Database-Management-System
Question 1 |
A | 698 |
Total no. of records = 150000
Block size = 4096 bytes
Key size = 12 bytes
Record pointer size = 7 bytes

Question 2 |
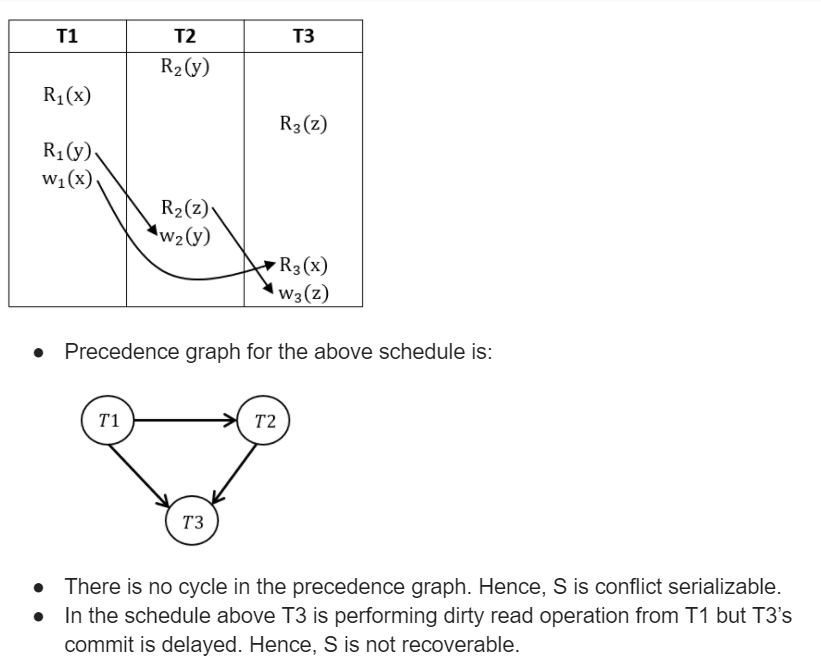
R2(Y), R1(X), R3(Z), R1(Y), W1(X), R2(Z), W2(Y), R3(X), W3(Z)
Consider the statements P and Q below:
P: S is conflict-serializable.
Q: If T3commits before T1finishes, then S is recoverable.
Which one of the following choices is correct?
A | P is true and Q is false. |
B | Both P and Q are false. |
C | Both P and Q are true. |
D | P is false and Q is true. |
Question 3 |
S1: A relation scheme can have at most one foreign key.
S2: A foreign key in a relation schema R cannot be used to refer to tuples of R.
Which one of the following choices is correct?
A | S1 is false and S2 is true. |
B | Both S1 and S2 are false. |
C | Both S1 and S2 are true.
|
D | S1 is true and S2 is false. |
- A database table may have more than one foreign key, and each foreign key can have a different parent table. Hence, the statement I is incorrect.
- A foreign key is a set of attributes in a table that refers to the primary key of another table or to the primary key of the same table (self-referential table). Hence, the statement II is also incorrect.
Question 4 |
emp(empId, name, gender, salary, deptId)
Consider the following SQL query:
select deptId, count (*)
from emp
where gender = “female” and salary > (select avg(salary) from emp)
group by deptId;
The above query gives, for each department in the company, the number of female employees whose salary is greater than the average salary of
A | employees in the department |
B | female employees in the company |
C | employees in the company |
D | female employees in the department |
The given SQL query is:
Select deptId, count(*)
from emp
where gender = “female” and
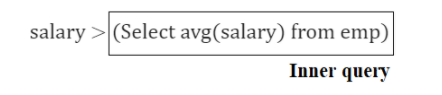
group by deptId
- The inner query will return the average salary of the emp table.
- Hence, the given query will return the deptId wise count of female employees whose salary is greater than the average salary of the emp table.
Question 5 |
P⟶ QR
RS⟶ T
Which of the following functional dependencies can be inferred from the above functional dependencies?
A | PS ⟶ Q |
B | PS ⟶ T |
C | R ⟶ T |
D | P ⟶ R |

