NTA-UGC-NET 2021 Dec & 2022 June Paper-2
Question 1 |
A trigger is
A statement that enables to start DBMS | |
A statement that is executed by the user when debugging an application program. | |
A condition the system tests for the validity of the database user. | |
A statement that is executed automatically by the system as a side effect of modification to the database. |
Question 1 Explanation:
A triggering event or statement is the SQL statement that causes a trigger to be fired.
A triggering event can be an INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE statement on a table.
A database trigger is procedural code that is automatically executed in response to certain events on a particular table or view in a database.
The trigger is mostly used for maintaining the integrity of the information on the database. For example, when a new record (representing a new worker) is added to the employees table, new records should also be created in the tables of the taxes, vacations and salaries.
Triggers can also be used to log historical data, for example to keep track of employees' previous salaries.
A triggering event can be an INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE statement on a table.
A database trigger is procedural code that is automatically executed in response to certain events on a particular table or view in a database.
The trigger is mostly used for maintaining the integrity of the information on the database. For example, when a new record (representing a new worker) is added to the employees table, new records should also be created in the tables of the taxes, vacations and salaries.
Triggers can also be used to log historical data, for example to keep track of employees' previous salaries.
Question 2 |
RAD software process model stands for
Rapid Application Development | |
Relative Application Development | |
Rapid Application Design | |
Recent Application Development |
Question 2 Explanation:
The Rapid Application Development (or RAD) model is based on prototyping and iterative models with no (or less) specific planning.
RAD approach to software development means putting lesser emphasis on planning tasks and more emphasis on development and coming up with a prototype
RAD approach to software development means putting lesser emphasis on planning tasks and more emphasis on development and coming up with a prototype
Question 3 |
Alpha and Beta testing are forms of
White- Box Testing | |
Black- Box Testing | |
Acceptance Testing | |
System Testing |
Question 3 Explanation:
Black-box testing is a method of software testing that examines the functionality of an application without peering into its internal structures or workings.
Alpha testing uses both black and white box testing while Beta testing uses only black box testing.
Alpha testing is performed by testers who are usually internal employees of the organization
Alpha testing uses both black and white box testing while Beta testing uses only black box testing.
Alpha testing is performed by testers who are usually internal employees of the organization
Question 4 |
Match List I with List II:
List I List II
(A) Least frequently used (I) Memory is distributed among processors
(B) Critical Section (II) Page replacement policy in cache memory
(C) Loosely coupled multiprocessor system (III) Program section that once begin must complete execution before another processor access the same shared resource
(D) Distributed operating system organization (IV) O/S routines are distributed among available processors.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
List I List II
(A) Least frequently used (I) Memory is distributed among processors
(B) Critical Section (II) Page replacement policy in cache memory
(C) Loosely coupled multiprocessor system (III) Program section that once begin must complete execution before another processor access the same shared resource
(D) Distributed operating system organization (IV) O/S routines are distributed among available processors.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(A)-(III), (B)-(II), (C)-(IV), (D)-(I) | |
(A)-(I), (B)-(II), (C)-(III), (D)-(IV) | |
(A)-(II), (B)-(III), (C)-(I), (D)-(IV) | |
(A)-(II), (B)-(I), (C)-(III), (D)-(IV) |
Question 4 Explanation:
A Page replacement algorithm is an algorithm that decides which pages should be written to disk or file, when a new page needs to be allocated.
Page replacement happens when a requested page is not in memory (page fault) and a free page cannot be used to satisfy the allocation, either because there are none, or because the number of free pages is lower than some threshold.
FIFO,LRU and optimal are examples of Page replacement algorithms
Critical section is a program section that once begin must complete execution before another processor accesses the same shared resource.
Page replacement happens when a requested page is not in memory (page fault) and a free page cannot be used to satisfy the allocation, either because there are none, or because the number of free pages is lower than some threshold.
FIFO,LRU and optimal are examples of Page replacement algorithms
Critical section is a program section that once begin must complete execution before another processor accesses the same shared resource.
