Software-Engineering
Question 1 |
In a software project, COCOMO (Constructive Cost Model) is used to estimate
A | effort and duration based on the size of the software |
B | size and duration based on the effort of the software |
C | effort and cost based on the duration of the software |
D | size, effort and duration based on the cost of the software |
Question 2 |
The diagram that helps in understanding and representing user requirements for a software project using UML (Unified Modeling Language) is:
A | Entity Relationship Diagram |
B | Deployment Diagram |
C | Data Flow Diagram |
D | Use Case Diagram |
Question 3 |
A software organization has been assessed at SEI CMM Level 4. Which of the following does the organization need to practice beside Process Change Management and Technology Change Management in order to achieve Level 5?
A | Defect Detection |
B | Defect Prevention |
C | Defect Isolation |
D | Defect Propagation |
Question 4 |
A software configuration management tool helps is
A | keeping track of the schedule based on the milestones reached |
B | maintaining different versions of the configurable items |
C | managing manpower distribution by changing the project structure |
D | all of the above |
Question 5 |
In a particular Unix OS, each data block is of size 1024 bytes, each node has 10 direct data block addresses and three additional addresses: one for single indirect block, one for double indirect block and one for triple indirect block. Also, each block can contain addresses for 128 blocks. Which one of the following is approximately the maximum size of a file in the file system?
A | 512 MB |
B | 2 GB |
C | 8 GB |
D | 16 GB |
= (10 + 27 + 27 × 27 + 7 × 7 × 7) × 210
≈ 231
≈ 2 GB
Question 6 |
A software project involves execution of 5 tasks T1, T2, T3, T4 and T5 of duration 10, 15, 18, 30 and 40 days, respectively. T2 and T4 can start only after T1 completes. T3 can start after T2 completes. T5 can start only after both T3 and T4 complete. What is the slack time of the task T3 in days?
A | 0 |
B | 3 |
C | 18 |
D | 30 |
Question 7 |
Consider the following program module:
int module1 (int x, int y) {
while (x! = y) {
if (x > y)
x = x - y,
else y = y - x;
}
return x;
}
What is Cyclomatic complexity of the above module? A | 1 |
B | 2 |
C | 3 |
D | 4 |
Question 8 |
Assume that the delivered lines of code L of a software is related to the effort E in person months and duration t in calendar months by the relation L = P* (E/B)1/3 * t4/3, where P and B are two constants for the software process and skills factor. For a software project, the effort was estimated to be 20 person months and the duration was estimated to be 8 months. However, the customer asked the project team to complete the software project in 4 months. What would be the required effort in person months?
A | 10 |
B | 40 |
C | 160 |
D | 320 |
Question 9 |
A software was tested using the error seeding strategy in which 20 errors were seeded in the code. When the code was tested using the complete test suite, 16 of the seeded errors were detected. The same test suite also detected 200 non-seeded errors. What is the estimated number of undetected errors in the code after this testing?
A | 4 |
B | 50 |
C | 200 |
D | 250 |
Question 10 |
What is the availability of a software with the following reliability figures?
Mean Time Between Failure (MTBF) = 25 days Mean Time To Repair (MTTR) = 6 hours
A | 1% |
B | 24% |
C | 99% |
D | 99.009% |
Question 11 |
The Function Point (FP) calculated for a software project are often used to obtain an estimate of Lines of Code (LOC) required for that project. Which of the following statements is FALSE in this context.
A | The relationship between FP and LOC depends on the programming language used to implement the software. |
B | LOC requirement for an assembly language implementation will be more for a given FP value, than LOC for implementation in COBOL |
C | On an average, one LOC of C++ provides approximately 1.6 times the functionality of a single LOC of FORTRAN |
D | FP and LOC are not related to each other |
Question 12 |
The availability of a complex software is 90%. Its Mean Time Between Failure (MTBF) is 200 days. Because of the critical nature of the usage, the organization deploying the software further enhanced it to obtain an availability of 95%. In the process, the Mean Time To Repair (MTTR) increased by 5 days.
What is the MTBF of the enhanced software?
