Routing
Question 1 |
The next hop router for a packet from R to P is Y. | |
The distance from R to Q will be stored as 7. | |
The next hop router for a packet from R to Q is Z. | |
The distance from R to P will be stored as 10. |
Given R gets the distance vector (3,2,5)
After the one iteration distance vector from X to P, Y to P, and Z to P is (7, 6, 5) respectively
The distance vector from R to P via X Y Z is (3+7, 2+6, 5+5) =(10, 8, 10)
So Take minimum distance from R to P which is 8 via Y
After the iteration distance vector from X to Q, Y to Q, Z to Q is ( 4, 6, 8) respectively
The distance vector from R to Q via X Y Z is (3+4, 2+6, 5+8) = (7, 8 13)
So Take minimum distance from R to Q which is 7 via X.
Question 2 |
The routers exchange distance vector routing information and have converged on the routing tables, after which the link Q−R fails. Assume that P and Q send out routing updates at random times, each at the same average rate. The probability of a routing loop formation (rounded off to one decimal place) between P and Q, leading to count-to-infinity problem, is___________.
1 |
If asked for R, from among P, Q, R
Probability = 1 /3
Question 3 |
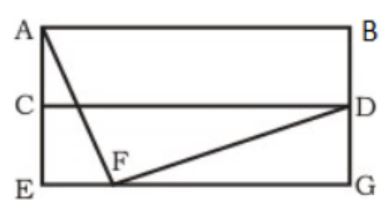
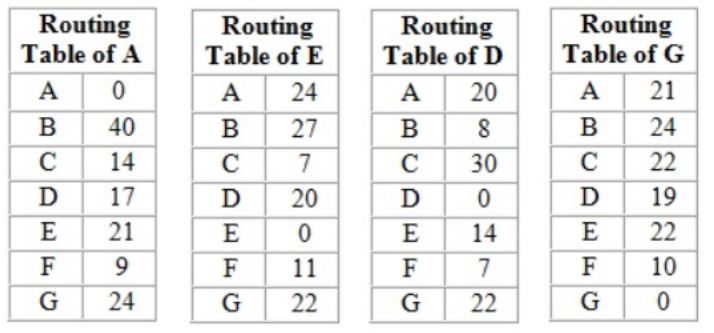
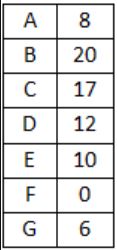
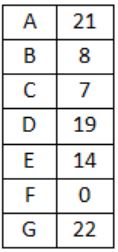
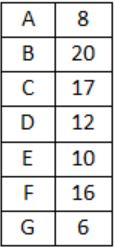
For the network given in the figure below, the routing tables of the four nodes A, E, D and G are shown. Suppose that F has estimated its delay to its neighbors, A, E, D and G as 8, 10, 12 and 6 msecs respectively and updates its routing table using distance vector routing technique.
 | |
 | |
 | |
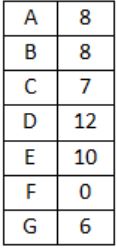 |
Using distance vector routing protocol, F→D→B yeilds distance as 20 which eliminates option (B) and (D).
Question 4 |
A group of 15 routers are interconnected in a centralized complete binary tree with a router at each tree node. Router j communicates with router j by sending a message to the root of the tree. The root then sends the message back down to router j. The mean number of hops per message, assuming all possible router pairs are equally likely is
3 | |
4.26 | |
4.53 | |
5.26 |
= (3×8) + (2×4) + (1×2) + (0×1)/15
= 2.267
So, Total hops = 2×2.267 = 4.53
Question 5 |
Two popular routing algorithms are Distance Vector(DV) and Link State (LS) routing. Which of the following are true?
-
- (S1) Count to infinity is a problem only with DV and not LS routing
-
- (S2) In LS, the shortest path algorithm is run only at one node
-
- (S3) In DV, the shortest path algorithm is run only at one node
- (S4) DV requires lesser number of network messages than LS
S1, S2 and S4 only | |
S1, S3 and S4 only | |
S2 and S3 only | |
S1 and S4 only |
→ In LSR shortest path is calculated at each every router. (B) is wrong.