Question 6 |
(a) Consider the relation scheme R(A, B, C) with the following functional dependencies:
A, B → C, C → A
Show that the scheme R is the Third Normal Form (3NF) but not in Boyce-Code Normal Form (BCNF).
(b) Determine the minimal keys of relation R.
A | Theory Explanation. |
Question 7 |
Consider the relation scheme.
AUTHOR (ANAME, INSTITUTION, ACITY, AGE) PUBLISHER (PNAME, PCITY) BOOK (TITLE, ANAME, PNAME)
Express the following queries using (one or more of )SELECT, PROJECT, JOIN and DIVIDE operations.
(a) Get the names of all publishers.
(b) Get values of all attributes of all authors who have published a book for the
publisher with PNAME = ‘TECHNICAL PUBLISHERS’.
(c) Get the names of all authors who have published a book for any publisher located in Madras.
A | Theory Explanation. |
Question 8 |
Consider a relational database containing the following schemas.
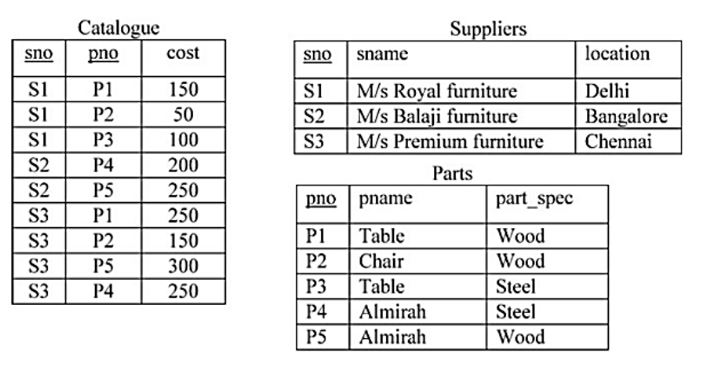
The primary key of each table is indicated by underlying the constituent fields.
SELECT s.sno, s.sname
FROM Suppliers s, Catalogue c
WHERE s.sno = c.sno AND
Cost > (SELECT AVG (cost)
FROM Catalogue
WHERE pno = ‘P4’
GROUP BY pno);
The number of rows returned by the above SQL query is
A | 0 |
B | 5 |
C | 4 |
D | 2 |
AVG(COST)
------------
225
The outer query “select s.sno, s.sname from suppliers s, catalogue c where s.sno=c.sno” returns:
SNO SNAME
----------------------------------------
S1 M/s Royal furniture
S1 M/s Royal furniture
S1 M/s Royal furniture
S2 M/s Balaji furniture
S2 M/s Balaji furniture
S3 M/s Premium furniture
S3 M/s Premium furniture
S3 M/s Premium furniture
S3 M/s Premium furniture
So, the final result of the query is:
SN SNAME
----------------------------------------
S2 M/s Balaji furniture
S3 M/s Premium furniture
S3 M/s Premium furniture
S3 M/s Premium furniture
Therefore, 4 rows will be returned by the query.
Question 9 |
Which one of the following is used to represent the supporting many-one relationships of a weak entity set in an entity-relationship diagram?
A | Ovals that contain underlined identifiers
|
B | Rectangles with double/bold border |
C | Diamonds with double/bold border
|
D | Ovals with double/bold border
|

Question 10 |
Consider a schedule of transactions T1 and T2:
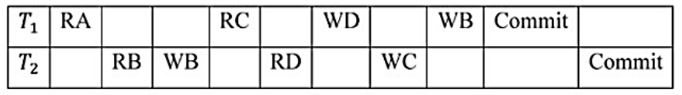
Here, RX stands for “Read(X)” and WX stands for “Write(X)”. Which one of the following schedules is conflict equivalent to the above schedule?
A |  |
B |  |
C | 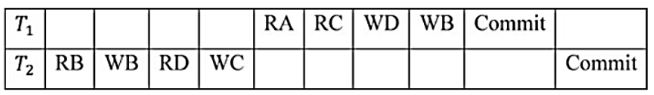 |
D |  |
• First, let’s list the conflict operations of each of the schedule given in the options and compare with the conflict operations of schedule which is given in the question.
Given schedule:
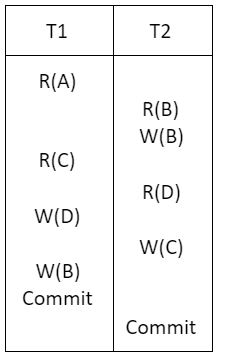
Conflict operations:
R2(B) → W1(B)
W2(B) → W1(B)
R1(C) → W2(C)
R2(D) → W1(D)
Option(1):

Conflict operations:
R1(C) → W2(C)
W1(D) → R2(D)
W1(B) → R2(B)
W1(B) → W2(B)
Option(2):
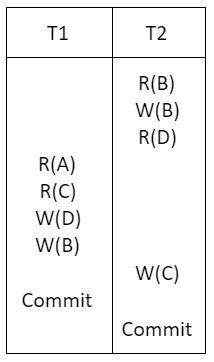
Conflict operations:
R2(B) → W1(B)
W2(B) → W1(B)
R2(D) → W1(D)
R1(C) → W2(C)
Option(3):
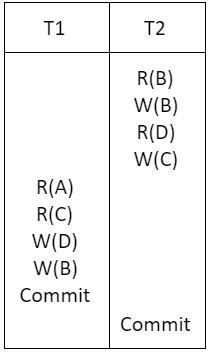
Conflict operations:
R2(B) → W1(B)
W2(B) → W1(B)
R2(D) → W1(D)
W2(C) → R1(C)
Option(4):

