GATE 2020
Question 1 |
Two straight lines are drawn perpendicular to each other in X-Y plane. If α and β are the acute angles the straight lines make with the X-axis, then α+β is ______.
60° | |
120° | |
180° | |
90° |
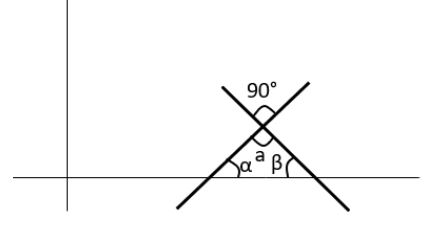
We know a + α + β = 180
α + β = 180 - 90
α + β = 90
Question 2 |
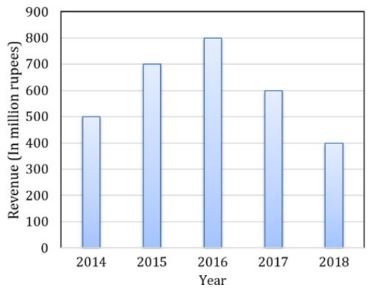
The total revenue of a company during 2014-2018 is shown in the bar graph. If the total expenditure of the company in each year is 500 million rupees, then the aggregate profit or loss (in percentage) on the total expenditure of the company during 2014-2018 is ______.
20% profit | |
20% loss | |
16.67% loss | |
16.67% profit |
2014-2018
Total expenditure = 500 million/year = 500 × 5 = 2500 million
Revenue total (from the graph)
= 400 + 500 + 600 + 700 + 800
= 3000 million
Profit = 3000 - 2500 = 500
⟹ 500/2500 = 20% profit
Question 3 |
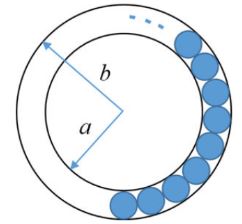
The figure below shows an annular ring with outer and inner radii as b and a, respectively. The annular space has been painted in the form of blue colour circles touching the outer and inner periphery of annular space. If maximum n number of circles can be painted, then the unpainted area available in annular space is ______.
π[(b2 - a2) + π/4(b - a)2] | |
π[(b2 - a2) - π/4(b - a)2] | |
π[(b2 - a2) - n(b - a)2] | |
π[(b2 - a2) + n(b - a)2] |
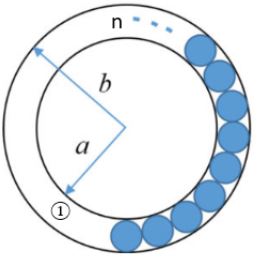
Area of non-painted between 2 circles area of part 1 = πb2 - πa2 = π(b2 - a2)
Radius of painted circles = b-a/2
Area of painted circle = π(b-a/2)2
For n circles = nπ(b-a/2)2
Non-painted area = π[b2 - a2- n/4(b - a)2]
Question 4 |
Goods and Services Tax (GST) is an indirect tax introduced in India in 2017 that is imposed on the supply of goods and services, and it subsumes all indirect taxes except few. It is a destination-based tax imposed on goods and services used, and it is not imposed at the point of origin from where goods come. GST also has a few components specific to state governments, central government and Union Territories (UTs).
Which one of the following statements can be inferred from the given passage?
GST includes all indirect taxes.
| |
GST is imposed at the point of usage of goods and services.
| |
GST does not have a component specific to UT. | |
GST is imposed on the production of goods and services.
|
Question 5 |
Select the word that fits the analogy:
Cook : Cook :: Fly : _____
Flyer | |
Flying | |
Flew | |
Flighter |
Fly-Flyer
Question 6 |
The drawn of the 21st century witnessed the melting glaciers oscillating between giving too much and too little to billions of people who depend on them for fresh water. The UN climate report estimates that without deep cuts to man-made emissions, at least 30% of the northern hemisphere’s surface permafrost could melt by the end of the century. Given this situation of imminent global exodus of billions of people displaced by rising seas, nation-states need to rethink their carbon footprint for political concerns, if not for environmental ones.