Question 5 |
If an operating system does not allow a child process to exist when the parent process has been terminated, this phenomenon is calls as-
Threading | |
Cascading termination | |
Zombie termination | |
Process killing |
Question 5 Explanation:
Whenever the process finishes executing its final statement and asks the operating system to delete it by using exit() system call.
If a process terminates either normally or abnormally, then all its children have to be terminated. This concept is referred to as cascading termination.
If a process terminates either normally or abnormally, then all its children have to be terminated. This concept is referred to as cascading termination.
Question 6 |
Size and complexity are a part of
People Metrics | |
Project Metrics | |
Process Metrics | |
Product Metrics |
Question 6 Explanation:
Software metrics can be classified into three categories −
Product metrics − Describes the characteristics of the product such as size, complexity, design features, performance, and quality level.
Process metrics − These characteristics can be used to improve the development and maintenance activities of the software.
Project metrics − These metrics describe the project characteristics and execution. Examples include the number of software developers, the staffing pattern over the life cycle of the software, cost, schedule, and productivity.
Product metrics − Describes the characteristics of the product such as size, complexity, design features, performance, and quality level.
Process metrics − These characteristics can be used to improve the development and maintenance activities of the software.
Project metrics − These metrics describe the project characteristics and execution. Examples include the number of software developers, the staffing pattern over the life cycle of the software, cost, schedule, and productivity.
Question 7 |
Consider the following statements:
Statement I: Conservative 2 PL is a deadlock-free protocol.
Statement II: Thomas's write rule enforces conflict serializability.
Statement III: Timestamp ordering protocol ensures serializability based on the order of transaction timestamps.
Which of the following is correct?
Statement I: Conservative 2 PL is a deadlock-free protocol.
Statement II: Thomas's write rule enforces conflict serializability.
Statement III: Timestamp ordering protocol ensures serializability based on the order of transaction timestamps.
Which of the following is correct?
Statement I, Statement II true and Statement III false | |
Statement I, Statement III true and Statement II false | |
Statement I, Statement II false and Statement III true | |
Statement I, Statement II and Statement III true |
Question 7 Explanation:
TRUE: Statement I: Conservative 2 PL is a deadlock-free protocol.
TRUE: Statement II: Thomas's write rule enforces conflict serializability.
TRUE: Statement III: Timestamp ordering protocol ensures serializability based on the order of transaction timestamps.
TRUE: Statement II: Thomas's write rule enforces conflict serializability.
TRUE: Statement III: Timestamp ordering protocol ensures serializability based on the order of transaction timestamps.
Question 8 |
Hidden surface removal problem with minimal 3D pipeline can be solved with
Painter's algorithm | |
Window Clipping algorithm | |
Brute force rasterization algorithm | |
Flood fill algorithm |
Question 8 Explanation:
Hidden surface removal problem with minimal 3D pipeline can be solved with Window Clipping algorithm.
The z-buffer algorithm is the most widely used method for solving the hidden surface problem. It has the following major advantages over other hidden surface removal algorithms:
-No sorting is required. Models can be rendered in any order.
-No geometric intersection calculations are required. The algorithm produces the correct output even for intersecting or overlapping triangles.
-The algorithm is very simple to implement.
Disadvantages of the z-buffer algorithm include:
-A z-buffer requires a non-trivial amount of memory. For example, assuming each value in a z-buffer is a 32 bit floating point value, a rendered image that is 1024x768 pixels requires 3MB of memory to store its z-buffer.
-Every pixel of every primitive element must be rendered, even if many of them never write their color to the frame buffer.
-If two primitives are in exactly the same place in 3D space, as their positions are interpolated across their respective surfaces, the z values for each object will typically be different by a very small amount due to floating-point round-off errors. These small differences will alternate between primitives for adjacent pixels resulting in random and weird patterns in a rendering. This is called “z-fighting” and it can be avoided by never placing two primitives in the same location in 3D space.
The z-buffer algorithm is the most widely used method for solving the hidden surface problem. It has the following major advantages over other hidden surface removal algorithms:
-No sorting is required. Models can be rendered in any order.