Conflict operations:
R1(C) → W2(C)
W1(D) → R2(D)
R2(B) → W1(B)
W2(B) → W1(B)
The conflict operations in the option (2) and given schedule are appearing in the same sequence order, so option (2) is the answer.
Question 11 |
Consider a relational table R that is in 3NF, but not in BCNF. Which one of the following statements is TRUE?
A | A cell in R holds a set instead of an atomic value. |
B | R has a nontrivial functional dependency X→A, where X is not a superkey and A is a non-prime attribute and X is not a proper subset of any key.
|
C | R has a nontrivial functional dependency X→A, where X is not a superkey and A is a non-prime attribute and X is a proper subset of some key. |
D | R has a nontrivial functional dependency X→A, where X is not a superkey and A is a prime attribute. |
FDs:
AB → C
BC → A
(BD)+ = BD ✖
(ABD)+ = ABDC ✔
(CBD)+ = CBDA ✔
Candidate keys = {ABD, CBD}
• The relation R is in 3NF, as there are no transitive dependencies.
• The relation R is not in BCNF, because the left side of both the FD’s are not Super keys.
• In R, BC → A is a non-trivial FD and in which BC is not a Super key and A is a prime attribute.
Question 12 |
Consider a database implemented using B+ tree for file indexing and installed on a disk drive with block size of 4 KB. The size of search key is 12 bytes and the size of tree/disk pointer is 8 bytes. Assume that the database has one million records. Also assume that no node of the B+ tree and no records are present initially in main memory. Consider that each record fits into one disk block. The minimum number of disk accesses required to retrieve any record in the database is ______.
A | 4 |
(1) Database BF = 1
No. of block = 106 } ➝ 1 block access from database
(2) ⎡106/204⎤ = 491
(3) ⎡491/204⎤ = 3
(4) ⎡3/204⎤ = 1
So, 1+3 = 4 disk accesses are required to retrieve any record in the database.
Question 13 |
A library relational database system uses the following schema
USERS (User#, UserName, HomeTown) BOOKS (Book#, BookTitle, AuthorName) ISSUED (Book#, User#, Date)
Explain in one English sentence, what each of the following relational algebra queries is designed to determine
(a) σ User #=6 (11 User #, Book Title ((USERS ISSUED) BOOKS)) (b) σ Author Name (BOOKS (σ Home Town) = Delhi (USERS ISSUED)))
A | Theory Explanation. |
Question 14 |
For a database relation R(a,b,c,d), where the domains a, b, c, d include only atomic values, only the following functional dependencies and those that can be inferred from them hold:
a → c b → d
This relation is
A | in first normal form but not in second normal form |
B | in second normal form but not in third normal form |
C | in third normal form |
D | None of the above |
Since all a, b, c, d are atomic. So the relation is in 1NF.
Checking the FD's
a → c
b → d
We can see that there is partial dependencies. So it is not 2NF.
So answer is option (A).
Question 15 |
Let R(a,b,c) and S(d,e,f) be two relations in which d is the foreign key of S that refers to the primary key of R. Consider the following four operations R and S
(a) Insert into R (b) Insert into S (c) Delete from R (d) Delete from S
Which of the following can cause violation of the referential integrity constraint above?
A | None of (a), (b), (c) or (d) can cause its violation |
B | All of (a), (b), (c) and (d) can cause its violation |
C | Both (a) and (d) can cause its violation |
D | Both (b) and (c) can cause its violation |

Here 'd' is the foreign key of S and let 'a' is the primary key of R.
(A) Insertion into R: will cause no violation.
(B) Insertion into S: may cause violation because there may not be entry of the tuple in relation R. Example entry of 〈S4, __, __〉 is not allowed.
(C) Delete from R: may cause violation. For example, deletion of tuple 〈S2, __, __〉 will cause violation as there is entry of S2 in the foreign key table.
(D) Delete from S: will cause no violation as it does not result inconsistency.
Question 16 |
In an Entity-Relationship (ER) model, suppose R is a many-to-one relationship from entity set E1 to entity set E2. Assume that E1 and E2 participate totally in R and that the cardinality of E1 is greater than the cardinality of E2.
Which one of the following is true about R?
A | Every entity in E1 is associated with exactly one entity in E2. |
B | Some entity in E1 is associated with more than one entity in E2. |
C | Every entity in E2 is associated with exactly one entity in E1. |
D | Every entity in E2 is associated with at most one entity in E1.
|

The M : 1 relationship holds between two entities E1 and E2, in which each tuple from E2 is in relation with many tuples of E1. One tuple from E1 is in relation with only one tuple of E2. It is given that participation from both the sides is total and the cardinality of E1 is greater than E2.

