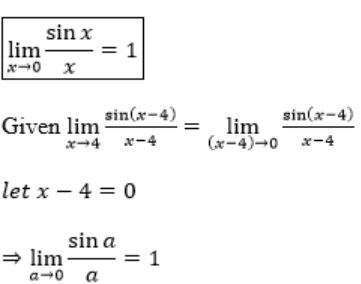Calculus
Question 1 |
The solution of differential equation y'' + 3y' + 2y = 0 is of the form
C1ex + C2e2x | |
C1e-x + C2e3x | |
C1e-x + C2e-2x | |
C1e-2x + C22-x |
Question 2 |
(a) Determine the number of divisors of 600.
(b) Compute without using power series expansion ![]()
Theory Explanation. |
Question 3 |
Consider the functions
- I. e-x
II. x2-sin x
III. √(x3+1)
Which of the above functions is/are increasing everywhere in [0,1]?
II and III only | |
III only | |
II only | |
I and III only |
I. e-x
II. f'(x) = -e-x
f'(x)<0 on the interval [0,1] so this is not an increasing function.
II. x2-sinx
f'(x) = 2x - cosx
at x=0, f'(0) = 2(0) - 1 = -1 < 0
f(x) = x2 - sinx is decreasing over some interval, increasing over some interval as cosx is periodic.
As the question is asked about increasing everywhere II is false.
III. √(x3+1) = (x3+1)1/2
f'(x) = 1/2(3x2/√(x3+1))>0
f(x) is increasing over [0,1].
Question 4 |
The formula used to compute an approximation for the second derivative of a function f at a point X0 is
f(x0+h) + f(x0-h)/2 | |
f(x0+h) - f(x0-h)/2h | |
f(x0+h) + 2f(x0) + f(x0-h)/h2 | |
f(x0+h) - 2f(x0) + f(x0-h)/h2 |
f(x0+h) - 2f(x0) + f(x0-h)/h2
Question 5 |
What is the maximum value of the function f(x) = 2x2 - 2x + 6 in the interval [0,2]?
6 | |
10 | |
12 | |
5.5 |
f'(x) = 4x - 2 = 0
⇒ x = 1/2
So at x = 1/2, f(x) is an extremum (either maximum or minimum).
f(2) = 2(2)2 - 2(2) + 6 = 10
f(1/2) = 2 × (1/2)2 - 2 × 1/2 + 6 = 5.5
f(0) = 6
So, the maximum value is at x=2 which is 10 as there are no other extremum for the given function.
Question 6 |
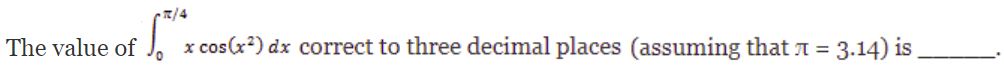
0.289 | |
0.298 | |
0.28 | |
0.29 |
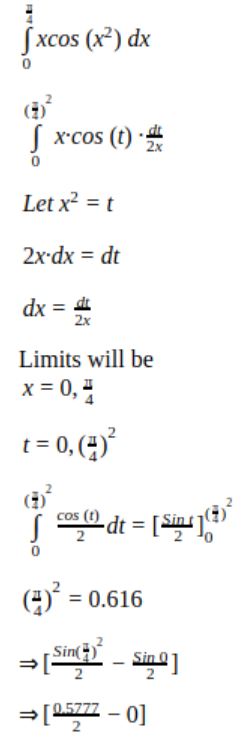
Question 7 |
Consider the function y = |x| in the interval [-1,1]. In this interval, the function is
continuous and differentiable | |
continuous but not differentiable | |
differentiable but not continuous | |
neither continuous nor differentiable |
→ The left side values of x=0 be negative and right side values are positive.
→ If the function is said to be differentiable then left side and right side values are to be same.
Question 8 |
(a) Find the points of local maxima and minima, if any, of the following function defined in 0 ≤ x ≤ 6.
x3 - 6x + 9x - 15
(b) Integrate ![]()
Theory Explanation. |
Question 9 |

Which of the following statements is true?
S > T | |
S = T | |
S < T and 2S > T | |
2S ≤ T |
Question 10 |
Backward Euler method for solving the differential equation dy/dx = f(x,y) is specified by, (choose one of the following).
yn+1 = yn + hf(xn, yn) | |
yn+1 = yn + hf(xn+1, yn+1) | |
yn+1 = yn-1 + 2hf(xn, yn) | |
yn+1 = (1 + h) f(xn+1, yn+1) |
With initial value y(x0) = y0. Here the function f and the initial data x0 and y0 are known. The function y depends on the real variable x and is unknown. A numerical method produces a sequence y0, y1, y2, ....... such that yn approximates y(x0 + nh) where h is called the step size.
→ The backward Euler method is helpful to compute the approximations i.e.,
yn+1 = yn + hf(x n+1, yn+1)
Question 11 |
The differential equation
d2y/dx2 + dy/dx + siny = 0 is:
linear | |
non-linear | |
homogeneous | |
of degree two |
d2y/dx2 + dy/dx + siny = 0
In this DE, degree is 1 then this represent linear equation.
Question 12 |
Fourier series of the periodic function (period 2π) defined by

