-1 - 1
= 2n - 1
≅ O(2n)
void move (int n, char A, char B, char C) {
if (n>0)
move(n-1, A, C, B);
printf("Move disk%d from pole%c to pole%c\n", n,A,C);
move(n-1, B, A, C);
}
}
move disk from source to dest //Step-2
move (disk-1, aux, dest, source) //Step-3
Recurrence: 2T(n - 1) + 1
T(n) = 2T (n - 1) + 1
= 2[2T(n - 2) + 1] + 1
= 22T(n - 2) + 3
⁞
2k T(n - k) + (2k - 1)
= 2n-1T(1) + (2n-1 - 1)
= 2n-1 + 2n-1 - 1
= 2n - 1
≅ O(2n)
void move (int n, char A, char B, char C) {
if (n>0)
move(n-1, A, C, B);
printf("Move disk%d from pole%c to pole%c\n", n,A,C);
move(n-1, B, A, C);
}
}
There are 3 questions to complete.