Therefore, every entity E1 is associated with exactly one entity in E2.
Question 17 |
Consider the following two tables and four queries in SQL.
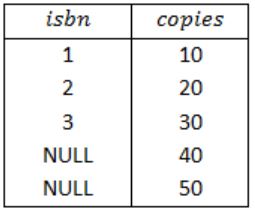
Book (isbn, bname), Stock (isbn, copies)Query 1: SELECT B.isbn, S.copies
FROM Book B INNER JOIN Stock S
ON B.isbn = S.isbn;
Query 2: SELECT B.isbn, S.copies
FROM Book B LEFT OUTER JOIN Stock S
ON B.isbn = S.isbn;
Query 3: SELECT B.isbn, S.copies
FROM Book B RIGHT OUTER JOIN Stock S
ON B.isbn = S.isbn;
Query 4: SELECT B.isbn, S.copies
FROM Book B FULL OUTER JOIN Stock S
ON B.isbn = S.isbn;
Which one of the queries above is certain to have an output that is a superset of the outputs of the other three queries?
A | Query 1 |
B | Query 2 |
C | Query 3 |
D | Query 4 |
Book (isbn, bname)
Stock (isbn, copies)
isbn is a primary key of Book and isbn is a foreign key of stock referring to Book table.
For example:

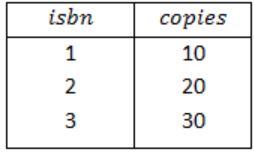
Query 1:
INNER JOIN keyword selects records that have matching values in both tables (Book and Stock).
So, the result of Query 1 is,
Query 2:
The LEFT OUTER JOIN keyword returns all records from the left table (Book) and the matched records from the right table (Stock).
The result is NULL from the right side, if there is no match.

So, the result of Query 2 is,

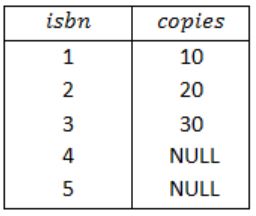
Query 3:
The RIGHT OUTER JOIN keyword returns all records from the right table (Stock), and the matched records from the left table(BOOK).
The result is NULL from the left side, when there is no match.
Query 4:
The FULL OUTER JOIN keyword return all records when there is a match in either left (Book) or right (Stock) table records.
So, the result of Query 4 is,
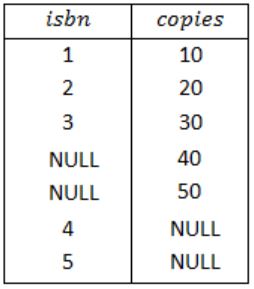
Therefore, from the result of above four queries, a superset of the outputs of the Query 1, Query 2 and Query 3 is Query 4.
Note:
If we take isbn as a primary key in both the tables Book and Stock and foreign key, in one of the tables then also will get option (D) as the answer.
Question 18 |
Consider the following four relational schemas. For each schema, all non-trivial functional dependencies are listed. The underlined attributes are the respective primary keys.
Schema I: Registration(rollno, courses)
Field ‘courses’ is a set-valued attribute containing the set of
courses a student has registered for.
Non-trivial functional dependency
rollno → courses
Schema II: Registration (rollno, coursid, email)
Non-trivial functional dependencies:
rollno, courseid → email
email → rollno
Schema III: Registration (rollno, courseid, marks, grade)
Non-trivial functional dependencies:
rollno, courseid, → marks, grade
marks → grade
Schema IV: Registration (rollno, courseid, credit)
Non-trivial functional dependencies:
rollno, courseid → credit
courseid → credit
Which one of the relational schemas above is in 3NF but not in BCNF?
A | Schema I |
B | Schema II |
C | Schema III |
D | Schema IV |
Registration (rollno, courses) rollno → courses
For the given schema Registration ‘rollno’ is a primary key.
Left-side of the functional dependency is a superkey so, Registration is in BCNF.
Schema II:
Registrstion (rollno, courseid, email)
rollno, courseid → email
email → rollno
From the given schema the candidate key is (rollno + courseid).
There is no part of the key in the left hand of the FD’s so, it is in 2NF.
In the FD email→rollno, email is non-prime attribute but rollno is a prime attribute.
So, it is not a transitive dependency.
No transitive dependencies so, the schema is in 3NF.
But in the second FD email→rollno, email is not a superkey.
So, it is violating BCNF.
Hence, the schema Registration is in 3NF but not in BCNF.
Schema III:
Registration (rollno, courseid, marks, grade)
rollno, courseid → marks, grade
marks → grade
For the schema the candidate key is (rollno + courseid).
There are no part of the keys are determining non-prime attributes.
So, the schema is in 2NF.
In the FD marks → grade, both the attributes marks and grade are non-prime.
So, it is a transitive dependency.
The FD is violating 3NF.
The schema Registration is in 2NF but not in 3NF.
Schema IV:
Registration (rollno, courseid, credit)
rollno, courseid → credit
courseid → credit
The candidate key is (rollno + courseid).
In the FD, courseid → credit, courseid is part of the key (prime attribute) and credit is non-prime.
So, it is a partial dependency.
The schema is violating 2NF.
Question 19 |
Q: r⋈(σ<B<5 (s))
Let LOJ denote the natural left outer-join operation. Assume that r and s contain no null values.
Which one of the following is NOT equivalent to Q?
A | σB<5 (r ⨝ s) |
B | σB<5 (r LOJ s)
|
C | r LOJ (σB<5(s))
|
D | σB<5(r) LOJ s |
Consider the following tables without NULL values.

