Storage-Classes
Question 1 |
An external variable
is globally accessible by all functions | |
has a declaration "extern" associated with it when declared within a function | |
will be initialized to 0 if not initialized | |
All of these |
Question 1 Explanation:
An external variable can be accessed by all the functions in all the modules of a program. It is a global variable. For a function to be able to use the variable, a declaration or the definition of the external variable must lie before the function definition in the source code. Or there must be a declaration of the variable, with the keyword extern, inside the function.
Question 2 |
The output of the following code is:
int main()
{
static int x[ ]={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8}
int i;
for(i=2;i<6;++i)
x[x[i]]=x[i];
for(i=0;i<8;++i)
printf(“%d”,x[i]);
Return 0;
}
12244668 | |
11335578 | |
12335578
| |
12343676 |
Question 2 Explanation:

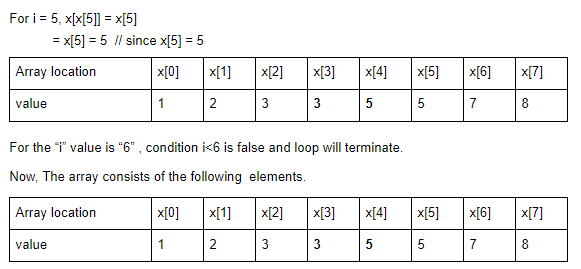
Question 3 |
What will be the output of following?
main()
{
static int a=3;
printf("%d",a--);
if(a)
main();
}
main()
{
static int a=3;
printf("%d",a--);
if(a)
main();
}
3 | |
3 2 1 | |
3 3 3 | |
Program will fall in continuous loop and print 3 |
Question 3 Explanation:
The variable is static variable, the value is retained during multiple function calls. Initial value is 3
“A--” is post decrement so it will print “3”
if(2) condition is true and main() function will call again , Here the “a” value is 2.
“A--” is post decrement so it will print “2”
if(1) condition is true and main() function will call again Here the “a” value is 1.
“A--” is post decrement so it will print “1”
if(0) condition is false it won’t call main() function
“A--” is post decrement so it will print “3”
if(2) condition is true and main() function will call again , Here the “a” value is 2.
“A--” is post decrement so it will print “2”
if(1) condition is true and main() function will call again Here the “a” value is 1.
“A--” is post decrement so it will print “1”
if(0) condition is false it won’t call main() function
There are 3 questions to complete.