-No geometric intersection calculations are required. The algorithm produces the correct output even for intersecting or overlapping triangles.
-The algorithm is very simple to implement.
Disadvantages of the z-buffer algorithm include:
-A z-buffer requires a non-trivial amount of memory. For example, assuming each value in a z-buffer is a 32 bit floating point value, a rendered image that is 1024x768 pixels requires 3MB of memory to store its z-buffer.
-Every pixel of every primitive element must be rendered, even if many of them never write their color to the frame buffer.
-If two primitives are in exactly the same place in 3D space, as their positions are interpolated across their respective surfaces, the z values for each object will typically be different by a very small amount due to floating-point round-off errors. These small differences will alternate between primitives for adjacent pixels resulting in random and weird patterns in a rendering. This is called “z-fighting” and it can be avoided by never placing two primitives in the same location in 3D space.
Question 9 |
Match List I with List II:
List I List II
(A) Firmware (I) Number of logical records into physical blocks
(B) Batch file (II) ASCII format
(C) Packing (III) Resource allocation
(D) Banker's Algorithm (IV) ROM
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
List I List II
(A) Firmware (I) Number of logical records into physical blocks
(B) Batch file (II) ASCII format
(C) Packing (III) Resource allocation
(D) Banker's Algorithm (IV) ROM
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(A)-(II), (B)-(I), (C)-(IV), (D)-(III) | |
(A)-(II), (B)-(I), (C)-(III), (D)-(IV) | |
(A)-(IV), (B)-(II), (C)-(I), (D)-(III) | |
(A)-(IV), (B)-(I), (C)-(II), (D)-(III) |
Question 9 Explanation:
Firmware --> ROM
Batch file --> Number of logical records into physical blocks
Packing --> ASCII format
Banker’s algorithm is a resource allocation algorithm.
Batch file --> Number of logical records into physical blocks
Packing --> ASCII format
Banker’s algorithm is a resource allocation algorithm.
Question 10 |
Consider the properties of recursively enumerable sets:
(A) Finiteness
(B) Context Freedom
(C) Emptiness
Which of the following is true?
(A) Finiteness
(B) Context Freedom
(C) Emptiness
Which of the following is true?
Only (A) and (B) are not decidable | |
Only (B) and (C) are not decidable | |
Only (C) and (A) are not decidable | |
All (A), (B) and (C) are not decidable |
Question 10 Explanation:
Finiteness and Emptiness are not decidable
Question 11 |
Fault base testing technique is
Unit testing | |
Beta testing | |
Stress testing | |
Mutation testing |
Question 11 Explanation:
Mutation testing is a software testing type that is based on changes or mutations.
Changes are introduced into the source code to check whether the defined test cases can detect errors in the code.
Changes are introduced into the source code to check whether the defined test cases can detect errors in the code.