Q: r⨝(σB<5(S))
The result of σB<5(S) is

The result of σB<5(S) is

Option (A):
The result of r⨝S is

The result of σB<5(r⨝S) is

Option (B):
The result of r LOJ S is

The result of σB<5(r LOJ S) is

Option (C):
The result of σB<5(S) is

Now, the result of r LOJ(σB<5(S))

Option (D):
The result of σB<5(r) is

Now, the result of σB<5(r) LOJ S is

Therefore, from the output of above four options, the results of options, the results of options (A), (B) and (D) are equivalent to Q.
Question 20 |
Given two union compatible relations R1(A,B) and R2(C,D), what is the result of the operation R1A = CAB = DR2?
A | R1 ∪ R2 |
B | R1 × R2 |
C | R1 - R2 |
D | R1 ∩ R2 |
Question 21 |
Which normal form is considered adequate for normal relational database design?
A | 2 NF |
B | 5 NF |
C | 4 NF |
D | 3 NF |
Question 22 |
There are 5 records in a database.

There is an index file associated with this and it contain the values 1, 3, 2, 5 and 4. Which one of the fields is the index built form?
A | Age |
B | Name |
C | Occupation |
D | Category |
Question 23 |
Which of the following query transformations (i.e. replacing the l.h.s. expression by the r.h.s. expression) is incorrect? R1 and R2 are relations, C1, C2 are selection conditions and A1, A2 are attributes of R1?
A | σC1(σC1(R1)) → σC2(σC2(R1)) |
B | σC1(σA1(R1)) → σA1(σC1(R1)) |
C | σC1(R1 ∪ R2) → σC1(R1) ∪ σC1 |
D | πA1(σC1(R1)) → σC1(σA1(R1)) |
Question 24 |
(a) Suppose we have a database consisting of the following three relations.
FREQUENTS(student, parlor) giving the parlors each student visits.
SERVES(parlor, ice-cream) indicating what kind of ice-creams each parlor serves.
LIKES(student, ice-cream) indicating what ice-creams each parlor serves.
(Assuming that each student likes at least one ice-cream and frequents at least one parlor)
Express the following in SQL:
Print the students that frequent at least one parlor that serves some ice-cream that they like.
(b) In a computer system where the 'best-fit' algorithm is used for allocating 'jobs' to 'memory partitions', the following situation was encountered:

When will the 20K job complete? Note - This question was subjective type.
A | Theory Explanation. |
Question 25 |
(a) Four jobs are waiting to be run. Their expected run times are 6, 3, 5 and x. In what order should they be run to minimize the average response time?
(b) Write a concurrent program using par begin - par end to represent the precedence graph shown below.

