Nielit Scientific Assistance IT 15-10-2017
Question 1 |
What will be the output of following?
main()
{
static int a=3;
printf("%d",a--);
if(a)
main();
}
main()
{
static int a=3;
printf("%d",a--);
if(a)
main();
}
3 | |
3 2 1 | |
3 3 3 | |
Program will fall in continuous loop and print 3 |
Question 1 Explanation:
The variable is static variable, the value is retained during multiple function calls. Initial value is 3
“A--” is post decrement so it will print “3”
if(2) condition is true and main() function will call again , Here the “a” value is 2.
“A--” is post decrement so it will print “2”
if(1) condition is true and main() function will call again Here the “a” value is 1.
“A--” is post decrement so it will print “1”
if(0) condition is false it won’t call main() function
“A--” is post decrement so it will print “3”
if(2) condition is true and main() function will call again , Here the “a” value is 2.
“A--” is post decrement so it will print “2”
if(1) condition is true and main() function will call again Here the “a” value is 1.
“A--” is post decrement so it will print “1”
if(0) condition is false it won’t call main() function
Question 2 |
The height of a binary tree is the maximum number of edges in any root to leaf path. The maximum number of nodes in a binary tree of height h is
2 h | |
2 h-1 -1 | |
2 h+1 -1 | |
2 h+1 |
Question 2 Explanation:
● The number of nodes n in a full binary tree, is at least n = 2 h + 1 and at most n = 2 h+1 − 1 , where h is the height of the tree. A tree consisting of only a root node has a height of 0.
● The number of leaf nodes l in a perfect binary tree, is l = ( n + 1 )/2 because the number of non-leaf (a.k.a. internal) nodes

● This means that a perfect binary tree with l leaves has n = 2 l − 1 nodes. ● In a balanced full binary tree, h = ⎡ log 2 (l)⎤ + 1 = ⎡ log 2 ((n + 1 )/2)⎤ + 1 = ⎡ log 2 (n + 1 )⎤
● In a perfect full binary tree, l = 2 h thus n = 2 h+1 − 1
● The maximum possible number of null links (i.e., absent children of the nodes) in a complete binary tree of n nodes is ( n + 1 ) , where only 1 node exists in bottom-most level to the far left.
●The number of internal nodes in a complete binary tree of n nodes is ⎣ n/2⎦ .
● The number of leaf nodes l in a perfect binary tree, is l = ( n + 1 )/2 because the number of non-leaf (a.k.a. internal) nodes
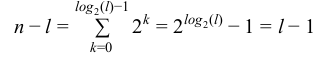
● This means that a perfect binary tree with l leaves has n = 2 l − 1 nodes. ● In a balanced full binary tree, h = ⎡ log 2 (l)⎤ + 1 = ⎡ log 2 ((n + 1 )/2)⎤ + 1 = ⎡ log 2 (n + 1 )⎤
● In a perfect full binary tree, l = 2 h thus n = 2 h+1 − 1
● The maximum possible number of null links (i.e., absent children of the nodes) in a complete binary tree of n nodes is ( n + 1 ) , where only 1 node exists in bottom-most level to the far left.
●The number of internal nodes in a complete binary tree of n nodes is ⎣ n/2⎦ .
Question 3 |
Web links are stored within the page itself and when you wish to 'jump' to the page that is linked, we select the hotspot or anchor. This technique is called
Hypertext | |
hypermedia | |
Both (A) and (B) | |
Anchoring |
Question 3 Explanation:
Web links are stored within the page itself and when you wish to 'jump' to the page that is linked, we select the hotspot or anchor. This technique is called hypertext or hypermedia.
Question 4 |
If the objects focus on the problem domain, then we are concerned with
Object Oriented Analysis | |
Object Oriented Design | |
Object Oriented Analysis and design | |
None of the above |
Question 4 Explanation:
→ The purpose of any analysis activity in the software life cycle is to create a model of the system's functional requirements that is independent of implementation constraints.
→ The main difference between object-oriented analysis and other forms of analysis is that by the object-oriented approach we organize requirements around objects, which integrate both behaviors (processes) and states (data) modeled after real world objects that the system interacts with. In other or traditional analysis methodologies, the two aspects: processes and data are considered separately.
→ For example, data may be modeled by ER diagrams, and behaviors by flow charts or structure charts.