But putting x = π, we get the sum of the series.
π2/4 | |
π2/6 | |
π2/8 | |
π2/12 |
Question 13 |
Which of the following improper integrals is (are) convergent?
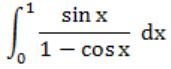 | |
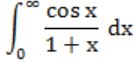 | |
 | |
 |
Question 14 |
1 |
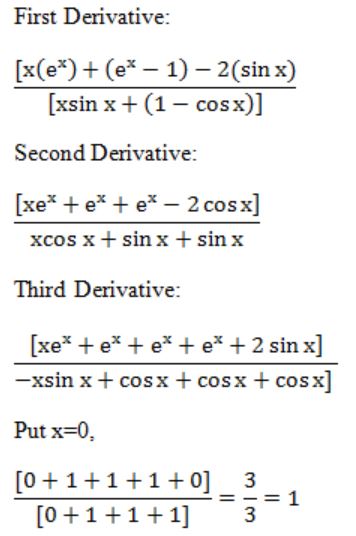
Question 15 |
The radius of convergence of the power series
Out of syllabus. |
Question 16 |
The value of the double integral ![]() is
is
1/3 |
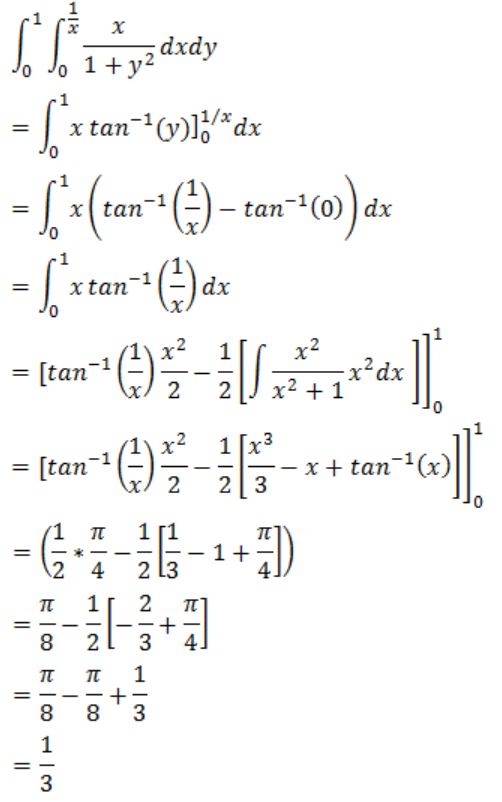
Question 17 |
The differential equation yn + y = 0 is subjected to the boundary conditions.
y (0) = 0 y(λ) = 0
In order that the equation has non-trivial solution(s), the general value of λ is __________
Out of syllabus. |
Question 18 |
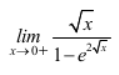
1/2 |
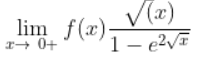
When 0 is substituted, we get 0/0
Apply L- Hospital rule
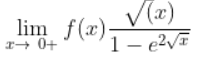
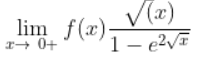
-1/2
Question 19 |
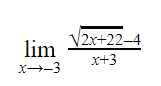
The value of the above expression (rounded to 2 decimal places) is _______
0.25 |

Question 20 |
If f(1) = 2, f(2) = 4 and f(4) = 16, what is the value of f(3) using Lagrange’s interpolation formula?
8 | |
8(1/3) | |
8(2/3) | |
9 |
Question 21 |
Consider the following iterative root finding methods and convergence properties:
Iterative root finding Convergence properties methods
(Q) False Position (I) Order of convergence = 1.62
(R) Newton Raphson (II) Order of convergence = 2
(S) Secant (III) Order of convergence = 1
with guarantee of convergence
(T) Successive Approximation (IV) Order of convergence = 1
with no guarantee of convergence Q-II, R-IV, S-II, T-I | |
Q-III, R-II, S-I, T-IV | |
Q-II, R-I, S-IV, T-III | |
Q-I, R-IV, S-II, T-III |
Question 22 |
If the trapezoidal method is used to evaluate the integral obtained 0∫1x2dx ,then the value obtained
is always > (1/3) | |
is always < (1/3) | |
is always = (1/3) | |
may be greater or lesser than (1/3) |
Question 23 |
What is the value of ![]()
-1 | |
1 | |
0 | |
π |

