Operating-Systems
October 15, 2023Digital-Logic-Design
October 15, 2023Boolean-Function
|
Question 9
|
In the truth table, f(x,y) represent the boolean function
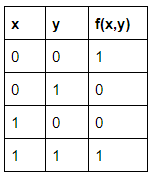

|
x ↔ y
|
|
|
x ⋀ y
|
|
|
x V y
|
|
|
x → y
|
Question 9 Explanation:
→ The output of a digital logic Exclusive-NOR gate ONLY goes “HIGH” when its two input terminals, A and B are at the “SAME” logic level which can be either at a logic level “1” or at a logic level “0”.
→ In other words, an even number of logic “1’s” on its inputs gives a logic “1” at the output, otherwise is at logic level “0”.
→ This type of gate gives and output “1” when its inputs are “logically equal” or “equivalent” to each other, which is why an Exclusive-NOR gate is sometimes called an Equivalence Gate
→ In other words, an even number of logic “1’s” on its inputs gives a logic “1” at the output, otherwise is at logic level “0”.
→ This type of gate gives and output “1” when its inputs are “logically equal” or “equivalent” to each other, which is why an Exclusive-NOR gate is sometimes called an Equivalence Gate
Correct Answer: A
Question 9 Explanation:
→ The output of a digital logic Exclusive-NOR gate ONLY goes “HIGH” when its two input terminals, A and B are at the “SAME” logic level which can be either at a logic level “1” or at a logic level “0”.
→ In other words, an even number of logic “1’s” on its inputs gives a logic “1” at the output, otherwise is at logic level “0”.
→ This type of gate gives and output “1” when its inputs are “logically equal” or “equivalent” to each other, which is why an Exclusive-NOR gate is sometimes called an Equivalence Gate
→ In other words, an even number of logic “1’s” on its inputs gives a logic “1” at the output, otherwise is at logic level “0”.
→ This type of gate gives and output “1” when its inputs are “logically equal” or “equivalent” to each other, which is why an Exclusive-NOR gate is sometimes called an Equivalence Gate
Subscribe
Login
0 Comments