A | Theory Explanation. |
Question 26 |
Consider the following database relations containing the attributes
Book_id Subject_Category_of_book Name_of_Author Nationality_of_Author with Book_id as the Primary Key.
(a) What is the highest normal form satisfied by this relation?
(b) Suppose the attributes Book_title and Author_address are added to the relation, and the primary key is changed to (Name_of_Author, Book_Title), what will be the highest normal form satisfied by the relation?
A | Theory Explanation. |
Question 27 |
Consider the following relational database schemes:
COURSES(Cno, name) PRE-REQ(Cno, pre_Cno) COMPLETED(student_no, Cno)
COURSES give the number and the name of all the available courses.
PRE-REQ gives the information about which course are pre-requisites for a given course.
COMPLETED indicates what courses have been completed by students.
Express the following using relational algebra:
List all the courses for which a student with student_no 2310 has completed all the pre-requisites.
A | Theory Explanation. |
Question 28 |
Consider the join of a relation R with a relation S. If R has m tuples and S has n tuples then the maximum and minimum sizes of the join respectively are
A | m + n and 0 |
B | mn and 0 |
C | m + n and |m – n| |
D | mn and m + n |
Suppose there is no common attribute in R and S due to which natural join will act as cross product. So then in cross product total no. of tuples will be mn.
For minimum:
Suppose there is common attribute in R and S, but none of the row of R matches with rows of S then minimum no. of tuples will be 0.
Question 29 |
The relational algebra expression equivalent to the following tuple calculus expression:
{t| t ∈ r ∧(t[A] = 10 ∧ t[B] = 20)} isA | σ(A=10∨B=20) (r) |
B | σ(A=10) (r) ∪ σ(B=20) (r) |
C | σ(A=10) (r) ∩ σ(B=20) (r) |
D | σ(A=10) (r) - σ(B=20) (r) |
σ(A=10) (r) ∩ σ(B=20) (r)
Question 30 |
Let R = (A, B, C, D, E, F) be a relation scheme with the following dependencies: C→F, E→A, EC→D, A→B. Which of the following is a key of R?
A | CD |
B | EC |
C | AE |
D | AC |
A) (CD)+ = cdf
Not a key.
B) (EC)+ = ecdabf
Yes, it is a key.
C) (AE)+ = aeb
Not a key. D) (AC)+ = abcf
Not a key.
Question 31 |
Which of the following is correct?
A | B-trees are for storing data on disk and B+ trees are for main memory. |
B | Range queries are faster on B* trees. |
C | B-trees are for primary indexes and B* trees are for secondary indexes. |
D | The height of a B* tree is independent of the number of records. |
Question 32 |
1 Read A
2 Read B
3 Write A
4 Read A
5 Write A
6 Write B
7 Read B
8 Write B
A | This schedule is serialized and can occur in a scheme using 2PL protocol |
B | This schedule is serializable but cannot occur in a scheme using 2PL protocol |
C | This schedule is not serialiable but can occur in a scheme using 2PL protocol |
D | This schedule is not seralisable and cannot occur in a scheme using 2PL protocol. |
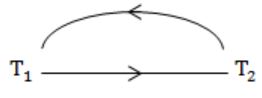
Since cycle exist so not conflict serializable.
And we know that if the schedule is not serializable then it is not 2PL.
Hence correct option is (D).
Question 33 |
Consider the schema R = (S T U V) and the dependencies S → T, T → U, U → V and V → S. Let R = (R1 and R2) be a decomposition such that R1 ∩ R2 ≠ ∅ . The decomposition is
A | not in 2NF |
B | in 2NF but not 3NF |
C | in 3NF but not in 2NF |
D | in both 2NF and 3NF |
And since every attribute is key so the decomposed relation will be in BCNF and hence in 3NF.
Question 34 |
Consider the circuit shown below. In a certain steady state, the line Y is at '1'. What are the possible values of A, B and C in this state?