Which one of the following statements can be inferred from the given passage?
Nation-states are responsible for providing fresh water to billions of people. | |
Billions of people are affected by melting glaciers.
| |
Nation-states do not have environmental concerns. | |
Billions of people are responsible for man-made emissions. |
Question 7 |
There are multiple routes to reach from node 1 to node 2, as shown in the network.
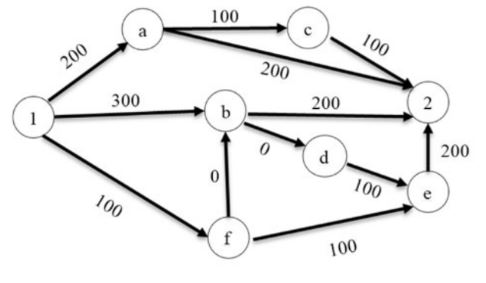
The cost of travel on an edge between two nodes is given in rupees. Nodes ‘a’, ‘b’, ‘c’, ‘d’, ‘e’, and ‘f’ are toll booths. The toll price at toll booths marked ‘a’ and ‘e’ is Rs.200, and is Rs.100 for the other toll booths. Which is the cheapest route from node 1 to node 2?
1-f-e-2
| |
1-f-b-2 | |
1-b-2 | |
1-a-c-2
|
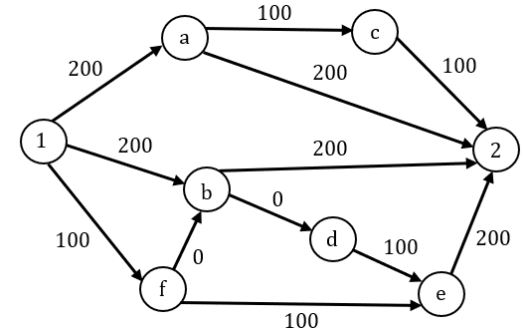
1 - f - e - 2 ─ 100 + 100 + 200 = 400
1 - f - b - 2 ─ 100 + 0 + 200 = 300 ⇾ shortest [Answer]
1 - b - 2 ─ 300 + 200 = 500
1 - a - c ─ 2 - 200 + 100 + 100 = 400
Question 8 |
Raman is confident of speaking English _____ six months as he has been practicing regularly_____the last three weeks.
for, in | |
during, for
| |
for, since
| |
within, for
|
Question 9 |
If P = 3, R = 27, T = 243, then Q+S = ______.
80 | |
110 | |
40 | |
90 |
P=31, Q=32, R=33, S=34, T=35
Q+S = 32 + 34 = 9+81 = 90
Question 10 |
His knowledge of the subject was excellent but his classroom performance was ______.
good
| |
praiseworthy | |
extremely poor | |
desirable
|
Question 11 |
Let G be a group of 35 elements. Then the largest possible size of a subgroup of G other than G itself is ______.
7 |
If ‘H” is a subgroup of finite group (G,*) then O(H) is the divisor of O(G).
Given that the order of group is 35. Its divisors are 1,5,7,35.
It is asked that the size of largest possible subgroup other than G itself will be 7.
Question 12 |
Consider a relational database containing the following schemas.
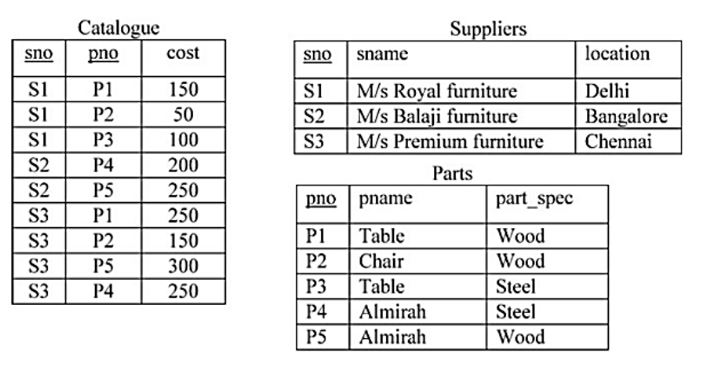
The primary key of each table is indicated by underlying the constituent fields.