In the limits are be -π to π, one is odd and another is even product of even and odd is odd function and integrating function from the same negative value to positive value gives 0.
Question 24 |
The following definite integral evaluates to 
1/2 | |
π √10 | |
√10 | |
π | |
None of the above |
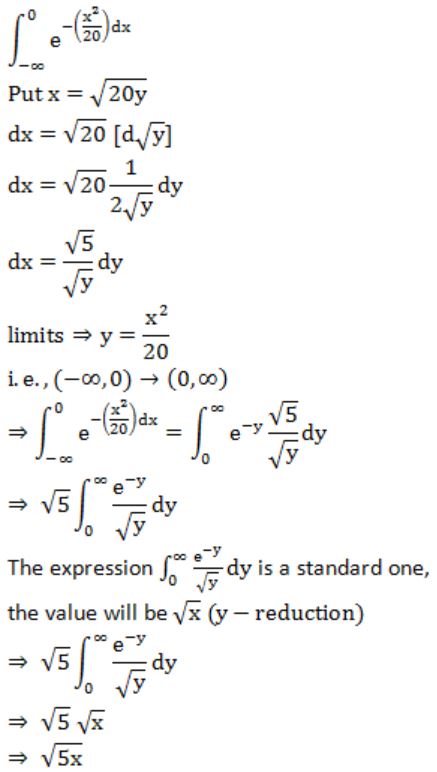
Question 25 |
If f(x) is defined as follows, what is the minimum value of f(x) for x∊(0,2] ?

2 | |
2(1/12) | |
2(1/6) | |
2(1/2) |
f(x) = 25/8x = 25/8(3/2) = 25/12 = 2(1/12)
Question 26 |
If f(x) = Rsin(πx/2) + S, f'(1/2) = √2 and ![]() , then the constants R and S are, respectively.
, then the constants R and S are, respectively.
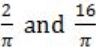 | |
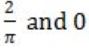 | |
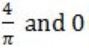 | |
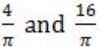 |
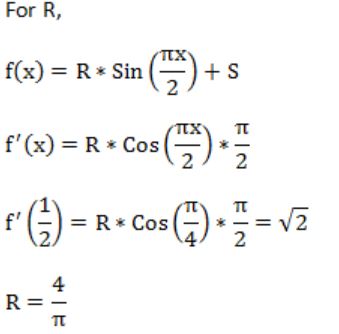
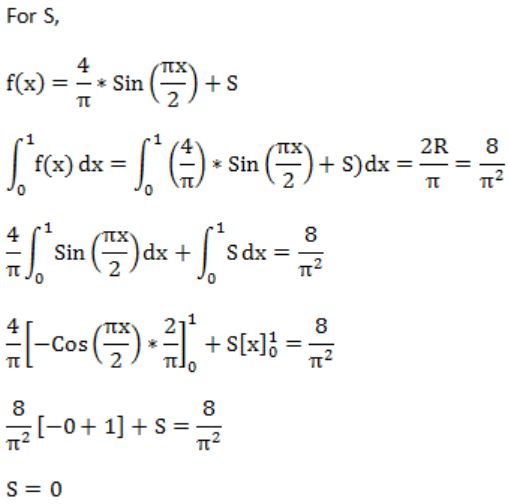
Question 27 |
Let f(x) = x -(1/3) and A denote the area of the region bounded bu f(x) and the X-axis, when x varies from -1 to 1. Which of the following statements is/are TRUE?
-
I) f is continuous in [-1,1]
II) f is not bounded in [-1,1]
III) A is nonzero and finite
II only | |
III only | |
II and III only | |
I, II and III |
∴ f is not bounced in [-1, 1] and hence f is not continuous in [-1, 1].

∴ Statement II & III are true.
Question 28 |
If g(x) = 1 - x and h(x) ![]() , then
, then ![]() is:
is:
h(x)/g(x) | |
-1/x | |
g(x)/h(x) | |
x/(1-x)2 |
Replace x by h(x) in (1), replacing x by g(x) in (2),
g(h(x))=1-h(x)=1-x/x-1=-1/x-1
h(g(x))=g(x)/g(x)-1=1-x/-x
⇒ g(h(x))/h(g(x))=x/(x-1)(1-x)=(x/x-1)/1-x=h(x)/g(x)
Question 29 |
-1 | |
-2 | |
-3 | |
-4 |

Question 30 |
0.99 | |
1.00 | |
2.00 | |
3.00 |
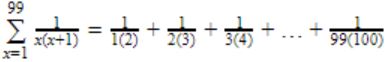
= 2-1/1(2)+3-2/2(3)+4-3/3(4)+…+100-99/99(100)
= 1/1-1/2+1/2-1/3+1/3…+1/98-1/99+1/99-1/100
= 1-1/100
= 99/100
= 0.99
Question 31 |
Let f(x) be a polynomial and g(x) = f'(x) be its derivative. If the degree of (f(x) + f(-x)) is 10, then the degree of (g(x) - g(-x)) is __________.
9 | |
10 | |
11 | |
12 |
It is given that f(x) + f(-x) degree is 10.
It means f(x) is a polynomial of degree 10.
Then obviously the degree of g(x) which is f’(x) will be 9.
Question 32 |
1 | |
Limit does not exist | |
53/12 | |
108/7 |
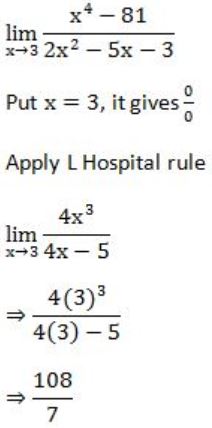
Question 33 |
4 | |
3 | |
2 | |
1 |