GATE 2014 [Set-2]
Question 1 |
Choose the most appropriate phrase from the options given below to complete the following sentence.
India is a post-colonial country because
It was a former British colony | |
Indian Information Technology professionals have colonized the world | |
India does not follow any colonial practices | |
India has helped other countries gain freedom |
India is a post-colonial country because "It was a former British colony" that means if a country is called post colonial then it came into existence after the colonies rules and it can become a independent.
Question 2 |
Who ___________ was coming to see us this evening?
you said | |
did you say | |
did you say that | |
had you said |
Question 3 |
Match the columns.
Column 1 Column 2 1) eradicate P) misrepresent 2) distort Q) soak completely 3) saturate R) use 4) utilize S) destroy utterly
1 : S, 2 : P, 3 : Q, 4 : R | |
1 : P, 2 : Q, 3 : R, 4 : S | |
1 : Q, 2 : R, 3 : S, 4 : P | |
1 : S, 2 : P, 3 : R, 4 : Q |
Distort = misrepresent
Saturate = Soak completely
Utilize = use
Question 4 |
What is the average of all multiples of 10 from 2 to 198?
90 | |
100 | |
110 | |
120 |
Average = 10+20+30+...+180+190 / 19 = (19/2 [10+190]) / 19 = 100
Question 5 |
The value of ![]() is
is
3.464 | |
3.932 | |
4.000 | |
4.444 |
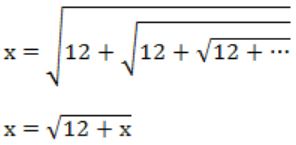
Squaring on both sides,
x2 = 12+x
x2 - x - 12 = 0
(x-4) (x+3) = 0
∴ x = 4 (x ≠ -3)
Question 6 |
The old city of Koenigsberg, which had a German majority population before World War 2, is now called Kaliningrad. After the events of the war, Kaliningrad is now a Russian territory and has a predominantly Russian population. It is bordered by the Baltic Sea on the north and the countries of Poland to the south and west and Lithuania to the east respectively. Which of the statements below can be inferred from this passage?
Kaliningrad was historically Russian in its ethnic make up | |
Kaliningrad is a part of Russia despite it not being contiguous with the rest of Russia | |
Koenigsberg was renamed Kaliningrad, as that was its original Russian name | |
Poland and Lithuania are on the route from Kaliningrad to the rest of Russia |
Question 7 |
The number of people diagnosed with dengue fever (contracted from the bite of a mosquito) in north India is twice the number diagnosed last year. Municipal authorities have concluded that measures to control the mosquito population have failed in this region.
Which one of the following statements, if true, does not contradict this conclusion?
A high proportion of the affected population has returned from neighbouring countries where dengue is prevalent | |
More cases of dengue are now reported because of an increase in the Municipal Office’s administrative efficiency | |
Many more cases of dengue are being diagnosed this year since the introduction of a new and effective diagnostic test | |
The number of people with malarial fever (also contracted from mosquito bites) has increased this year |
Question 8 |
If x is real and |x2 - 2x + 3| = 11, then possible values of |- x3 + x2 - x| include
2, 4 | |
2, 14 | |
4, 52 | |
14, 52 |
|x2 - 2x + 3| = 11, x is real
x2-2x+3 = 11
x2-2x+8 = 0
(x-4)(x+2) = 0
x = 4, -2
x2-2x+3 = -11
x2-2x+14 = 0
x is not real in this case.
|-x3+x2-x|
when x=-2
⇒ |-(-2)3+(-2)2-(-2)|
= |(-(8) + (4) + 2| = 14
x=4
⇒ |-(4)3+(4)2-(4)|
= |-64 + 16 -4|
= 52
Possible values of |-x3+x2-x| include 14, 52.
Question 9 |
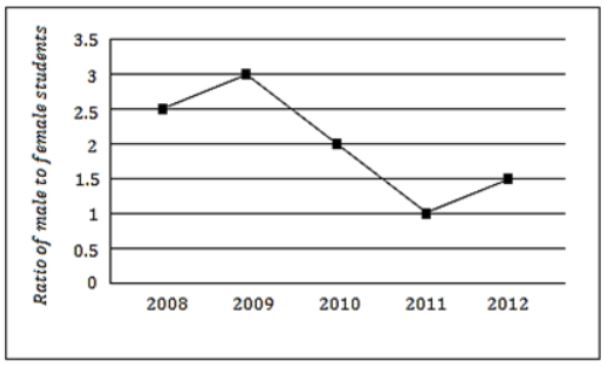
The ratio of male to female students in a college for five years is plotted in the following line graph. If the number of female students doubled in 2009, by what percent did the number of male students increase in 2009?
140 | |
141 | |
142 | |
143 |
Number of female in 2008 = y
Number of female in 2009 = 2y
Given,
x/y = 2.5 ⇒ y = 2x/5
Let, number of male in 2009 = M
Given, M/2y = 3
M/2(2x/5) = 3 ⇒ M = 12x/5
Percentage increase = M-x/x × 100
= 12x/5-x/ x × 100
= 7/5 × 100
= 140%
Question 10 |
At what time between 6 a.m. and 7 a.m. will the minute hand and hour hand of a clock make an angle closest to 60°?