Question 12 |
The condition num!=65 cannot be replaced by
num > 65 || num<65 | |
!(num==65) | |
num-65 | |
!(num-65) |
Question 12 Explanation:
Except !(num-65) can be replaced by num!=65
Question 13 |
Match List I with List II:
List I List II
(A) BCNF (I) It remove multivalued dependency
(B) 3NF (II) It is not always dependency preserving
(C) 2NF (III) It removes transitive dependency
(D) 4NF (IV) It removes partial functional dependency
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
List I List II
(A) BCNF (I) It remove multivalued dependency
(B) 3NF (II) It is not always dependency preserving
(C) 2NF (III) It removes transitive dependency
(D) 4NF (IV) It removes partial functional dependency
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(A)-(III), (B)-(II), (C)-(IV), (D)-(I) | |
(A)-(II), (B)-(IV), (C)-(I), (D)-(III) | |
(A)-(II), (B)-(III), (C)-(IV), (D)-(I) | |
(A)-(II), (B)-(I), (C)-(IV), (D)-(III) |
Question 13 Explanation:
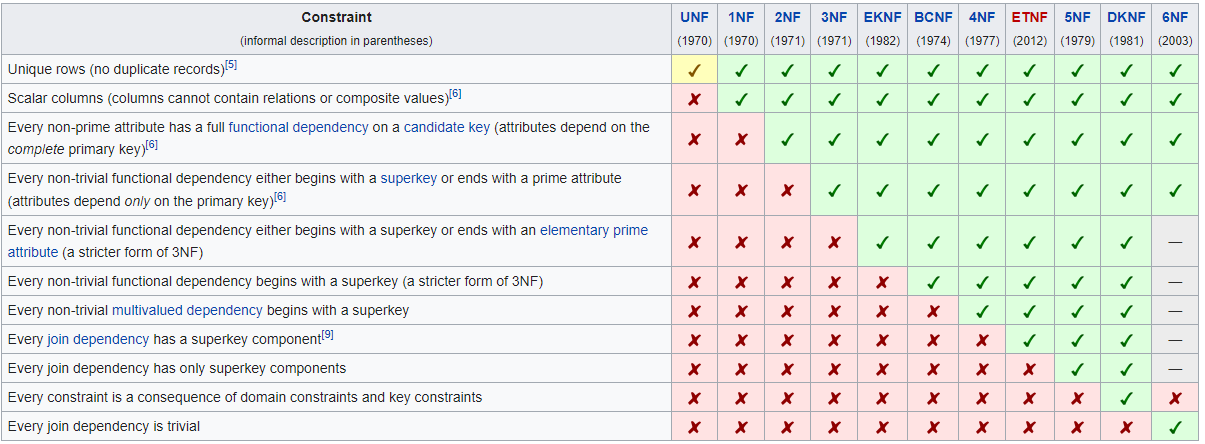
Question 14 |
Given below are two statements : one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R):
Assertion (A): A load-and-go assembler avoids the overhead of writing the object program out and reading it back in.
Reason (R): This can be done with either one-pass or two-pass assembler
Assertion (A): A load-and-go assembler avoids the overhead of writing the object program out and reading it back in.
Reason (R): This can be done with either one-pass or two-pass assembler
Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A) | |
Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is NOT the correct explanation of (A) | |
(A) is true but (R) is false | |
(A) is false but (R) is true |
Question 14 Explanation:
Load-and-go assemblers generate their object code in memory for immediate execution.
No object program is written out, no loader is needed.
No object program is written out, no loader is needed.
Question 15 |
Match List I with List II:
List I List II
(A) Stack Algorithm (I) Deadloack
(B) Elevator algorithm (II) Disk Scheduling
(C) Priority scheduling algorithm (III) Page replacement
(D) Havender algorithm (IV) CPU Scheduling
CHoose the correct answer from the options given below:
List I List II
(A) Stack Algorithm (I) Deadloack
(B) Elevator algorithm (II) Disk Scheduling
(C) Priority scheduling algorithm (III) Page replacement
(D) Havender algorithm (IV) CPU Scheduling
CHoose the correct answer from the options given below:
(A)-(III), (B)-(II), (C)-(IV), (D)-(I) | |
(A)-(II), (B)-(III), (C)-(IV), (D)-(I) | |
(A)-(III), (B)-(II), (C)-(I), (D)-(IV) | |
(A)-(II), (B)-(III), (C)-(I), (D)-(IV) |
Question 15 Explanation:
Priority scheduling is CPU scheduling algorithm.
Elevator algorithm is Disk scheduling algorithm.
Stack Algorithm is Page replacement algorithm.
Havender's algorithm is Deadlock Prevention.
Elevator algorithm is Disk scheduling algorithm.
Stack Algorithm is Page replacement algorithm.
Havender's algorithm is Deadlock Prevention.
Question 16 |
In a game playing search tree, up to which depth α-β pruning can be applied?
(A) Root (0) level
(B) 6 level
(C) 8 level
(D) Depends on utility value in a breadth first order
(A) Root (0) level
(B) 6 level
(C) 8 level
(D) Depends on utility value in a breadth first order
(B) and (C) only | |
(A) and (B) only | |
(A),(B) and (C) only | |
(A) and (D) only |
Question 16 Explanation:
Alpha-beta pruning is a modified version of the minimax algorithm. It is an optimization technique for the minimax algorithm.