→ The main difference between object-oriented analysis and other forms of analysis is that by the object-oriented approach we organize requirements around objects, which integrate both behaviors (processes) and states (data) modeled after real world objects that the system interacts with. In other or traditional analysis methodologies, the two aspects: processes and data are considered separately.
→ For example, data may be modeled by ER diagrams, and behaviors by flow charts or structure charts.
Question 5 |
Which of the following is not a form of main memory?
Instruction cache | |
Instruction register | |
Instruction Opcode | |
Translation lookaside buffer |
Question 5 Explanation:
In computing, an opcode (abbreviated from operation code, also known as instruction syllable, instruction parcel or opstring) is the portion of a machine language instruction that specifies the
operation to be performed. Beside the opcode itself, most instructions also specify the data they will process, in the form of operands. In addition to opcodes used in the instruction set
architectures of various CPUs, which are hardware devices, they can also be used in abstract computing machines as part of their byte code specifications.
Note: Instruction opcode not in a form of main memory.
Note: Instruction opcode not in a form of main memory.
Question 6 |
which of the following is useful in traversing a given graph by breadth first search?
Stack | |
Set | |
List | |
Queue |
Question 6 Explanation:
Queue can be generally thought as horizontal in structure i.e, breadth/width can be attributed to it - BFS, whereas Stack is visualized as a vertical structure and hence has depth - DFS.
Question 7 |
M is a square matrix of order 'n' and its determinant value is 5, If all the elements of M are multiplied by 2, its determinant value becomes 40. he value of 'n' is
2 | |
3 | |
5 | |
4 |
Question 7 Explanation:
M has n rows. If all the elements of a row are multiplied by , the determinant value becomes 2*5. Multiplying all the n rows by 2, will make the determinant value 2 n *5=40. Solving n= 3.
Question 8 |
Is null an object?
yes | |
No | |
Sometimes yes | |
None of these |
Question 8 Explanation:
If null were an Object, it would support the methods of java.lang.Object such as equals().
However, this is not the case - any method invocation on a null results in a NullPointerException.
There is also a special null type, the type of the expression null, which has no name. Because the null type has no name, it is impossible to declare a variable of the null type or to cast to the null type. The null reference is the only possible value of an expression of null type. The null reference can always be cast to any reference type. In practice, the programmer can ignore the null type and just pretend that null is merely a special literal that can be of any reference type
However, this is not the case - any method invocation on a null results in a NullPointerException.
There is also a special null type, the type of the expression null, which has no name. Because the null type has no name, it is impossible to declare a variable of the null type or to cast to the null type. The null reference is the only possible value of an expression of null type. The null reference can always be cast to any reference type. In practice, the programmer can ignore the null type and just pretend that null is merely a special literal that can be of any reference type
Question 9 |
Which of the following scheduling algorithm could result in starvation?
Priority | |
Round Robin | |
FCFS | |
none of the above |
Question 9 Explanation:
Priority scheduling algorithm could result starvation. Starvation is nothing but indefinite blocking.
Question 10 |
Which of the following is a desirable property of module?
Independency | |
low cohesiveness | |
High coupling | |
Multifunctional |
Question 10 Explanation:
The goal of software engineering is high cohesion and low coupling. The desirable property of module is independency.
Question 11 |
Which of these events will be generated if we close an applet's window?
ActionEvent | |
ComponentEvent | |
AdjustmentEvent | |
WindowEvent |
Question 11 Explanation:
A low level event that indicates that a window has changed its status. This low-level event is generated by a Window object when it is opened, closed, activated, deactivated, iconified, or deiconified, or when focus is transferred into or out of the Window.
Question 12 |
If queue is implemented using arrays, what would be the worst run time complexity of queue and dequeue operations?
O(n), O(n) | |
O(n), O(1) | |
O(1), O(n) | |
O(1), O(1) |
Question 12 Explanation:
Everyone thought that answer in worst case time is O(n) for both the cases but using circular queue, we can implement in constant amount of time.
Question 13 |
The following program fragment prints
int i=5;
do
{
putchar(i+100);
printf("%d",i--);
}
while(i);
int i=5;
do
{
putchar(i+100);
printf("%d",i--);
}
while(i);
i5h4g3f2el | |
14h3g2f1e0 | |
An error message | |
None of the above |
Question 13 Explanation:
Here, i=5 and putchar(i+100) it means actually putchar(5+100) ⇒ putchar(105);
It will print the ASCII equivalent of 105 which is lower case ' i '. The printf statement prints the current value of i. i.e. 5 and then decrements it. So, h4 will be printed in the next pass. This continues until ' i ' becomes 0, at which point the loop gets terminated.
