GATE 1992
Question 1 |
The Boolean function in sum of products form where K-map is given below (figure) is:___________
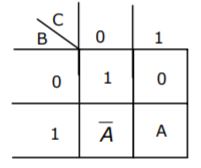
ABC + B'C' + A'C' |
⇒ ABC + B'C' + A'C'
Question 2 |
Consider a 3-bit error detection and 1-bit error correction hamming code for 4-bit date. The extra parity bits required would be ________ and the 3-bit error detection is possible because the code has a minimum distance of ________
Fill in the blanks |
Question 3 |
Many microprocessors have a specified lower limit on clock frequency (apart from the maximum clock frequency limit) because ______
clock frequency can't go below this value. |
Question 4 |
Many of the advanced microprocessors prefetch instructions and store it in an instruction buffer to speed up processing. This speed up is achieved because _________
prefetching the instructions to be executed can save considerable amount of waiting time. |
Question 5 |
A simple and reliable data transfer can be accomplished by using the ‘handshake protocol’. It accomplishes reliable data transfer because for every data item sent by the transmitter __________.
in this case receiver has to respond that receiver can be able to receive the data item. |
Question 6 |
In an 11-bit computer instruction format, the size of address field is 4-bits. The computer uses expanding OP code technique and has 5 two-address instructions and 32 two-address instructions and the number of zero-address instructions it can support is _________
256 |
The possibility of no. of encoding taken by two-address instructions = 5×24×24 = 1280
By one-address instructions = 32×24 = 512
So, the possibility of zero-address instructions = 2048 - (1280 + 512) = 256
Question 7 |
Macro expansion is done in pass one instead of pass two in a pass macro assembler because _________
all macro definitions are processed during the first pass only due to all macro expansions done during pass 1 only not in pass 2. |
Question 8 |
The purpose of instruction location counter in an assembler is _______
used to assign storage address to the program's statements. |
Question 9 |
Complexity of Kruskal’s algorithm for finding the minimum spanning tree of an undirected graph containing n vertices and m edges if the edges are sorted is __________
O(m log n) |
Question 10 |
Maximum number of edges in a planar graph with n vertices is ________
3n - 6 |
⇒ (3n - 2) = 3n - 6
Question 11 |
The operation which is commutative but not associative is:
AND | |
OR | |
EX-OR | |
NAND |
Question 12 |
All digital circuits can be realized using only
Ex-OR gates | |
Multiplexers | |
Half adders | |
OR gates | |
Both B and C |