SELECT s.sno, s.sname
FROM Suppliers s, Catalogue c
WHERE s.sno = c.sno AND
Cost > (SELECT AVG (cost)
FROM Catalogue
WHERE pno = ‘P4’
GROUP BY pno);
The number of rows returned by the above SQL query is
0 | |
5 | |
4 | |
2 |
AVG(COST)
------------
225
The outer query “select s.sno, s.sname from suppliers s, catalogue c where s.sno=c.sno” returns:
SNO SNAME
----------------------------------------
S1 M/s Royal furniture
S1 M/s Royal furniture
S1 M/s Royal furniture
S2 M/s Balaji furniture
S2 M/s Balaji furniture
S3 M/s Premium furniture
S3 M/s Premium furniture
S3 M/s Premium furniture
S3 M/s Premium furniture
So, the final result of the query is:
SN SNAME
----------------------------------------
S2 M/s Balaji furniture
S3 M/s Premium furniture
S3 M/s Premium furniture
S3 M/s Premium furniture
Therefore, 4 rows will be returned by the query.
Question 13 |
Consider the language L = {an| n≥0} ∪ {anbn| n≥0} and the following statements.
- I. L is deterministic context-free.
II. L is context-free but not deterministic context-free.
III. L is not LL(k) for any k.
Which of the above statements is/are TRUE?
II only | |
III only | |
I only | |
I and III only |
We can make DPDA for this.

L is not LL(k) for any “k” look aheads. The reason is the language is a union of two languages which have common prefixes. For example strings {aa, aabb, aaa, aaabbb,….} present in language. Hence the LL(k) parser cannot parse it by using any lookahead “k” symbols.
Question 14 |
For parameters a and b, both of which are ω(1), T(n) = T(n1/a)+1, and T(b)=1.
Then T(n) is
θ(loga logb n) | |
θ(logb loga n)
| |
θ(log2 log2 n)
| |
θ(logab n)
|
T(n) = [T(n1/a2)+1] + 1
= [T(n1/a3)+1] + 2
= [T(n1/a3)] + 3
= [T(n1/ak)] + b
= logb n = ak
= log logb n = k log a
= k= loga logb n
T(n)=1+loga logb n
T(n)=O(loga logb n)
Question 15 |
Consider the following statements.
- I. If L1 ∪ L2 is regular, then both L1 and L2 must be regular.
II. The class of regular languages is closed under infinite union.
Which of the above statements is/are TRUE?
Both I and II
| |
II only | |
Neither I nor II | |
I only
|
Assume L1 = {an bn | n>0} and L2 = complement of L1
L1 and L2 both are DCFL but not regular, but L1 U L2 = (a+b)* which is regular.
Hence even though L1 U L2 is regular, L1 and L2 need not be always regular.
Statement II is wrong.
Assume the following finite (hence regular) languages.
L1 = {ab}
L2 = {aabb}
L3 = {aaabbb}
.
.
.
L100 = {a100 b100}
.
.
.
If we take infinite union of all above languages i.e,
{L1 U L2 U ……….L100 U ……}
then we will get a new language L = {an bn | n>0}, which is not regular.
Hence regular languages are not closed under infinite UNION.
Question 16 |
Consider the following statements.
- I. Daisy chaining is used to assign priorities in attending interrupts.
II. When a device raises a vectored interrupt, the CPU does polling to identify the source of the interrupt.
III. In polling, the CPU periodically checks the status bits to know if any device needs its attention.
IV. During DMA, both the CPU and DMA controller can be bus masters at the same time.
Which of the above statements is/are TRUE?
I and IV only | |
I and II only
| |
III only | |
I and III only
|
Statement-II is false as vectored interrupt doesn’t involve polling but non-vectored interrupt involves polling.
Statement-III is true as polling means that CPU periodically checks the status bits to know if any device needs attention.
Statement-IV is false as during DMA only one of the CPU or DMA can be bus master at a time.