A | 205 days |
B | 300 days |
C | 500 days |
D | 700 days |
Question 13 |
In a data flow diagram, the segment shown below is identified as having transaction flow characteristics, with p2 identified as the transaction center
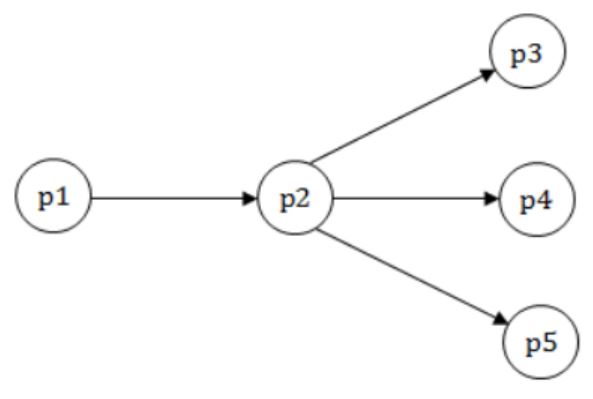
A first level architectural design of this segment will result in a set of process modules with an associated invocation sequence. The most appropriate architecture is
A | p1 invokes p2, p2 invokes either p3, or p4, or p5 |
B | p2 invokes p1, and then invokes p3, or p4, or p5 |
C | A new module Tc is defined to control the transaction flow. This module Tc first invokes p1 and then invokes p2, p2 in turn invokes p3, or p4, or p5 |
D | A new module Tc is defined to control the transaction flow. This module Tc invokes p2, p2 invokes p1, and then invokes p3, or p4, or p5 |
Question 14 |
The cyclomatic complexity of the flow graph of a program provides
A | an upper bound for the number of tests that must be conducted to ensure that all statements have been executed at most once |
B | a lower bound for the number of tests that must be conducted to ensure that all statements have been executed at most once |
C | an upper bound for the number of tests that must be conducted to ensure that all statements have been executed at least once |
D | a lower bound for the number of tests that must be conducted to ensure that all statements have been executed at least once |
Question 15 |
With respect to software testing, consider a flow graph G with one connected component. Let E be the number of edges, N be the number of nodes, and P be the number of predicate nodes of G. Consider the following four expressions:
1. E - N + P
2. E - N + 2
3. P + 2
4. P + 1
The cyclomatic complexity of G is given by
A | 1 or 3 |
B | 2 or 3 |
C | 2 or 4 |
D | 1 or 4 |
Question 16 |
A software program consists of two modules M1 and M2 that can fail independently, but never simultaneously. The program is considered to have failed if any of these modules fails. Both the modules are ‘repairable’ and so the program starts working again as soon as the repair is done. Assume that the mean time to failure (MTTF) of M1is T1 with a mean time to repair (MTTR) of R1. The MTTF of M2 is T2 with an MTTR of R2. What is the availability of the overall program given that the failure and repair times are all exponentially distributed random variables?
A |  |
B |  |
C |  |
D |  |
Question 17 |
Consider the following structure chart diagram. The boxes have function names embedded in them, while the variables are indicated along the arcs.
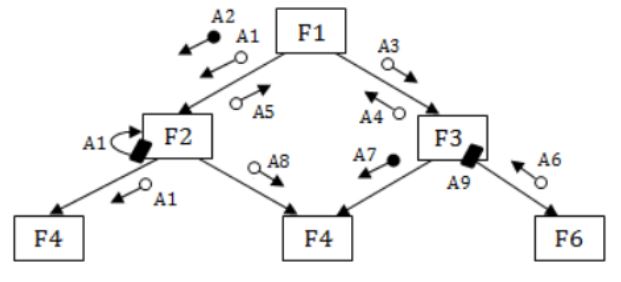
Given below are a set of statements relevant to the above diagram.
I. F3 and F6 can be in the same module.
II. F4 and F6 can be in the same module.
III. A4 is both an output and a control variable.
IV. It is incorrect to pass A1 as data and use it as a control variable.
Which combination of these statements is TRUE?
A | III and IV |
B | I and IV |
C | II and IV |
D | I, II and IV |
Question 18 |
Consider the following program module:
void swap(float* A1, float* A2)
{
float temp;
if (*A1 = = *A2) return;
temp = *A1;
*A1 = *A2;
*A2 = temp;
return;
}
The program volume for the above module using Halstead's method is
A | 60 |
B | 63 |
C | 66 |
D | 69 |
Question 19 |
Consider the following program module:
void swap(float* A1, float* A2)
{
float temp;
if (*A1 = = *A2) return;
temp = *A1;
*A1 = *A2;
*A2 = temp;
return;
}
The program effort for the above module using Halstead's method is
A | 315 |
B | 330 |
C | 393 |
D | 403 |
Question 20 |
A software project has four phases P1, P2, P3 and P4. Of these phases, P1 Is the first one and needs to be completed before any other phase can commence. Phases P2 and P3 can be executed in parallel. Phase P4 cannot commence until both P2 and P3 are completed. The optimistic, most likely, and pessimistic estimates of the phase completion times in days, for Pl, P2, P3 and P4 are, respectively, (11, 15, 25), (7, 8, 15), (8, 9, 22), and (3, 8, 19).