It will print the ASCII equivalent of 105 which is lower case ' i '. The printf statement prints the current value of i. i.e. 5 and then decrements it. So, h4 will be printed in the next pass. This continues until ' i ' becomes 0, at which point the loop gets terminated.
Question 14 |
The running time of an algorithm T(n),where 'n' is the input size, is given by
T(n)=8T(n/2)+qn, if n>1
=p, if n=1
Where p,q are constants. The order of this algorithm is
T(n)=8T(n/2)+qn, if n>1
=p, if n=1
Where p,q are constants. The order of this algorithm is
n2 | |
nn | |
n3 | |
N |
Question 14 Explanation:
Apply master theorem.
a=8,b=2,k=0,p=0;
So, according to masters theorem, a>b k
=O(n^log 2 8 )
=O(n 3 )
a=8,b=2,k=0,p=0;
So, according to masters theorem, a>b k
=O(n^log 2 8 )
=O(n 3 )
Question 15 |
Consider a system having 'm' resources of the same type. these resources are shared by 3 processes A,B,C; which have peak time demands of 3,4,6 respectively. The
minimum value of 'm' that ensures that deadlock will never occur is
11 | |
12 | |
13 | |
14 |
Question 15 Explanation:
A requires 3, B-4, C-6;
→ If A have 2, B have 3, C have 5 then deadlock will occur i.e., 2+3+5=10.
→ If we have one extra resource then deadlock will not occur i.e., 10+1=11.
→ If we have equal (or) more than 11 resources then deadlock will never occur.
→ If A have 2, B have 3, C have 5 then deadlock will occur i.e., 2+3+5=10.
→ If we have one extra resource then deadlock will not occur i.e., 10+1=11.
→ If we have equal (or) more than 11 resources then deadlock will never occur.
There are 15 questions to complete.
Scientific Assistance CS 15-10-2017
Question 1 |
The difference between the compound interest and the simple earned at the end of 3 rd year on a sum of money at a rate of 10% per annul is Rs. 77.5. What is the sum?
Rs. 3,500 | |
Rs. 2,500 | |
Rs. 3,000 | |
Rs. 2,000 |
Question 1 Explanation:
Let principal be ‘x’
S.I = P T R / 100
S.I = X * 3 * 10 / 100
C.I = [ P (1 + (R / 100)T) - P]
C.I = [ X (1+ (10 / 100)3) - X]
C.I = 331X / 1000
Difference between Compound interest and Simple interest is 77.5
( 331X / 1000 ) - ( 3X / 10) = 77.5
31x / 1000 = 77.5
x = 2500.
S.I = P T R / 100
S.I = X * 3 * 10 / 100
C.I = [ P (1 + (R / 100)T) - P]
C.I = [ X (1+ (10 / 100)3) - X]
C.I = 331X / 1000
Difference between Compound interest and Simple interest is 77.5
( 331X / 1000 ) - ( 3X / 10) = 77.5
31x / 1000 = 77.5
x = 2500.
Question 2 |
Aamir and Birju can cut 5000g of wood in 20 min. Birju and Charles can cut 5000g of wood in 40 min. Charles and Aamir cut 5 kg of wood in 30 min. How much time Charles will take to cut 5 kg wood alone?
120 min | |
48 min | |
240 min | |
120 min |
Question 2 Explanation:
Here in this question 5000g means 5kg only
So from that question Aamir (A) Birju (B) Charles (C)
Let Aamir, Birju and Charles alone can complete the work in A, B and C minutes respectively, then
1 min. work of (A+B)=1/20, (B+C)=1/40 and (C+A)=1/30
A + B + C = 13/240
1 min. work of C = (A+B+C) - (A+B) = 13/240 - 1/20 = 1/240
So C alone can complete the work in 240 min.
So from that question Aamir (A) Birju (B) Charles (C)
Let Aamir, Birju and Charles alone can complete the work in A, B and C minutes respectively, then
1 min. work of (A+B)=1/20, (B+C)=1/40 and (C+A)=1/30
A + B + C = 13/240
1 min. work of C = (A+B+C) - (A+B) = 13/240 - 1/20 = 1/240
So C alone can complete the work in 240 min.
Question 3 |
An alloy contains copper and zinc in the ratio 5 : 3 and another contains copper and tin in the ratio 8 : 5, If equal weights of the two are melted together to form a 3 rd alloy, find the weight of tin per kg in the new alloy.