6:22 am | |
6:27 am | |
6:38 am | |
6:45 am |
And for every minute, the angle between them decreases by 6° - (1/2)° = 5 (1/2)°
∴ For the angle to be closest to 60°, the angle must be reduced by atmost 120°.
1 min - 5(1/2)°
x min - 120°
x = 2/11 × 120 = 240/11 = 21.81 m ≈ 22 min
i.e. 6.22 a.m. the angle between minute hand and hour hand will be closest to 60°.
Question 11 |
The security system at an IT office is composed of 10 computers of which exactly four are working. To check whether the system is functional, the officials inspect four of the computers picked at random (without replacement). The system is deemed functional if at least three of the four computers inspected are working. Let the probability that the system is deemed functional be denoted by p. Then 100p =_____________.
11.90 | |
11.91 | |
11.92 | |
11.93 |
Out of which ‘4’ are chosen at random without replaced and created.
If at least three of them are working then system is deemed functional
i.e., there should be only ‘one’ non-working system in set of ‘4’.
It is possible with combination
W – W – W – N,
W – W – N – W,
W – N – W – W,
N – W – W – W.
For W – W – W – N, the probability = (choosing working out of 10) × (choosing working out of 9) × (choosing working out of 8) × (choosing non-working out of 7)
= 4/10×3/9×2/8×1/7
where 4/10 ⇒ 4 working out of 10
3/9 ⇒ 3 working are remaining out of ‘9’ as ‘1’ is already taken
For ‘4’ Sum combinations
Total probability = 4×[4/10×3/9×2/8×1/7] = 600/5040
We need 100p ⇒ 100×600/5040 = 11.90
Question 12 |
Each of the nine words in the sentence "The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog" is written on a separate piece of paper. These nine pieces of paper are kept in a box. One of the pieces is drawn at random from the box. The expected length of the word drawn is _____________. (The answer should be rounded to one decimal place.)
3.9 | |
4.0 | |
4.1 | |
4.2 |
There are ‘9’ words in this sentence.
No. of characters in each word
The (3)
quick (5)
brown (5)
fox (3)
jumps (5)
over (4)
the (3)
lazy (4)
dog (3)
Each word has equal probability.
So expected length = 3×1/9+5×1/9+5×1/9+3×1/9+5×1/9+ 4×1/9+3×1/9+4×1/9+3×1/9
= 35/9
= 3.9
Question 13 |
The maximum number of edges in a bipartite graph on 12 vertices is ______.
36 | |
37 | |
38 | |
39 |

Total no. of edges = 6×6 = 36
Question 14 |
If the matrix A is such that

then the determinant of A is equal to
0 | |
1 | |
2 | |
3 |
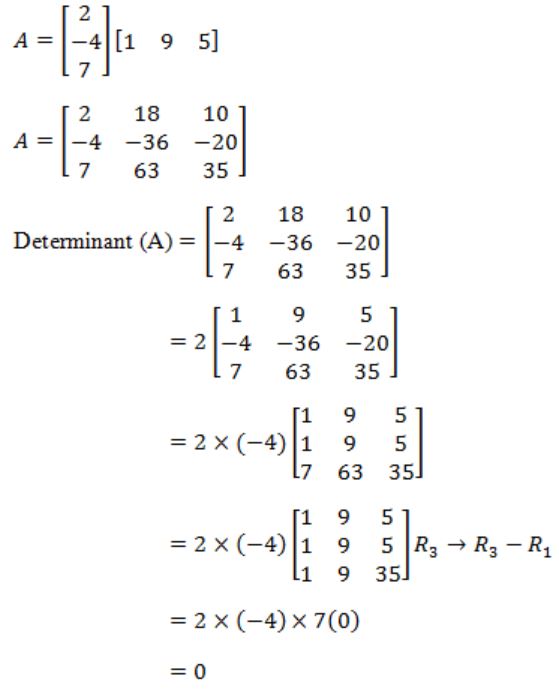
Question 15 |
A non-zero polynomial f(x) of degree 3 has roots at x = 1, x = 2 and x = 3. Which one of the following must be TRUE?
f(0)f(4) < 0 | |
f(0)f(4) > 0 | |
f(0) + f(4) > 0 | |
f(0) + f(4) < 0 |
Polynomial will be
f(x) = (x-1)(x-2)(x-3)
f(0) = -1 × -2 × -3 = -6
f(4) = 3 × 2 × 1 = 6
f(0) ∙ f(4) = - 36
f(0) + f(4) = 6 - 6 = 0
Option (A) is correct.
Question 16 |
The dual of a Boolean function F(x1, x2, ..., xn, +, ⋅, '), written as FD, is the same expression as that of F with + and ⋅ swapped. F is said to be self-dual if F = FD. The number of self-dual functions with n Boolean variables is
2n | |
2(n-1) | |
2(2n ) | |
2(2(n-1) ) |
Number of mutually exclusive pairs of minterms = 2n-1.
There are 2 choices for each pair i.e., we can choose one of the two minterms from each pair of minterms for the function.
Therefore number of functions = 2 x 2 x …. 2n-1 times.
= 2(2(n-1))
![GATE 2014 [Set-2]](https://solutionsadda.in/wp-content/uploads/2019/05/green-new-logo.png)