The critical path for the above project and the slack of P2 are, respectively,
A | P1-P2-P4, 1 day |
B | P1-P3-P4, 1 day |
C | P1-P3-P4, 2 days |
D | P1-P2-P4, 2 days |
Question 21 |
A software project has four phases P1, P2, P3 and P4. Of these phases, P1 Is the first one and needs to be completed before any other phase can commence. Phases P2 and P3 can be executed in parallel. Phase P4 cannot commence until both P2 and P3 are completed. The optimistic, most likely, and pessimistic estimates of the phase completion times in days, for Pl, P2, P3 and P4 are, respectively, (11, 15, 25), (7, 8, 15), (8, 9, 22), and (3, 8, 19).
The costs (in Rupees per day) of crashing the expected phase completion times for the four phases, respectively, are 100, 2000, 50, and 1000. Assume that the expected phase completion times of the phases cannot be crashed below their respective most likely completion times. The minimum and the maximum amounts (in Rupees) that can be spent on crashing so that ALL paths are critical are, respectively.
A | 100 and 1000 |
B | 100 and 1200 |
C | 150 and 1200 |
D | 200 and 2000 |
Question 22 |
In the Spiral model of software development, the primary determinant in selecting activities in each iteration is
A | Iteration size |
B | Cost |
C | Adopted process such as Rational Unified Process or Extreme Programming |
D | Risk |
Question 23 |
The following table shoes the time between failures for a software system
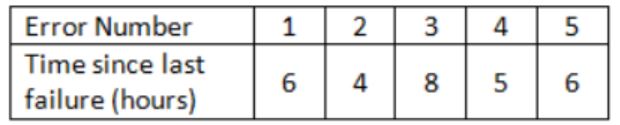
The reliability of the system for one hour of operation assuming an exponential model is
A | 0.45 |
B | 0.63 |
C | 0.84 |
D | 0.95 |
MIBF = (6+4+8+5+6)/5 = 29/5
The probability or reliability that the product will work for a defined period of time without failure is given by
R(T) = exp(-T/MTBF); T = 1 hour
R(1) = e(-1/(29/5)) = e(-5/29) = 0.84
Question 24 |
In the simplified flowchart given below, the shaded boxes represent code that is executed during a test case.
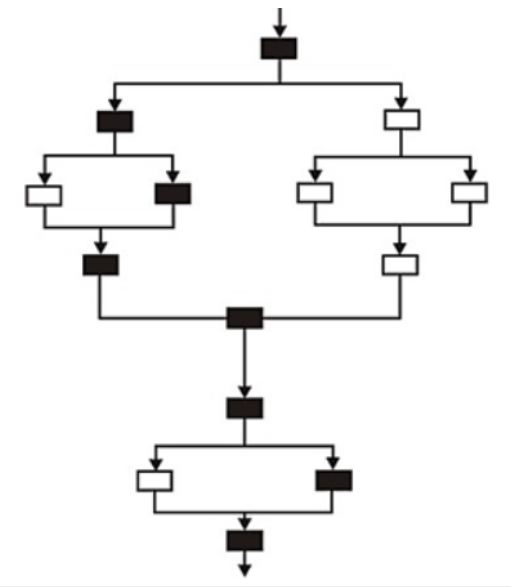
The Branch coverage is
A | 3/4 |
B | 2/3 |
C | 1/2 |
D | 3/8 |
Question 25 |
Consider the CPM activity chart where an arc connecting two milestones is labeled with a task identifier and the time taken in days. For example in order to go from A to B, task T1 takes 180 days. A dashed line depicts an additional dependency that is equivalent to a zero time task.

The set of activities that lie on the critical path are
A | T1, T2, T8, T10 |
B | T1, T3, T8, T10 |
C | T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10 |
D | T1, T4, T5, T7, T8, T10 |
Question 26 |
Consider the following pseudo-code:
IF ((A > B) AND (C > D)) THEN
A = A + 1
B = B + 1
ENDIF
The cyclomatic complexity of the pseudo-code is
A | 2 |
B | 3 |
C | 4 |
D | 5 |
Question 27 |
Which of the following are NOT considered when computing function points for a software project?
