HCU PHD CS MAY 2015
Question 1 |
When the most significant byte of a word is at the smallest address, the architecture is called
Big Indian | |
Little Endian | |
Big Endian
| |
Little Indian
|
Question 1 Explanation:
If the hardware is built so that the highest ,most significant byte of a multi-byte scalar is stored first , at the lowest memory address then the hardware is said to be big endian
Question 2 |
Polymorphisms means
that data fields should be declared private | |
that a class can extend another class | |
that a class can contain another class | |
that a variable of supertype can refer to a subtype object |
Question 3 |
A computer system has a RAM of 4 GB and a cache of 512MB. Assuming that the least significant bit is b0 ,the cache location using direct mapping is given by
the bits b31. . .b4 | |
the bits b2. . .b0 | |
the bits b31.. .b29 | |
the bits b28. . .b0 |
Question 3 Explanation:
Since the size of cache is 512MB = 2^29 B
So to determine we need 29 bits from the left side of the address which is of 32 bits( Size of RAM is 4GB = 2^32 B ). So the cache location using direct mapping is given by the bits b28. . .b0
So to determine we need 29 bits from the left side of the address which is of 32 bits( Size of RAM is 4GB = 2^32 B ). So the cache location using direct mapping is given by the bits b28. . .b0
Question 4 |
Which of the following is TRUE about Vectors interrupts?
the interrupt service routine is determined by the interrupt-generating device | |
the interrupt service routine polls the devices to find the device that generated the interrupt | |
the interrupt is generated not by one device but by several devices simultaneously | |
None of the above |
Question 5 |
The maximum number of items in a B-tree of order m and height h is
mh -1 | |
mh-1 + I | |
mh+1 - 1 | |
mh +1 |
Question 5 Explanation:
The maximum number of items in a B-Tree of order m and height h is :
m^h+1 -1
m^h+1 -1
Question 6 |
Each B-tree node can have at-most p tree pointers, p-1 data pointers and p-1 search key field values. These must fit into a single disk block if each B-tree node is to correspond to a disk block. Suppose the search field is V =9 bytes long, the disk block size is B=512 bytes, record (data) pointer is Pr =7 bytes and a block pointer is P=6 bytes. What is the value of p?
22 | |
23 | |
24 | |
25 |
Question 6 Explanation:
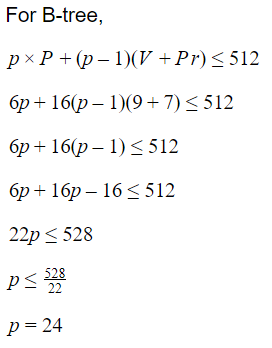
Question 7 |
What is the order p of a B+-tree given that the search key field is V=9 bytes long, the block size is B= 512 bytes, record pointer is Pr=7 bytes and a block pointer is P=6 bytes.
32 | |
33 | |
34 | |
24 |
Question 7 Explanation:
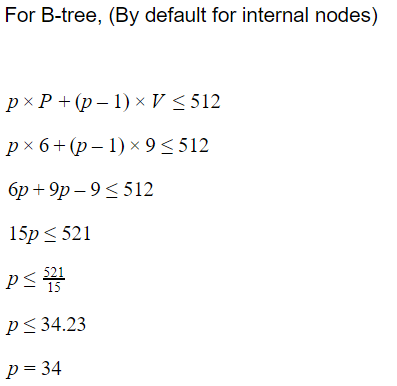
Question 8 |
Consider a schema R(A, B, C, D, E) with functional dependencies A → B, B→ C, BC → A , A→D , E→A, D→E. Which of the following is not a key?
A | |
E | |
B,C | |
D | |
None of the above |
Question 8 Explanation:

Question 9 |
The tuples in relation R(A,B) are {(1,2),(1,3), (3,4)) and the tuples in relation S(B,C) are (2,5), (4,6), (7,8)}. The number of tuples in the result of the following SQL query are:
Select * from R Natural Outer Join S;
2 | |
4 | |
6 | |
None of the above
|
Question 9 Explanation:
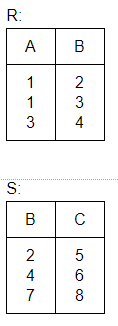

Question 10 |
A unit of storage that can store one or more records in a hash fiIe organization is denoted as
Buckets | |
Disk Pages | |
Blocks | |
Nodes |
Question 10 Explanation:
A unit of storage that can store one or more records in a hash file organization is denoted as buckets. Because all systems in the cluster share a common file structure via NFS, but not all disks are mounted on all other systems.
Question 11 |
Which of the following will undo all statements upto commit?
Transaction | |
Flashback | |
Rollback | |
Abort |
Question 11 Explanation:
Rollback will undo all the statements upto commit.
Question 12 |
If a system has a 32-bit processor, what are the number of page table entries if the page size is 16KB?
16K entries | |
256K entries | |
8K entries | |
64K entries |
Question 12 Explanation:
Page size is 16KB = 2^14B. So offset bit is 14 bit .
Hence no. of page table entries are 2^(32-14) = 2^18 = 256K entries.
Hence no. of page table entries are 2^(32-14) = 2^18 = 256K entries.
Question 13 |
Zombie process is a process
that lives forever in all situations | |
has terminated and is waiting for its parent to check its status | |
whose parent has died | |
None of the above |
Question 13 Explanation:
A zombie process or defunct process is a process that has completed execution (via the exit system call) but still has an entry in the process table: it is a process in the "Terminated state".
Question 14 |
Wireless LANs do not use CSMA/CD because
CSMA/CD is not efficient
| |
CSMA/CD requires duplex operation | |
Wireless networks have a high BER | |
Wireless networks are not secure |
Question 15 |
If a host has an IP address 201.40.67.31/25, what are the network ID and broadcast address of the network to which this host belongs:
201.40.67.31, 201.40.67.63 | |
201.40.67.0, 201.40.67.255 | |
201.40.67.0, 201.40.67.63 | |
201.40.67.31, 201.40.67.255
| |
None of the above |
Question 15 Explanation:
Correct answer is 201.40.67.0, 201.40.67.127
Question 16 |
If the MF bit-0, Fragment Offset : 1480 and Total Length : 520 in an IP datagram, then the length of datagram is
520 | |
1490 | |
1500 | |
2000 |
Question 16 Explanation:
It is clearly given in the question that total length = 520.Hence length of datagram is 520
Question 17 |
When the TTL of a datagram sent from a host H1 is 1, the data can reach a host which is
within the same network | |
any host in the world
| |
within the same network and the network reached through one router | |
no host at all |
Question 17 Explanation:
Option A is false because if there is one or more router between the two hosts then TTl will become at the first router itself and it will discard it.
Option B is false.Reason is same as in option A
Option C is false
Option D seems to be more appropriate answer.
Option B is false.Reason is same as in option A
Option C is false
Option D seems to be more appropriate answer.
Question 18 |
Five segments of data of sizes 100B, 400B, 200B, 300B and 50B are sent using TCP and PSH bit is set on each of the segments. There are no retransmission timeouts. The acks received are 101, 101, 701, 701 and 1051. In which order are the segments received
100B, 200B, 400B, 300B, 50B | |
100B, 400B, 200B, 50B, 300B | |
100B, 400B, 200B, 300B, 50B | |
100B, 200B, 400B, 50B, 300B |
There are 18 questions to complete.
