SQL
October 4, 2023DFD
October 4, 2023Software-process-models
|
Question 5
|
Consider the following models:
M1: Mamdani model
M2: Takagi-Sugeno-Kang model
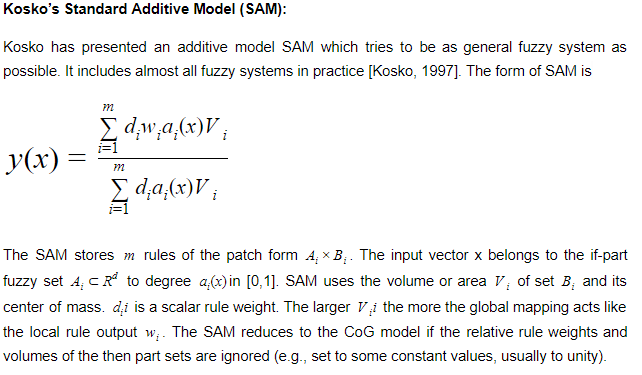
M3: Kosko’s additive model(SAM)
Which of the following option contains example of additive rule model?
|
Only M1 and M2
|
|
|
Only M2 and M3
|
|
|
Only M1 and M3
|
|
|
M1, M2 and M3
|
Question 5 Explanation:
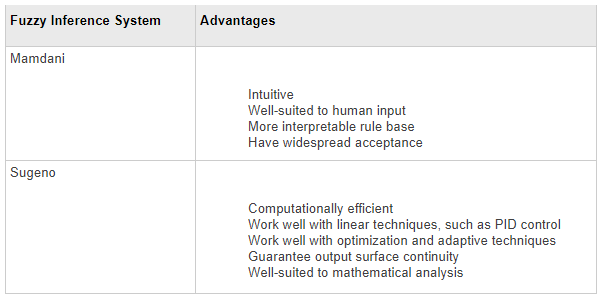
Mamdani Fuzzy Inference Systems
Mamdani fuzzy inference was first introduced as a method to create a control system by synthesizing a set of linguistic control rules obtained from experienced human operators [1]. In a Mamdani system, the output of each rule is a fuzzy set.
Since Mamdani systems have more intuitive and easier to understand rule bases, they are well-suited to expert system applications where the rules are created from human expert knowledge, such as medical diagnostics.
Sugeno Fuzzy Inference Systems
Sugeno fuzzy inference, also referred to as Takagi-Sugeno-Kang fuzzy inference, uses singleton output membership functions that are either constant or a linear function of the input values. The defuzzification process for a Sugeno system is more computationally efficient compared to that of a Mamdani system, since it uses a weighted average or weighted sum of a few data points rather than compute a centroid of a two-dimensional area.
You can convert a Mamdani system into a Sugeno system using the convert To Sugeno function. The resulting Sugeno system has constant output membership functions that correspond to the centroids of the Mamdani output membership functions.
Mamdani fuzzy inference was first introduced as a method to create a control system by synthesizing a set of linguistic control rules obtained from experienced human operators [1]. In a Mamdani system, the output of each rule is a fuzzy set.
Since Mamdani systems have more intuitive and easier to understand rule bases, they are well-suited to expert system applications where the rules are created from human expert knowledge, such as medical diagnostics.
Sugeno Fuzzy Inference Systems
Sugeno fuzzy inference, also referred to as Takagi-Sugeno-Kang fuzzy inference, uses singleton output membership functions that are either constant or a linear function of the input values. The defuzzification process for a Sugeno system is more computationally efficient compared to that of a Mamdani system, since it uses a weighted average or weighted sum of a few data points rather than compute a centroid of a two-dimensional area.
You can convert a Mamdani system into a Sugeno system using the convert To Sugeno function. The resulting Sugeno system has constant output membership functions that correspond to the centroids of the Mamdani output membership functions.
Correct Answer: B
Question 5 Explanation:
Mamdani Fuzzy Inference Systems
Mamdani fuzzy inference was first introduced as a method to create a control system by synthesizing a set of linguistic control rules obtained from experienced human operators [1]. In a Mamdani system, the output of each rule is a fuzzy set.
Since Mamdani systems have more intuitive and easier to understand rule bases, they are well-suited to expert system applications where the rules are created from human expert knowledge, such as medical diagnostics.
Sugeno Fuzzy Inference Systems
Sugeno fuzzy inference, also referred to as Takagi-Sugeno-Kang fuzzy inference, uses singleton output membership functions that are either constant or a linear function of the input values. The defuzzification process for a Sugeno system is more computationally efficient compared to that of a Mamdani system, since it uses a weighted average or weighted sum of a few data points rather than compute a centroid of a two-dimensional area.
You can convert a Mamdani system into a Sugeno system using the convert To Sugeno function. The resulting Sugeno system has constant output membership functions that correspond to the centroids of the Mamdani output membership functions.
Mamdani fuzzy inference was first introduced as a method to create a control system by synthesizing a set of linguistic control rules obtained from experienced human operators [1]. In a Mamdani system, the output of each rule is a fuzzy set.
Since Mamdani systems have more intuitive and easier to understand rule bases, they are well-suited to expert system applications where the rules are created from human expert knowledge, such as medical diagnostics.
Sugeno Fuzzy Inference Systems
Sugeno fuzzy inference, also referred to as Takagi-Sugeno-Kang fuzzy inference, uses singleton output membership functions that are either constant or a linear function of the input values. The defuzzification process for a Sugeno system is more computationally efficient compared to that of a Mamdani system, since it uses a weighted average or weighted sum of a few data points rather than compute a centroid of a two-dimensional area.
You can convert a Mamdani system into a Sugeno system using the convert To Sugeno function. The resulting Sugeno system has constant output membership functions that correspond to the centroids of the Mamdani output membership functions.