- (O1) External inputs and outputs
(O2) Programming language to be used for the implementation
(O3) User interactions
(O4) External interfaces
(O5) Number of programmers in the software project
(O6) Files used by the system
A | 02, 03 |
B | 01, 05 |
C | 04, 06 |
D | 02, 05 |
Question 28 |
A software project plan has identified ten tasks with each having dependencies as given in the following table:
Task Depends On
T1 -
T2 T1
T3 T1
T4 T1
T5 T2
T6 T3
T7 T3, T4
T8 T4
T9 T5, T7, T8
T10 T6, T9
Answer the following questions:
(Q1) What is the maximum number of tasks that can be done concurrently?
(Q2) What is the minimum time required to complete the project, assuming that each task requires one time unit and there is no restriction on the number of tasks that can be done in parallel?
A | 5, 5 |
B | 4, 5 |
C | 5, 4 |
D | 4, 4 |
Question 29 |
Consider the basic COCOMO model where E is the effort applied in person-months, D is the development time in chronological months, KLOC is the estimated number of delivered lines of code (in thousands) and ab, bb, cb, db have their usual meanings. The basic COCOMO equations are of the form
A | E = a b(KLOC)exp (b b, D = c b(E)exp (d b) |
B | E = a b(KLOC)exp (b b, D = c b(E)exp (d b) |
C | E = a bexp(b b), D = c b(KLOC)exp (d b) |
D | E = a bexp(D b), D = c b(KLOC)exp (b b) |
Effort applied (E) = ab(KLOC)bb
Development time (D) = cb(E)db
Question 30 |
A software requirements specification(SRS) document should avoid discussing which one of the following?
A | User interface issues |
B | Non-functional requirements |
C | Design specification |
D | Interfaces with third party software
|
Question 31 |
Which one of the following assertions concerning code inspection and code walkthrough is true?
A | Code inspection is carried out once the code has been unit tested |
B | Code inspection and code walkthrough are synonyms |
C | Adherence to coding standards is checked during code inspection
|
D | Code walkthrough is usually carried out by an independent test team |
Question 32 |
Match the following:
(P) Condition coverage (i) Black-box testing (Q) Equivalence class partitioning (ii) System testing (R) Volume testing (iii) White-box testing (S) Alpha testing (iv) Performance testing
A | P-ii, Q-iii, R-i, S-iv |
B | P-iii, Q-iv, R-ii, S-i |
C | P-iii, Q-i, R-iv, S-ii |
D | P-iii, Q-i, R-ii, S-iv |
Equivalence class partitioning ⇒ is a software testing technique that divides the input data of a software unit into partitions of equivalent data from which test cases can be derived, which is nothing but black box testing. Hence B-1.
Volume testing ⇒ Performance testing - C-4.
Alpha testing ⇒ System Testing D-2.
Question 33 |
Consider the following C program segment.
while (first <= last)
{
if (array [middle] < search)
first = middle +1;
else if (array [middle] == search)
found = True;
else last = middle – 1;
middle = (first + last)/2;
}
if (first < last) not Present = True;
The cyclomatic complexity of the program segment is __________.
A | 5 |
B | 6 |
C | 7 |
D | 8 |
Question 34 |
Consider a software project with the following information domain characteristic for calculation of function point metric.
-
Number of external inputs (I) = 30
Number of external output (O) = 60
Number of external inquiries (E) = 23
Number of files (F) = 08
Number of external interfaces (N) = 02
It is given that the complexity weighting factors for I, O, E, F and N are 4, 5, 4, 10 and 7, respectively. It is also given that, out of fourteen value adjustment factors that influence the development effort, four factors are not applicable, each of he other four factors have value 3, and each of the remaining factors have value 4. The computed value of function point metric is __________.
A | 612.06 |
B | 612.07 |
C | 612.08 |
D | 612.09 |
Question 35 |
Consider a software program that is artificially seeded with 100 faults. While testing this program, 159 faults are detected, out of which 75 faults are from those artificially seeded faults. Assuming that both are and seeded faults are of same nature and have same distribution, the estimated number of undetected real fault is _____ .
