Software-design
Question 1 |
Match each application/software design concept in List – I to its definition in List – II.


I-(b), II-(a), III-(d), IV-(c) | |
I-(b), II-(d), III-(a), IV-(b) | |
I-(d), II-(c), III-(b), IV-(a) | |
I-(d), II-(a), III-(c), IV-(b) |
Question 1 Explanation:
Coupling → Reliance of a code module upon other code modules
Cohesion → Focus of a code upon a single goal.
Scalable → Easy to add functionality to the software without having to redesign it.
Readable → Easy to visually inspect the design of the software and understand its purpose.
→ Cohesion is a measure of internal strength within a module, whereas coupling is a measure of inter dependency among the modules.
→ In a functional oriented design/modular software design there should be high cohesion and low coupling.
→ It requires High Fan-In and Low fan-out.
Cohesion → Focus of a code upon a single goal.
Scalable → Easy to add functionality to the software without having to redesign it.
Readable → Easy to visually inspect the design of the software and understand its purpose.
→ Cohesion is a measure of internal strength within a module, whereas coupling is a measure of inter dependency among the modules.
→ In a functional oriented design/modular software design there should be high cohesion and low coupling.
→ It requires High Fan-In and Low fan-out.
Question 2 |
Which of the following approaches is generally applied for module design phase while developing new software?
Top-down approach | |
Bottom-up approach | |
centre fringing | |
depends on the size of software |
Question 3 |
In the context of Object oriented software design, which of the following consequences of use of inheritance is disadvantageous?
Increased coupling between classes | |
Reusable code development
| |
Supports building class hierarchy | |
Supports development of classes with less number of arguments and methods |
Question 4 |
Which of the following software development process is not necessarily useful for developing software for automating an existing manual system for a client?
Prototyping | |
Iterative enhancement | |
Spiral model | |
Waterfall model |
Question 5 |
In Software Engineering Jackson's Principle based on
A. Designation
B. Definitions
C. Refutable Assertions
D. Formal Review
E. Requirement Elicitation
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
A. Designation
B. Definitions
C. Refutable Assertions
D. Formal Review
E. Requirement Elicitation
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
A, B & C Only | |
B, C & D Only | |
C, D & E Only | |
B, D & C Only |
Question 6 |
Match List - I with List - II.
List - I(software design principles)
(A)Cohesion
(B)Coupling
(C)Abstraction
(D)Modularity
List - I1(Definition)
(I)Degree to which one module relies on another module.
(II)Dividing a software system into distinct modules.
(III)Degree to which elements of a module belong together.
(IV)Simplifying complex reality by modeling classes appropriate to the problem.
List - I(software design principles)
(A)Cohesion
(B)Coupling
(C)Abstraction
(D)Modularity
List - I1(Definition)
(I)Degree to which one module relies on another module.
(II)Dividing a software system into distinct modules.
(III)Degree to which elements of a module belong together.
(IV)Simplifying complex reality by modeling classes appropriate to the problem.
(A)-(I),(B)-(II),(C)-(III),(D)-(IV)
| |
(A)-(II),(B)-(III),(C)-(IV),(D)-(I)
| |
(A)-(III),(B)-(I),(C)-(IV),(D)-(II)
| |
(A)-(III),(B)-(IV),(C)-(II),(D)-(I)
|
Question 7 |
Arrange the following steps of feature Drive Development (FDD) process in the correct sequence :
A)Develop an overall model
B)Build by feature
C)Plan by feature
D)Design by feature
E)Build a feature list
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
A)Develop an overall model
B)Build by feature
C)Plan by feature
D)Design by feature
E)Build a feature list
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(A), (C), (B), (E), (D)
| |
(A), (E), (C), (D), (B)
| |
(B), (A), (D), (E), (C) | |
(A), (B), (C), (E), (D)
|
Question 8 |
In software project planning, work Breakdown structure must be __________ .
A graph | |
A tree | |
A Eulars graph | |
None of the above |
Question 8 Explanation:
Work Breakdown structure(WBS) must be tree. The tree structure will give overall view of a project. Normally we can divide two types of WBS
1. Functional WBS
2. Activity WBS
WBS tree structure:

1. Functional WBS
2. Activity WBS
WBS tree structure:

Question 9 |
In a good software design, __________ coupling is desirable between modules.
Highest | |
Lowest | |
Internal | |
External |
Question 9 Explanation:
→ Cohesion is a measure of internal strength within a module, whereas coupling is a measure of inter dependency among the modules.
→ So in the context of modular software design there should be high cohesion and low coupling.
→ So in the context of modular software design there should be high cohesion and low coupling.
Question 10 |
Which of the following is not one of three software product aspects addressed by McCall’s software quality factors ?
Ability to undergo change | |
Adaptability to new environments | |
Operational characteristics | |
Production costs and scheduling |
Question 10 Explanation:
McCall’s software quality factors
1. Product operation factors − Correctness, Reliability, Efficiency, Integrity, Usability.
2. Product revision factors − Maintainability, Flexibility, Testability.
3. Product transition factors − Portability, Reusability, Interoperability.
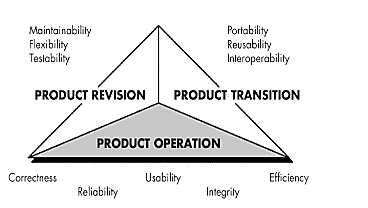
1. Product operation factors − Correctness, Reliability, Efficiency, Integrity, Usability.
2. Product revision factors − Maintainability, Flexibility, Testability.
3. Product transition factors − Portability, Reusability, Interoperability.

Question 11 |
The prototyping model of software development is:
a reasonable approach when requirements are well-defined | |
a useful approach when a customer cannot define requirements clearly. | |
the best approach to use for projects with large development teams. | |
a risky model that rarely produces a meaningful product. |
Question 11 Explanation:
→ The prototyping model of software development is a useful approach when a customer cannot define requirements clearly.
Advantage:
1. We can develop the software where requirements are unclear
2. Customer satisfaction
Disadvantage:
1. Who pay cost of prototype
2. Required the design expertise
Advantage:
1. We can develop the software where requirements are unclear
2. Customer satisfaction
Disadvantage:
1. Who pay cost of prototype
2. Required the design expertise
Question 12 |
A software design pattern used to enhance the functionality of an object at run-time is:
Adapter | |
Decorator | |
Delegation | |
Proxy |
Question 12 Explanation:
→ Software design pattern used to enhance the functionality of an object at run-time is Decorator.
→ Decorator will attach additional responsibilities to an object dynamically keeping the same interface.
→ Decorators provide a flexible alternative to subclassing for extending functionality.
→ Decorator will attach additional responsibilities to an object dynamically keeping the same interface.
→ Decorators provide a flexible alternative to subclassing for extending functionality.
There are 12 questions to complete.