A | A = 0, B = 0, C = 1 |
B | A = 0, B = 1, C = 1 |
C | A = 1, B = 0, C = 1 |
D | A = 1, B = 1, C = 1 |
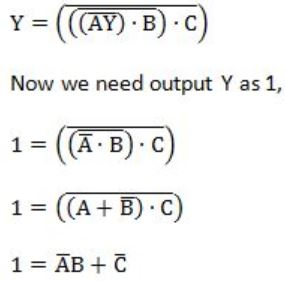
So the above equation is satisfied if either C=0 or A=0 and B=1.
Hence, Option (B) is correct.
Question 35 |
Which of the following sets of component(s) is/are sufficient to implement any arbitrary Boolean function?
A | XOR gates, NOT gates |
B | 2 to 1 multiplexors |
C | AND gates, XOR gates |
D | Three-input gates that output (A⋅B) + C for the inputs A⋅B and C |
E | Both B and C |
(B) 2 to 1 multiplexors is functionally complete.
(C) XOR gate can be used to make a NOT gate. So, (AND, NOT) is functionally complete.
(D) With given gates and inputs NOT gate cannot be derived.
Hence, not complete.
Question 36 |
Which of the following is/are correct?
A | An SQL query automatically eliminates duplicates |
B | An SQL query will not work if there are no indexes on the relations |
C | SQL permits attribute names to be repeated in the same relation |
D | None of the above |
→ If there are no indexes on the relation SQL, then also it works.
→ SQL does not permit 2 attributes to have same name in a relation.
Question 37 |
Consider a B-tree with degree m, that is, the number of children, c, of any internal node (except the root) is such that m ≤ c ≤ 2m-1. Derive the maximum and minimum number of records in the leaf nodes for such a B-tree with height h, h≥1. (Assume that the root of a tree is at height 0.)
A | Theory Explanation. |
Question 38 |
Consider the set of relations
EMP(Employee-no, Dept-no, Employee-name, Salary) DEPT(Dept-no, Dept-name, Location)
Write an SQL query to:
(a) Find all employee names who work in departments located at "Calcutta" and whose salary is greater than Rs. 50,000.
(b) Calculate, for each department number, the number of employees with a salary greater than Rs. 100,000.
A | Theory Explanation. |
Question 39 |
B+-trees are preferred to binary trees in databases because
A | Disk capacities are greater than memory capacities |
B | Disk access is much slower than memory access |
C | Disk data transfer rates are much less than memory data transfer rates |
D | Disks are more reliable than memory |
Question 40 |
Given the relations
employee (name, salary, deptno) and department (deptno, deptname, address)
Which of the following queries cannot be expressed using the basic relational algebra operations (σ, π, ×, ⋈, ∪, ∩, -)?
A | Department address of every employee |
B | Employees whose name is the same as their department name |
C | The sum of all employees’ salaries |
D | All employees of a given department |
Question 41 |
Given the following relation instance.
x y z
1 4 2
1 5 3
1 6 3
3 2 2
Which of the following functional dependencies are satisfied by the instance?
A | XY → Z and Z → Y |
B | YZ → X and Y → Z |
C | YZ → X and X → Z |
D | XZ → Y and Y → X |
If for t1[A] = t2[A] then t1[Y] = t2[Y].
Question 42 |
Given relations r(w, x) and s(y, z), the result of
select distinct w, x
from r, s
is guaranteed to be same as r, provided
A | r has no duplicates and s is non-empty |
B | r and s have no duplicates |
C | s has no duplicates and r is non-empty |
D | r and s have the same number of tuples |
Question 43 |
In SQL, relations can contain null values, and comparisons with null values are treated as unknown. Suppose all comparisons with a null value are treated as false. Which of the following pairs is not equivalent?
A | x = 5 not AND (not (x = 5) |
B | x = 5 AND x > 4 and x < 6, where x is an integer |
C | x ≠ 5 AND not (x = 5) |
D | None of the above |
Question 44 |
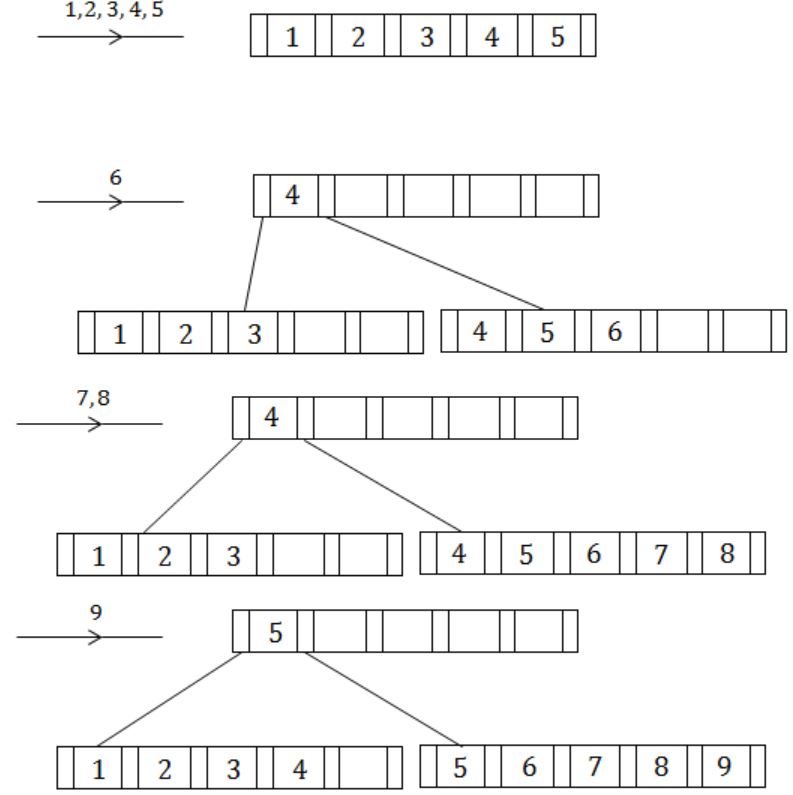
(a) Suppose you are given an empty B+-tree where each node (leaf and internal) can store up to 5 key values. Suppose values 1,2,….. 10 are inserted, in order, into the tree, Show the tree pictorially
(i) After 6 insertions, and
(ii) After all 10 insertions
Do NOT show intermediate stages.
(b) Suppose instead of splitting a node when it is full, we try to move a value to the left sibling. If there is no left sibling, or the left sibling is full, we split the node. Show the tree after values, 1, 2,….., 9 have been inserted. Assume, as in (a) that each node can hold up to 5 keys.
(c) In general, suppose a B+-tree node can hold a maximum of m keys, and you insert a long sequence of keys in increasing order. Then what approximately is the average number of keys in each leaf level node.
(i) In the normal case, and
(ii) With the insertion as in (b).
A | Theory Explanation is given below. |
(i)
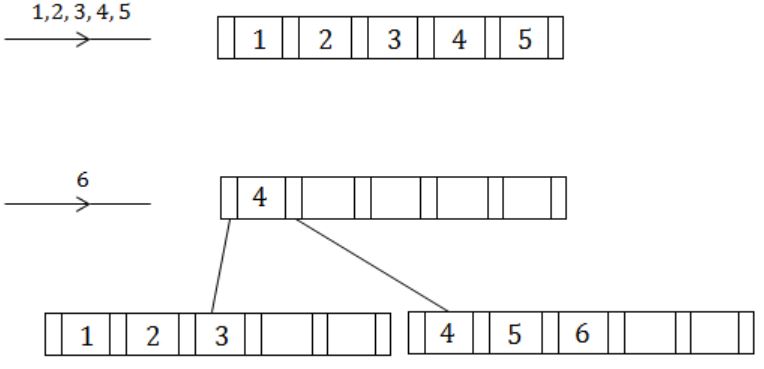
(ii)