A | 28 |
B | 176 |
C | 177 |
D | 178 |
Question 36 |
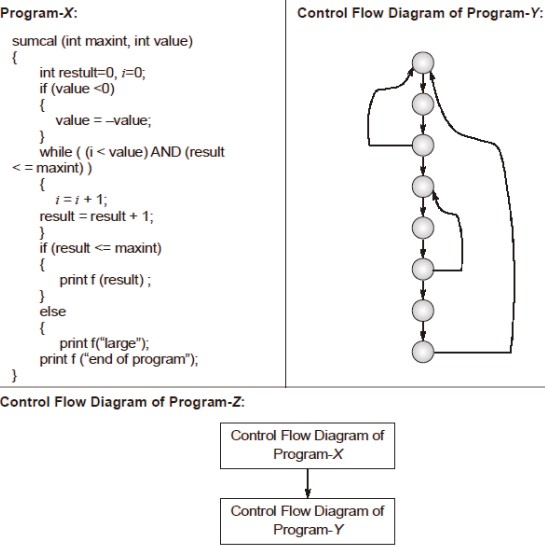
The values of McCabe’s Cyclomatic complexity of Program-X, Program-Y and Program-Z respectively are
A | 4,4,7 |
B | 3,4,7 |
C | 4,4,8 |
D | 4,3,8 |
Question 37 |
The cyclomatic complexity of each of the modules A and B shown below is 10. What is the cyclomatic complexity of the sequential integration shown on the right hand side?
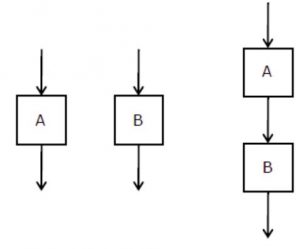
A | 19 |
B | 21 |
C | 20 |
D | 10 |
Question 38 |
What is the appropriate pairing of items in the two columns listing various activities encountered in a software life cycle?
P. Requirements Capture 1. Module Development and Integration Q. Design 2. Domain Analysis R. Implementation 3. Structural and Behavioral Modeling S. Maintenance 4. Performance Tuning
A | P-3, Q-2, R-4, S-1 |
B | P-2, Q-3, R-1, S-4 |
C | P-3, Q-2, R-1, S-4 |
D | P-2, Q-3, R-4, S-1 |
Question 39 |
The following program is to be tested for statement coverage:
begin
if (a== b) {S1; exit;}
else if (c== d) {S2;]
else {S3; exit;}
S4;
end
The test cases T1, T2, T3 and T4 given below are expressed in terms of the properties satisfied by the values of variables a, b, c and d. The exact values are not given. T1 : a, b, c and d are all equal T2 : a, b, c and d are all distinct T3 : a = b and c != d T4 : a != b and c = d Which of the test suites given below ensures coverage of statements S1, S2, S3 and S4?
A | T1, T2, T3 |
B | T2, T4 |
C | T3, T4 |
D | T1, T2, T4 |
T2 covers S3
T4 covers S2, S4.
Question 40 |
The coupling between different modules of a software is categorized as follows:
- I. Content coupling
II. Common coupling
III. Control coupling
IV. Stamp coupling
V. Data coupling
Coupling between modules can be ranked in the order of strongest (least desirable) to weakest (most desirable) as follows:
A | I-II-III-IV-V |
B | V-IV-III-II-I |
C | I-III-V-II-IV
|
D | IV-II-V-III-I |
Question 41 |
Which of the following statements are TRUE?
-
I. The context diagram should depict the system as a single bubble.
II. External entities should be identified clearly at all levels of DFDs.
III. Control information should not be represented in a DFD.
IV. A data store can be connected either to another data store or to an external entity.
A | II and III |
B | II and III |
C | I and III |
D | I, II and III |
Question 42 |
- I. The cyclomatic complexity of a module is equal to the maximum number of linearly independent circuits in the graph.
II. The cyclomatic complexity of a module is the number of decisions in the module plus one, where a decision is effectively any conditional statement in the module.
III. The cyclomatic complexity can also be used as a number of linearly independent paths that should be tested during path coverage testing.
A | I and II |
B | II and III |
C | I and III |
D | I, II and III |
Question 43 |
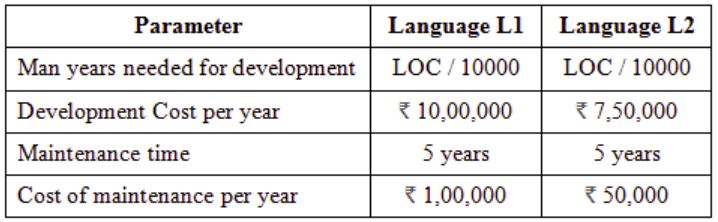
Total cost of the project includes cost of development and maintenance. What is the LOC for L1 for which the cost of the project using L1 is equal to the cost of the project using L2?
