GATE 1989
Question 1 |
A hash table with ten buckets with one slot per bucket is shown in the following figure. The symbols S1 to S7 initially entered using a hashing function with linear probing. The maximum number of comparisons needed in searching an item that is not present is
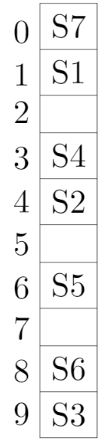
4 | |
5 | |
6 | |
3 |
Question 1 Explanation:
In this, maximum size of cluster = 4 (S6, S3, S7, S1)
→ Worst case of finding a number is equal to maximum size of cluster + 1(after searching all the cluster it enters into empty cluster)
→ Maximum no. of comparisons = 4 + 1 = 5
→ Worst case of finding a number is equal to maximum size of cluster + 1(after searching all the cluster it enters into empty cluster)
→ Maximum no. of comparisons = 4 + 1 = 5
Question 2 |
In which of the following case(s) is it possible to obtain different results for call-by-reference and call-by-name parameter passing?
Passing an expression as a parameter | |
Passing an array as a parameter | |
Passing a pointer as a parameter | |
Passing as array element as a parameter | |
Both A and D |
Question 2 Explanation:
Option D:
Passing array element as a parameter.
Consider an example:
{
.......
a[ ] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
fun (a[i]);
print a[0];
}
fun (int x)
{
int i=1;
}
O/P:
Call-by-reference: 6
Call-by-name: 1
Result is different.
Option A:
While we passing an expression as a parameter due to precedence (higher (or) lower), the output may changes.
If we pass 1+2 to the below function
int foo (int x)
{
return x*x;
}
O/P:
Call by reference = 3*3 = 9
Call by name = 1+2*1+2 (* has higher precedence e)
= 1+2+2
= 5
Output differs.
Answer: A, D
Passing array element as a parameter.
Consider an example:
{
.......
a[ ] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
fun (a[i]);
print a[0];
}
fun (int x)
{
int i=1;
}
O/P:
Call-by-reference: 6
Call-by-name: 1
Result is different.
Option A:
While we passing an expression as a parameter due to precedence (higher (or) lower), the output may changes.
If we pass 1+2 to the below function
int foo (int x)
{
return x*x;
}
O/P:
Call by reference = 3*3 = 9
Call by name = 1+2*1+2 (* has higher precedence e)
= 1+2+2
= 5
Output differs.
Answer: A, D
Question 3 |
Merging states with a common core may produce __________ conflicts and does not produce ___________ conflicts in an LALR purser.
Reduce-Reduce, Shift-Reduce |
Question 3 Explanation:
Merge states with a common core may produce Reduce-Reduce conflicts and does not produce Shift-Reduce conflicts in an LALR parser.
Question 4 |
The transitive closure of the relation {(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4), (5, 4)} on the set {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} is ___________.
{(1,2), (2,3), (1,3), (3,4), (2,4), (1,4), (5,4)} |
Question 4 Explanation:
Transitive closure of the relation {(1,2), (2,3), (3,4), (5,4)} = {(1,2), (2,3), (1,3), (3,4), (2,4), (1,4), (5,4)}
Transitive closure of R:
(a) It is transitive.
(b) It contains R.
(c) It is minimal, satisfies a & b.
Transitive closure of R:
(a) It is transitive.
(b) It contains R.
(c) It is minimal, satisfies a & b.
There are 4 questions to complete.
