Interrupt
Question 1 |
The details of an interrupt cycle are shown in figure.
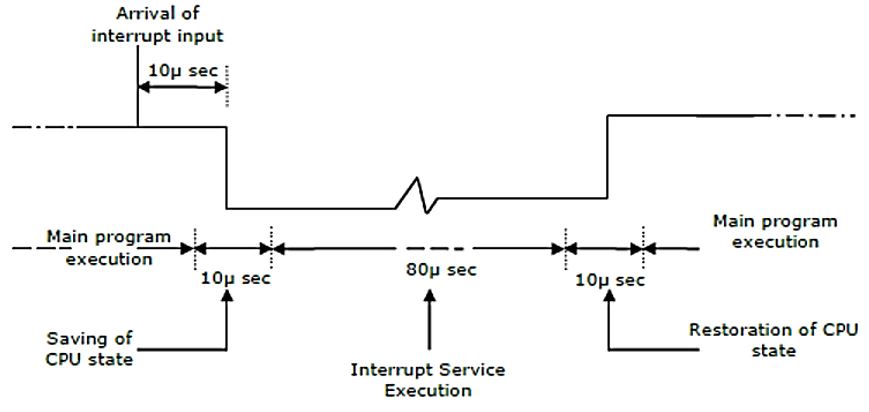
Given that an interrupt input arrives every 1 msec, what is the percentage of the total time that the CPU devotes for the main program execution.
90% |
Question 1 Explanation:
Time to service an interrupt
= saving state of CPU + ISR execution + restoring of CPU state
= (80 + 10 + 10) × 10-6
= 100 μs
For every 1ms an interrupt occurs which is served for 100 μs.
1ms = 1000μs
Thus, for every 1000μs, (1000 - 100) = 900 μs of main program and 100μs of interrupt overhead exists.
Thus, 900/1000 is usage of CPU to execute main program .
∴ % of CPU to execute main program is (900/1000) × 100 = 90%
= saving state of CPU + ISR execution + restoring of CPU state
= (80 + 10 + 10) × 10-6
= 100 μs
For every 1ms an interrupt occurs which is served for 100 μs.
1ms = 1000μs
Thus, for every 1000μs, (1000 - 100) = 900 μs of main program and 100μs of interrupt overhead exists.
Thus, 900/1000 is usage of CPU to execute main program .
∴ % of CPU to execute main program is (900/1000) × 100 = 90%
Question 2 |
In a vectored interrupt
the branch address is assigned to a fixed location in memory | |
the interrupt source supplies the branch information to the processor through an interrupt vector | |
the branch address is obtained from a register in the processor | |
none of the above |
Question 2 Explanation:
A vectored interrupt is a processing technique in which the interrupting device directs the processor to the appropriate interrupt service routine vector.
Question 3 |
For the daisy chain scheme of connecting I/O devices, which of the following statements is true?
It gives non-uniform priority to various devices. | |
It gives uniform priority to all devices | |
It is only useful for connecting slow devices to a processor device. | |
It requires a separate interrupt pin on the processor for each device. |
Question 3 Explanation:
Daisy chaining technique tells the processor in which order the interrupt should be handle by providing priority devices.
→ In this all devices connected serially.
→ High priority devices placed first, followed by low priority devices.
→ In this all devices connected serially.
→ High priority devices placed first, followed by low priority devices.
Question 4 |
When an interrupt occurs, an operating system
ignores the interrupt | |
always changes state of interrupted process after processing the interrupt | |
always resumes execution of interrupted process after processing the interrupt
| |
may change state of interrupted process to 'blocked’ and schedule another process
|
Question 4 Explanation:
Option A: Based on the priority.
Option B: Not always.
Option C: Not always. If some high priority interrupt comes during execution of current interrupt then it fails.
Option D: It is True always.
Option B: Not always.
Option C: Not always. If some high priority interrupt comes during execution of current interrupt then it fails.
Option D: It is True always.
There are 4 questions to complete.