A | 4000 |
B | 5000 |
C | 4333 |
D | 4667 |
Question 44 |
A company needs to develop digital signal processing software for one of its newest inventions. The software is expected to have 40000 lines of code. The company needs to determine the effort in person-months needed to develop this software using the basic COCOMO model. The multiplicative factor for this model is given as 2.8 for the software development on embedded systems, while the exponentiation factor is given as 1.20. What is the estimated effort in person-months?
A | 234.25 |
B | 932.50 |
C | 287.80 |
D | 122.40 |
Question 45 |
Which of the following is NOT desired in a good Software Requirement Specifications (SRS) document?
A | Functional Requirements |
B | Non-Functional Requirements |
C | Goals of Implementation |
D | Algorithms for Software Implementation |
Question 46 |
The following is the comment written for a C function
/* This function computes the roots of a quadratic equation a.x^2 + b.x + c = . The function stores two real roots in *root1 and *root2 and returns the status of validity of roots. It handles four different kinds of cases. (i) When coefficient a is zero irrespective of discriminant (ii) When discreminant is positive (iii) When discriminant is zero (iv) When discriminant is negative. Only in case (ii) and (iii) the stored roots are valid. Otherwise 0 is stored in roots. The function returns 0 when the roots are valid and -1 otherwise. The function also ensures root1 >= root2 int get_QuadRoots( float a, float b, float c, float *root1, float *root2); */A software test engineer is assigned the job of doing black box testing. He comes up with the following test cases, many of which are redundant.
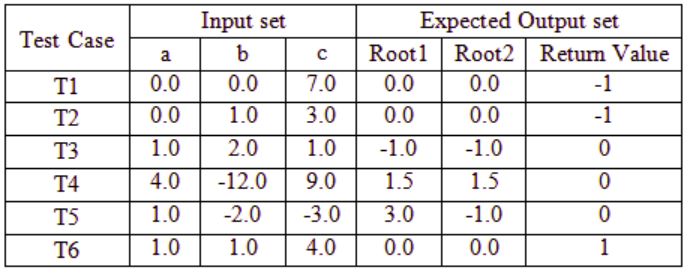
Which one of the following option provide the set of non-redundant tests using equivalence class partitioning approach from input perspective for black box testing?
A | T1, T2, T3, T6 |
B | T1, T3, T4, T5 |
C | T2, T4, T5, T6 |
D | T2, T3, T4, T5 |
T1 and T2 checking same condition a = 0 hence, any one of T1 and T2 is redundant.
T3, T4: in both case discriminant (D) = b2 – 4ac = 0. Hence any one of it is
T5 : D > 0
T6 : D < 0
Question 47 |
Match the problem domains in GROUP I with the solution technologies in GROUP II
GROUP I GROUP II (P) Service oriented computing (1) Interoperability (Q) Heterogeneous communicating systems (2) BPMN (R) Information representation (3) Publish-find-bind (S) Process description (4) XML
A | P-1, Q-2, R-3, S-4 |
B | P-3, Q-4, R-2, S-1 |
C | P-3, Q-1, R-4, S-2 |
D | P-4, Q-3, R-2, S-1 |
Question 48 |
The following figure represents access graphs of two modules M1 and M2. The filled circles represent methods and the unfilled circles represent attributes. If method m is moved to module M2 keeping the attributes where they are, what can we say about the average cohesion and coupling between modules in the system of two modules?

A | There is no change. |
B | Average cohesion goes up but coupling is reduced. |
C | Average cohesion goes down and coupling also reduces. |
D | Average cohesion and coupling increase. |
Question 49 |
Match the following:
1) Waterfall model a) Specifications can be
developed incrementally
2) Evolutionary model b) Requirements compromises
are inevitable
3) Component-based c) Explicit recognition of risk
software engineering
4) Spiral development d) Inflexible partitioning of
the project into stages
A | 1-a, 2-b, 3-c, 4-d |
B | 1-d, 2-a, 3-b, 4-c |
C | 1-d, 2-b, 3-a, 4-c |
D | 1-c, 2-a, 3-b, 4-d |
Question 50 |
In the context of modular software design, which one of the following combinations is desirable?
A | High cohesion and high coupling |
B | High cohesion and low coupling |
C | Low cohesion and high coupling |
D | Low cohesion and low coupling |
Cohesion is a measure of internal strength within a module, whereas coupling is a measure of inter dependency among the modules. So in the context of modular software design there should be high cohesion and low coupling.
