Software-testing
Question 1 |
The following is the comment written for a C function
/* This function computes the roots of a quadratic equation a.x^2 + b.x + c = . The function stores two real roots in *root1 and *root2 and returns the status of validity of roots. It handles four different kinds of cases. (i) When coefficient a is zero irrespective of discriminant (ii) When discreminant is positive (iii) When discriminant is zero (iv) When discriminant is negative. Only in case (ii) and (iii) the stored roots are valid. Otherwise 0 is stored in roots. The function returns 0 when the roots are valid and -1 otherwise. The function also ensures root1 >= root2 int get_QuadRoots( float a, float b, float c, float *root1, float *root2); */A software test engineer is assigned the job of doing black box testing. He comes up with the following test cases, many of which are redundant.
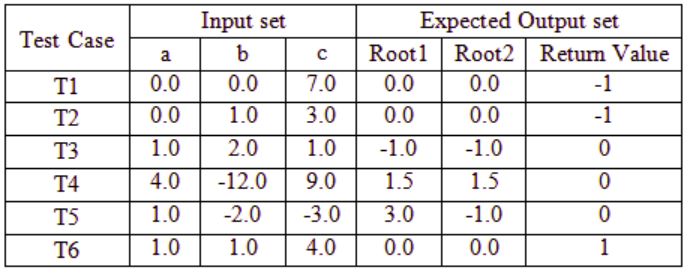
Which one of the following option provide the set of non-redundant tests using equivalence class partitioning approach from input perspective for black box testing?
T1, T2, T3, T6 | |
T1, T3, T4, T5 | |
T2, T4, T5, T6 | |
T2, T3, T4, T5 |
Question 1 Explanation:
Note: Out of syllabus.
T1 and T2 checking same condition a = 0 hence, any one of T1 and T2 is redundant.
T3, T4: in both case discriminant (D) = b2 – 4ac = 0. Hence any one of it is
T5 : D > 0
T6 : D < 0
T1 and T2 checking same condition a = 0 hence, any one of T1 and T2 is redundant.
T3, T4: in both case discriminant (D) = b2 – 4ac = 0. Hence any one of it is
T5 : D > 0
T6 : D < 0
Question 2 |
Which of the following is/are behavioral testing technique(s)?
(A) Equivalence Partitioning
(B) Graph-Based Testing Method
(C) Boundary Value Analysis
(D) Data flow Testing
(E) Loop Testing
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(B) and (D) only | |
(A), (B) and (C) only | |
(D) and (E) only | |
(A), (C) and (E) only |
Question 2 Explanation:
Black-box testing, also called behavioral testing, focuses on the functional requirements of the software. That is, black-box testing enables the software engineer to derive sets of input conditions that will fully exercise all functional requirements for a program. The following are behavioral testing techniques
(1) Graph-Based Testing Methods
(2) Equivalence Partitioning
(3) Boundary Value Analysis
(4) Comparison testing
(5) Orthogonal Array Testing
(1) Graph-Based Testing Methods
(2) Equivalence Partitioning
(3) Boundary Value Analysis
(4) Comparison testing
(5) Orthogonal Array Testing
Question 3 |
Which of the following is not a part of the Test Implementation and Execution Phase?
Creating test suites from the test cases | |
Executing test cases either manually or by using test execution tools | |
Comparing actual results | |
Designing the tests |
Question 3 Explanation:
TRUE: Creating test suites from the test cases
TRUE: Executing test cases either manually or by using test execution tools
TRUE: Comparing actual results
FALSE: Designing the tests
TRUE: Executing test cases either manually or by using test execution tools
TRUE: Comparing actual results
FALSE: Designing the tests
Question 4 |
Black Box Software Testing method focuses on the:
Boundary condition of the software | |
Control structure of the software | |
Testing of User Interface only | |
Cyclomatic Complexity |
Question 4 Explanation:
Black Box Software testing method focuses on the functional requirement of the software.
Note: The question is ambiguous. We marked the answer according to official key.
Question 5 |
Regression testing is primarily related to
Functional testing | |
Development testing | |
Data flow testing | |
Maintenance testing |
Question 5 Explanation:
→ Regression testing is re-running functional and non-functional tests to ensure that previously developed and tested software still performs after a change. If not, that would be called a regression.
→ Changes that may require regression testing include bug fixes, software enhancements, configuration changes, and even substitution of electronic components.
→ As regression test suites tend to grow with each found defect, test automation is frequently involved.
→ Regression testing is primarily related to Maintenance testing.
→ Changes that may require regression testing include bug fixes, software enhancements, configuration changes, and even substitution of electronic components.
