GATE 2002
Question 1 |
The rank of the matrix ![]() is
is
4 | |
2 | |
1 | |
0 |
Question 2 |
The trapezoidal rule for integration give exact result when the integrand is a polynomial of degree:
0 but not 1 | |
1 but not 0 | |
0 or 1 | |
2 |
Question 3 |
The solution to the recurrence equation T(2k) = 3 T(2k-1) + 1, T(1)=1, is:
 | |
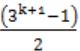 | |
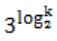 | |
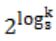 |
T(1)=1
k=0; T(1) = 3T(2-1)+1
k=1; T(2) = 3T(20)+1 = 3(1)+1 = 4
k=2; T(4) = 3T(21)+1 = 3(4)+1 = 13
k=3; T(8) = 3T(22)+1 = 3(13)+1 = 40
k=4; T(16) = 3T(23)+1 = 3(40)+1 = 121
Simply go through the options.
Option B:
k=4 ⇒ (34+1-1)/2
⇒ (243-1)/2
⇒ 121
Question 4 |
The minimum number of colours required to colour the vertices of a cycle with η nodes in such a way that no two adjacent nodes have the same colour is
2 | |
3 | |
4 | |
n - 2[n/2] + 2 |
Question 5 |
log n | |
n/2 | |
(log2)n - 1 | |
n |
Question 6 |
Which of the following is true?
The set of all rational negative numbers forms a group under multiplication. | |
The set of all non-singular matrices forms a group under multiplication. | |
The set of all matrices forms a group under multiplication. | |
Both B and C are true. |
a. Closure: result of a * b must be in group G.
b. There must be an identity element i.e. e * a = a * e = a
c. There must be an inverse element b for every element a such that a * b = b * a = e
d. Associativity i.e. (a * b) * c = a * (b * c)
Rational negative numbers don't form a group under multiplication, as multiplying two negative numbers results into a positive number, so closure property is not satisfied.
Set of non-singular matrices forms a group under multiplication.
The set of all matrices doesn't form a group under multiplication, since there may not be an inverse for a matrix (in particular, for singular matrices).
Question 7 |
The language accepted by a Pushdown Automaton in which the stack is limited to 10 items is best described as
Context free | |
Regular | |
Deterministic Context free | |
Recursive |
Question 8 |
“If X then Y unless Z” is represented by which of the following formulas in prepositional logic? (“¬“, is negation, “∧” is conjunction, and “→” is implication)
(X∧¬Z)→Y | |
(X∧Y)→¬Z | |
X→(Y∧¬Z) | |
(X→Y)∧¬Z |
⇒ Z ∨ ¬X ∨ Y
⇒ ¬X ∨ Z ∨ Y
Option A:
(X ∧ ¬Z) → Y = ¬(X ∧ ¬Z ) ∨ Y = ¬X ∨ Z ∨ Y Hence, option (A) is correct.
Question 9 |
A device employing INTR line for device interrupt puts the CALL instruction on the data bus while
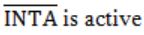 | |
HOLD is active | |
READY is active | |
None of the above |
Question 10 |
In 8085 which of the following modifies the program counter?
Only PCHL instruction | |
Only ADD instructions | |
Only JMP and CALL instructions | |
All instructions |
ADD Instruction: increments the program counter.
JMP & CALL: Change the values of PC.
Question 11 |
In serial data transmission, every byte of data is padded with a ‘0’ in the beginning and one or two ‘1’s at the end of byte because
Receiver is to be synchronized for byte reception | |
Receiver recovers lost ‘0’s and ‘1’s from these padded bits | |
Padded bits are useful in parity computation | |
None of the above |
Question 12 |
Minimum sum of product expression for f(w,x,y,z) shown in Karnaugh-map below is

xz+y'z | |
xz'+zx' | |
x'y+zx' | |
None of the above |
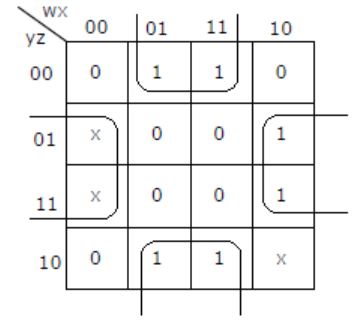
⇒ xz' + zx'
Question 13 |
Which of the following is not a form of memory?
instruction cache | |
instruction register | |
instruction opcode | |
translation look-a-side buffer |
Question 14 |
The decimal value 0.25
is equivalent to the binary value 0.1 | |
is equivalent to the binary value 0.01 | |
is equivalent to the binary value 0.00111… | |
cannot be represented precisely in binary |
Multiply 0.25 by 2.
0.25×2 = 0.50 (product)
Fractional part = 0.50
Carry = 0
2nd Multiplication iteration:
Multiply 0.50 by 2.
0.50×2 = 1.00 (product)
Fractional part = 0.00
Carry = 1
The fractional part in the 2nd iteration becomes zero and so we stop the multiplication iteration.
Carry from 1st multiplication iteration becomes MSB and carry from 2nd iteration becomes LSB. So the result is 0.01.
Question 15 |
The 2’s complement representation of the decimal value -15 is
1111 | |
11111 | |
111111 | |
10001 |
-15 = 11111
1's complement = 10000
2's complement = 10001
Question 16 |
Sign extension is a step in
floating point multiplication | |
signed 16 bit integer addition | |
arithmetic left shift | |
converting a signed integer from one size to another |
Question 17 |
In the C language
At most one activation record exists between the current activation record and the activation record for the main | |
The number of activation records between the current activation record and the activation record for the main depends on the actual function calling sequence. | |
The visibility of global variables depends on the actual function calling sequence. | |
Recursion requires the activation record for the recursive function to be saved on a different stack before the recursive fraction can be called. |