(b)
Question 45 |
Consider a bank database with only one relation
transaction (transno, acctno, date, amount)
The amount attribute value is positive for deposits and negative for withdrawals.
(a) Define an SQL view TP containing the information.
(acctno, T1.date, T2.amount)
for every pair of transactions T1, T2 such that T1 and T2 are transaction on the same account and the date of T2 is ≤ the date of T1.
(b) Using only the above view TP, write a query to find for each account the minimum balance it ever reached (not including the 0 balance when the account is created). Assume there is at most one transaction per day on each account, and each account has had atleast one transaction since it was created. To simply your query, break it up into 2 steps by defining an intermediate view V.
A | Theory Explanation is given below. |
Question 46 |
Consider a schema R(A,B,C,D) and functional dependencies A → B and C → D. Then the decomposition of R into R1(AB) and R2(CD) is
A | dependency preserving and lossless join |
B | lossless join but not dependency preserving |
C | dependency preserving but not lossless join |
D | not dependency preserving and not lossless join |
R1∩R2 ≠ 0
Given R1(A,B), R2
R1∩R2 = 0
Not lossless.
The given relation decomposed into R1(A,B) and R2(C,D) and there are only two functional dependencies A→B and C→D. So the given decomposition is dependency preserving.
Question 47 |
Suppose the adjacency relation of vertices in a graph is represented in a table Adj(X,Y). Which of the following queries cannot be expressed by a relational algebra expression of constant length?
A | List of all vertices adjacent to a given vertex |
B | List all vertices which have self loops |
C | List all vertices which belong to cycles of less than three vertices |
D | List all vertices reachable from a given vertex |
(b) Finding a self loop is also simple (Oop(X,X))
(c) If a → b, b → c then c!=a, finding this is also simple.
(d) List all the elements reachable from a given vertex is too difficult in Relational Algebra.
Question 48 |
Let r and s be two relations over the relation schemes R and S respectively, and let A be an attribute in R. Then the relational algebra expression σA=a(r⋈s) is always equal to
A | σA=a (r) |
B | r |
C | σA=a (r)⨝s |
D | None of the above |
(b) Display table
(c) A=a for all Tables r and s
Question 49 |
R(A,B,C,D) is a relation. Which of the following does not have a lossless join, dependency preserving BCNF decomposition?
A | A → B, B → CD |
B | A → B, B → C, C → D |
C | AB → C, C → AD |
D | A → BCD |
Question 50 |
Which of the following relational calculus expressions is not safe?
A | {t|∃u ∈ R1 (t[A] = u[A])∧ ¬∃s ∈ R2 (t[A] = s[A])} |
B | {t|∀u ∈ R1 (u[A]= "x" ⇒ ∃s ∈ R2 (t[A] = s[A] ∧ s[A] = u[A]))} |
C | {t|¬(t ∈ R1)} |
D | {t|∃u ∈ R1 (t[A] = u[A])∧ ∃s ∈ R2 (t[A] = s[A])} |