→ As regression test suites tend to grow with each found defect, test automation is frequently involved.
→ Regression testing is primarily related to Maintenance testing.
Question 6 |
What is the availability of the software with following reliability figures
Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) is 20 days
Mean Time To Repair (MTTR) is 20 hours
Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) is 20 days
Mean Time To Repair (MTTR) is 20 hours
90%
| |
96%
| |
24%
| |
50%
|
Question 6 Explanation:
Mean time between failures is not the average time something works then fail.
It’s the average time between failures Mean time between failure(MTBF)s= total uptime / number of breakdowns Mean time to repair is the average time taken to repair something. Mean time to repair(MTTR)= total time down/number of breakdowns
Availability = Total uptime/(total uptime+total downtime)
= MTBF/(MTBF+MTTR)*100
= 20*24/(20*24 + 20) * 100
= 96 %
It’s the average time between failures Mean time between failure(MTBF)s= total uptime / number of breakdowns Mean time to repair is the average time taken to repair something. Mean time to repair(MTTR)= total time down/number of breakdowns
Availability = Total uptime/(total uptime+total downtime)
= MTBF/(MTBF+MTTR)*100
= 20*24/(20*24 + 20) * 100
= 96 %
Question 7 |
Which of the following techniques are used for selection of test cases during structural testing?
Data flow based testing | |
Equivalence class partitioning | |
Cause-effect graphing | |
Boundary value analysis |
Question 8 |
Regression testing is primarily related to
function testing | |
data flow testing | |
development testing | |
maintenance testing
|
Question 9 |
Acceptance testing is done by
developers | |
customers | |
testers
| |
None of the given options |
Question 10 |
The approach to software testing is to design test cases to
break the software | |
understand the software
| |
analyze the design of sub processes in the software
| |
analyze the output of the software
|
Question 11 |
Beta testing is carried out by
users
| |
developers
| |
managers | |
None of the given options
|
Question 12 |
Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R
Assertion A: Validity checks real need of system users
Reason R: Completeness checks system user defined requirements
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below
Assertion A: Validity checks real need of system users
Reason R: Completeness checks system user defined requirements
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below
Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
| |
Both A and R are correct and R is the NOT correct explanation of A
| |
A is true but R is false
| |
A is false but R is true |
Question 12 Explanation:
Both A and R are correct, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Assertion A: This statement is correct. Validity checks are essential to ensure that the system meets the real needs and requirements of the system users.
Reason R: Completeness checks are indeed about verifying that the system user-defined requirements are fully captured, but this doesn't directly explain the concept of validity checks.
Both A and R are independently valid statements, but Reason R doesn't directly provide an explanation for Assertion A. So, the correct answer is:
Both A and R are correct, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Question 13 |
Match List I with List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
| List I | List II | ||
| A | Scenario testing | I | To verify the I/O behaviour of text object |
| B | Regression testing | II | user acceptance methodology |
| C | Component testing | III | No new bugs after changes in the program |
| D | Beta testing | IV | The documentation of a use case |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
A-IV B-III C-II D-I
| |
A-II B-I C-III D-IV
| |
A-IV B-III C-I D-II
| |
A-III B-I C-IV D-II |
Question 14 |
For a function of two variables, boundary value analysis yields,
4n+3 test cases | |
4n+1 test cases | |
n+4 test cases | |
2n+4 test cases |
Question 15 |
Alpha and Beta testing are forms of
White- Box Testing | |
Black- Box Testing | |
Acceptance Testing | |
System Testing |
Question 15 Explanation:
Black-box testing is a method of software testing that examines the functionality of an application without peering into its internal structures or workings.
Alpha testing uses both black and white box testing while Beta testing uses only black box testing.
Alpha testing is performed by testers who are usually internal employees of the organization
Alpha testing uses both black and white box testing while Beta testing uses only black box testing.
Alpha testing is performed by testers who are usually internal employees of the organization
Question 16 |
Fault base testing technique is
Unit testing | |
Beta testing | |
Stress testing | |
Mutation testing |
Question 16 Explanation:
Mutation testing is a software testing type that is based on changes or mutations.
Changes are introduced into the source code to check whether the defined test cases can detect errors in the code.
Changes are introduced into the source code to check whether the defined test cases can detect errors in the code.
Question 17 |
For a program of k variables, boundary value analysis yields ______ test cases.
4k – 1 | |
4k | |
4k + 1 | |
2 k – 1 |
Question 17 Explanation:
For a program of k variables, boundary value analysis yields 4k + 1 test cases.
There are 17 questions to complete.