40/129 | |
5/13 | |
5/26 | |
28/5 |
Question 3 Explanation:
Amount of copper in first alloy is 5x/8 and zinc is 3x/8.
Amount of copper in second alloy is 8x/13 and tin is 5x/13.
So after mixing tin is available in 2 alloy only that means in 3rd alloy 5x/13/2x
Tin present in 3rd alloy is 5/26.
Amount of copper in second alloy is 8x/13 and tin is 5x/13.
So after mixing tin is available in 2 alloy only that means in 3rd alloy 5x/13/2x
Tin present in 3rd alloy is 5/26.
Question 4 |
X is a whole number. If the only common factors of X and X2 are 1 and X, then X is _______
1 | |
a perfect square | |
an odd number | |
a prime number |
Question 4 Explanation:
A number that is divisible only by itself and 1 is called prime number.
Question 5 |
Line AB is 24 metres in length and tangent to the inner one of the two concentric circles at point C, Points A and B lie on the circumference of the outer circle. It is known that the radii of the two circles are integers. The radius of the outer circle is
13m | |
5 m | |
7 m | |
4m |
Question 5 Explanation:

Given data,
AB=24cm
CB=12cm
θC=5cm(Assume)
θB=5 2 +12 2 =169
θB=13cm
Note: They forgot to mention the value 5. If we are considering value=5 then answer should be A.
Question 6 |
Monisha is working with a real estate agent to find a location for the kids’ toy store she plans to open in her town. She is looking for a place that is either in the centre or not too far from the centre of town. It should also be attractive for the right kind of footfall too. Which of the following locations should Monisha’s agent call to her attention?
a storefront in a new high-rise building near the train station in the center of town whose occupants are mainly young, childless professionals who use the train to commute to their offices each day | |
a little shop three blocks away from the town’s main street, located across the street from an elementary school and next door to an ice cream store | |
a stand-alone storefront on a quiet residential street ten blocks away from the town’s center | |
a storefront in a small a strip mall located on the outskirts of town that is also occupied by a pharmacy and a dry cleaner |
Question 6 Explanation:
This option is both near the center of town and in a location where children and their parents are sure to be around. This is the only option that meets both of Monisha’s requirements.
Question 7 |
Reading is a psycholinguistic guessing game. To read critically is a skill as it is a demanding process. One must slow down one’s reading and, with a pencil in hand, perform specific operations on the text. Mark up the text with reactions, conclusions and questions. When one reads, one becomes an active participant.
critical reading is a slow, dull, but essential process. | |
the best critical reading happens at critical times in a person’s life. | |
readers should get in the habit of questioning the truth of what they read. | |
critical reading requires thoughtful and careful attention |
Question 7 Explanation:
Option-A FALSE: The author never says that reading is dull.
Option-B,C FALSE: Not related to given paragraph.
Option-D TRUE: The author stresses the need to read critically by performing thoughtful and careful operations on the text.
Option-B,C FALSE: Not related to given paragraph.
Option-D TRUE: The author stresses the need to read critically by performing thoughtful and careful operations on the text.
Question 8 |
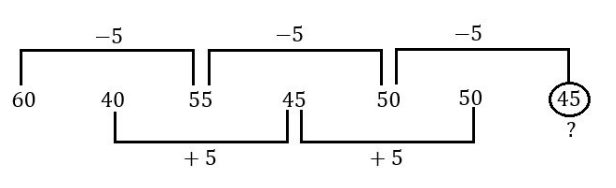
Find the missing term:
60, 40, 55, 45, 50, 50,?
60, 40, 55, 45, 50, 50,?
45 | |
50 | |
55 | |
60 |
Question 8 Explanation:
Question 9 |
Find the missing alphabet:
T, r, O, m, J,?
T, r, O, m, J,?
h | |
i | |
I | |
g |
Question 9 Explanation:
In between r and T there is letter is s
Likewise m and O letter is n
Same h is the next letter to fit in that sequence
Likewise m and O letter is n
Same h is the next letter to fit in that sequence
Question 10 |
Here are some words translated from an artificial language.
Qmelaqali means fruitcake
Qalitiimmeo means cakewalk
Useguamao means buttercup
Which word could mean “cupcake”?
Qmelaqali means fruitcake
Qalitiimmeo means cakewalk
Useguamao means buttercup
Which word could mean “cupcake”?
qalitiiqali | |
amaotiimmeo | |
pakitreft | |
amaoqali |
Question 10 Explanation:
Qmelaqali→ fruitcake
We can divide artificial language into parts.