→ In DVR also shortest path is calculated at each and every router. (C) is wrong.
→ Since DVR is based upon local knowledge whereas LSR is based upon global knowledge.
Question 6 |
Packets of the same session may be routed through different paths in:
TCP, but not UDP | |
TCP and UDP | |
UDP, but not TCP | |
Neither TCP nor UDP |
Question 7 |
Consider the following statements about the routing protocols, Routing Information Protocol (RIP) and Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) in an IPv4 network.
-
- I: RIP uses distance vector routing
-
- II: RIP packets are sent using UDP
-
- III: OSPF packets are sent using TCP
- IV: OSPF operation is based on link-state routing
Which of the statements above are CORRECT?
I and IV only | |
I, II and III only | |
I, II and IV only | |
II, III and IV only |
RIP is one of the oldest DVR protocol which employ the hop count as a routing metric.
II: RIP packets are sent using UDP. “TRUE”
RIP uses the UDP as its transport protocol, and is assigned the reserved port no 520.
III: OSPF packets are sent using TCP. “FASLE”
OSPF encapsulates its data directly into IP Packets and does not use either TCP or UDP.
IV: OSPF operation is based on link state routing. “TRUE”
OSPF is a routing protocol which uses link state routing (LSR) and works within a single autonomous system.
Hence correct is answer “C”.
Question 8 |
8.000 | |
8.008 | |
15.992 | |
16.000 |
Question 9 |
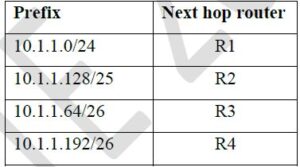 This router forwards 20 packets each to 5 hosts. The IP addresses of the hosts are 10.1.1.16, 10.1.1.72, 10.1.1.132, 10.1.1.191, and 10.1.1.205 . The number of packets forwarded via the next hop router R2 is _______
This router forwards 20 packets each to 5 hosts. The IP addresses of the hosts are 10.1.1.16, 10.1.1.72, 10.1.1.132, 10.1.1.191, and 10.1.1.205 . The number of packets forwarded via the next hop router R2 is _______ 40 | |
Question 10 |
OSPF implements Bellman-Ford algorithm to find shortest paths. | |
OSPF uses Dijkstra’s shortest path algorithm to implement least-cost path routing. | |
OSPF is used as an inter-domain routing protocol. | |
OSPF implements hierarchical routing. |
Question 11 |
Consider a network with 6 routers R1 to R6 connected with links having weights as shown in the following diagram:
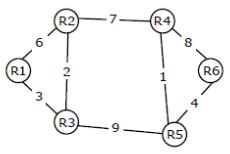
All the routers use the distance vector based routing algorithm to update their routing tables. Each router starts with its routing table initialized to contain an entry for each neighbour with the weight of the respective connecting link. After all the routing tables stabilize, how many links in the network will never be used for carrying any data?
4 | |
3 | |
2 | |
1 |
Similarly, link R4-R6 will not be used, instead this link we can use R4-R5-R6 link which costs only 5 unit.
Question 12 |
Consider a network with 6 routers R1 to R6 connected with links having weights as shown in the following diagram:

Suppose the weights of all unused links in the previous question are changed to 2 and the distance vector algorithm is used again until all routing tables stabilize. How many links will now remain unused?
0 | |
1 | |
2 | |
4 |
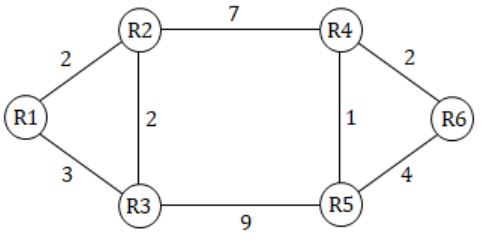
And only link that will be removed is R5-R6 link.
