2012 December UGC NET Paper 1
Question 1 |
The English word ‘Communication’ is derived from the words
Communis and Communicare | |
Communist and Commune | |
Communism and Communalism | |
Communion and Common sense |
Question 2 |
Chinese Cultural Revolution leader Mao Zedong used a type of communication to talk to the masses is known as
Mass line communication | |
Group communication | |
Participatory communication | |
Dialogue communication |
Question 3 |
Conversing with the spirits and ancestors is termed as
Transpersonal communication | |
Intrapersonal communication | |
Interpersonal communication | |
Face-to-face communication |
Question 4 |
The largest circulated daily newspaper among the following is
The Times of India | |
The Indian Express | |
The Hindu | |
The Deccan Herald |
Question 5 |
The pioneer of the silent feature film in India was
K.A. Abbas | |
Satyajit Ray | |
B.R. Chopra | |
Dada Sahib Phalke |
Question 6 |
Classroom communication of a teacher rests on the principle of
Infotainment | |
Edutainment | |
Entertainment | |
Power equation |
Question 7 |
The missing number in the series :
0, 6, 24, 60, 120, ?, 336, is
240 | |
220 | |
280 | |
210 |
Question 7 Explanation:
The difference is 6, 18, 36, 60.
These are multiples of 6 i.e.,
6 = 6 × 1
18 = 6 × 3
36 = 6 × 6
60 = 6 × 10
→ The order is 1, 3, 6, 10, next one is 15. Like 1, 1+2, 1+2+3, 1+2+3+4, 1+2+3+4+5.
→ Next multiple = 6 × 15 = 90
→ 120 + 90 = 210
These are multiples of 6 i.e.,
6 = 6 × 1
18 = 6 × 3
36 = 6 × 6
60 = 6 × 10
→ The order is 1, 3, 6, 10, next one is 15. Like 1, 1+2, 1+2+3, 1+2+3+4, 1+2+3+4+5.
→ Next multiple = 6 × 15 = 90
→ 120 + 90 = 210
Question 8 |
A group of 7 members having a majority of boys is to be formed out of 6 boys and 4 girls. The number of ways the group can be formed is
80 | |
100 | |
90 | |
110 |
Question 8 Explanation:
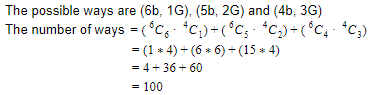
Question 9 |
The number of observations in a group is 40. The average of the first 10 members is 4.5 and the average of the remaining 30 members is 3.5. The average of the whole group is
4 | |
15/2 | |
15/4 | |
6 |
Question 9 Explanation:
The Avg of first 10 numbers = 4.5
Total observations =104.5=45
The Avg of next 30 members = 3.5
Total observations = 30 × 3.5 = 105
40 members total observations = 45 + 105 = 150
Avg. of 40 members observation = 150/40 = 15/4
Total observations =104.5=45
The Avg of next 30 members = 3.5
Total observations = 30 × 3.5 = 105
40 members total observations = 45 + 105 = 150
Avg. of 40 members observation = 150/40 = 15/4
Question 10 |
If MOHAN is represented by the code KMFYL, then COUNT will be represented by
AMSLR | |
MSLAR | |
MASRL | |
SAMLR |
Question 10 Explanation:
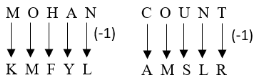
Question 11 |
The sum of the ages of two persons A and B is 50. 5 years ago, the ratio of their ages was 5/3. The present age of A and B are
30, 20 | |
35, 15 | |
38, 12 | |
40, 10 |
Question 11 Explanation:
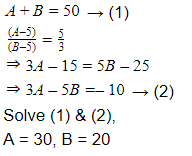
Question 12 |
Let a means minus (–), b means multiplied by (X), C means divided by (/) and D means plus (+). The value of 90 D 9 a 29 C 10 b 2 is
8 | |
10 | |
12 | |
14 |
Question 13 |
Consider the Assertion–I and Assertion–II and select the right code given below:
Assertion–I: Even Bank-lockers are not safe. Thieves can break them and take away your wealth. But thieves cannot go to heaven. So you should keep your wealth in heaven.
Assertion–II: The difference of skin-colour of beings is because of the distance from the sun and not because of some permanent traits. Skin-colour is the result of body’s reaction to the sun and its rays.
Assertion–I: Even Bank-lockers are not safe. Thieves can break them and take away your wealth. But thieves cannot go to heaven. So you should keep your wealth in heaven.
Assertion–II: The difference of skin-colour of beings is because of the distance from the sun and not because of some permanent traits. Skin-colour is the result of body’s reaction to the sun and its rays.
Both the assertions-I and II are forms of argument. | |
The assertion-I is an argument but the assertion-II is not. | |
The assertion-II is an argument but the assertion-I is not. | |
Both the assertions are explanations of facts. |
Question 13 Explanation:
Option is the correct one.
Yes, assertion - I is argument but assertion - II is not.
Question 14 |
By which of the following proposition, the proposition ‘some men are not honest’ is contradicted?
All men are honest. | |
Some men are honest. | |
No men are honest. | |
All of the above. |
Question 14 Explanation:
The contradicted sentence is “All men are honest” is most suitable.
Contradict:- Deny the truth of a statement by asserting the opposite.
Question 15 |
A stipulative definition is
always true | |
always false | |
sometimes true sometimes false | |
neither true nor false |
There are 15 questions to complete.