Qmela→ fruit
qali→ cake
Qalitiimmeo→ cakewalk
We can divide artificial language into parts.
Qali→ cake
tiimmeo→ walk
Useguamao → buttercup
We can divide artificial language into parts.
Usegu→ butter
amao→ cup
cupcake→ ?
amao→ cup
qali→ cake
So, option-D is correct answer.
We can divide artificial language into parts.
Qmela→ fruit
qali→ cake
Qalitiimmeo→ cakewalk
We can divide artificial language into parts.
Qali→ cake
tiimmeo→ walk
Useguamao → buttercup
We can divide artificial language into parts.
Usegu→ butter
amao→ cup
cupcake→ ?
amao→ cup
qali→ cake
So, option-D is correct answer.
Question 11 |
A man walks 5 Km towards south and then turns to the right. After walking 3 Km he turns to the left and walks 5 Km. Now in which direction is he from the starting place?
West | |
South | |
North-East | |
South- West |
Question 11 Explanation:
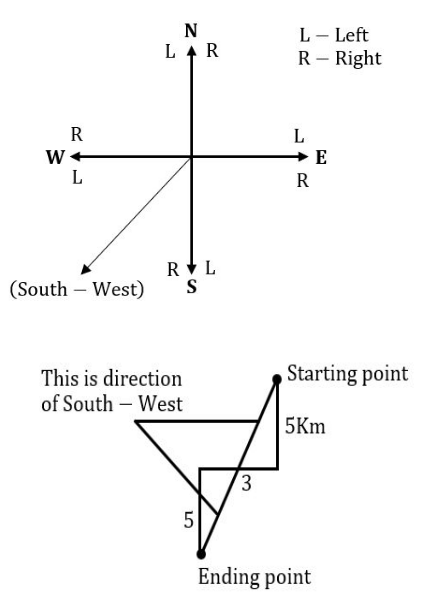
Question 12 |
If the consonants in the word ‘DROVE’ are first arranged alphabetically and the vowels are put in between two pairs of consonants in the alphabetical order, which of the following will be the fourth from the right end after the rearrangement?
D | |
E | |
R | |
O |
Question 12 Explanation:
In the word DROVE we have two vowels
Those are O and E
After consonants are arranged in alphabetically we got the word like DRV
But we have two place vowels in between two pairs of consonants we got finally DEROV
So right from fourth letter is E
Those are O and E
After consonants are arranged in alphabetically we got the word like DRV
But we have two place vowels in between two pairs of consonants we got finally DEROV
So right from fourth letter is E
Question 13 |
There is a queue in a ticketing office. Amanda is 10 th from the front while Murthy is 25 th from behind and Marta is just in the middle of the two. If there be 50 persons in the queue. What position does Marta occupy from the front?
16 | |
18 | |
15 | |
17 |
Question 13 Explanation:
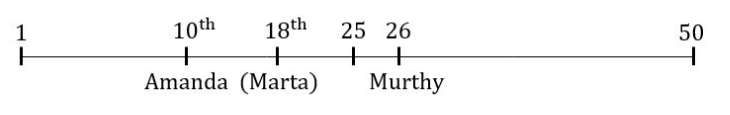
Question 14 |
There are five janitors. Pali, Qureshi, Rohan, Sant and Timber. They all have a different height, Qureshi is shorter than only Timber and Sant is shorter than Pali and Qureshi. Who among them is the shortest?
Rohan | |
Sant | |
Pali | |
Data inadequate |
Question 14 Explanation:
From that question we can decide Pali Quereshi sant and timber but Rohan is not mentioned there. So Data inadequate is answer.
Question 15 |
A $ B means A is the father of B; A # B means A is the sister of B; A * B means A is the daughter of B and A @ B means A is the brother of B. Which of the following indicates that M is the wife of Q?
Q $ R # T @ M | |
Q $ R @ T # M | |
Q $ R * T # M | |
Q $ R @ T * M |
Question 15 Explanation:
Q $ R means R’s father is Q
R @ T means T’s brother is R
T * M means M’s Daughter T
Finally M’s Daughter is T and T’s Brother is R and R’s father is Q so Q’s wife is M.
R @ T means T’s brother is R
T * M means M’s Daughter T
Finally M’s Daughter is T and T’s Brother is R and R’s father is Q so Q’s wife is M.
There are 15 questions to complete.