Alpha-beta Algorithm:
- Uses Depth first search
- only considers nodes along a single path from root at any time
α = highest-value choice found at any choice point of path for MAX (initially, α = −infinity)
β = lowest-value choice found at any choice point of path for MIN (initially, β = +infinity)
- Pass current values of α and β down to child nodes during search.
- Update values of α and β during search:
- MAX updates α at MAX nodes
- MIN updates β at MIN nodes
When to Prune:
- Prune whenever α ≥ β.
- Prune below a Max node whose alpha value becomes greater than or equal to the beta value of its ancestors.
- Max nodes update alpha based on children’s returned values. - Prune below a Min node whose beta value becomes less than or equal to the alpha value of its ancestors.
- Min nodes update beta based on children’s returned values.
Effectiveness of Alpha-Beta Search:
- Alpha/beta best case is O(b(d/2)) rather than O(bd)
- This is the same as having a branching factor of sqrt(b),
- (sqrt(b))d/ = b(d/2) (i.e., we have effectively gone from b to square root of b)
- In chess go from b ~ 35 to b ~ 6
- permitting much deeper search in the same amount of time
- In practice it is often b(2d/3)
Alpha-beta Algorithm:
- Uses Depth first search
- only considers nodes along a single path from root at any time
α = highest-value choice found at any choice point of path for MAX (initially, α = −infinity)
β = lowest-value choice found at any choice point of path for MIN (initially, β = +infinity)
- Pass current values of α and β down to child nodes during search.
- Update values of α and β during search:
- MAX updates α at MAX nodes
- MIN updates β at MIN nodes
When to Prune:
- Prune whenever α ≥ β.
- Prune below a Max node whose alpha value becomes greater than or equal to the beta value of its ancestors.
- Max nodes update alpha based on children’s returned values. - Prune below a Min node whose beta value becomes less than or equal to the alpha value of its ancestors.
- Min nodes update beta based on children’s returned values.
Effectiveness of Alpha-Beta Search:
- Alpha/beta best case is O(b(d/2)) rather than O(bd)
- This is the same as having a branching factor of sqrt(b),
- (sqrt(b))d/ = b(d/2) (i.e., we have effectively gone from b to square root of b)
- In chess go from b ~ 35 to b ~ 6
- permitting much deeper search in the same amount of time
- In practice it is often b(2d/3)
Question 17 |
A 4-stage pipeline has the stage delay as 150,120,160 and 140ns respectively. Registers that are used between the stages have delay of 5ns. Assuming constant locking rate, the total time required to process 1000 data items on this pipeline is____?
160.5 ms | |
165.5 ms | |
120.5 ms | |
590.5 ms |
Question 17 Explanation:
First instruction will take complete four cycle for execution. And then after that all 999 instruction will take only 1 cycle for execution to be completed. So time required to process 1000 instruction or data items is,
1st instruction × 4 × clock time + 999 instruction × 1 × clock time
1 × 4 × 165ns + 999 × 1 × 165ns
= 1654.95ns
= 165.5μs
1st instruction × 4 × clock time + 999 instruction × 1 × clock time
1 × 4 × 165ns + 999 × 1 × 165ns
= 1654.95ns
= 165.5μs
Question 18 |
There are three boxes, first box has 2 white, 3 black and 4 red balls. Second box has 3 white, 2 black and 2 red balls. Third box has 4 white, 1 black and 3 red balls. A box is chosen at random, and 2 balls are drawn out of which 1 is white, and 1 is red. What is the probability that the balls came from first box?
0.237 | |
0.723 | |
0.18 | |
0.452 |
Question 19 |
Given below are two statements : one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R):
Assertion (A) : P'
Reason (R): (r→q', rVs, s→q', p→q)
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Assertion (A) : P'
Reason (R): (r→q', rVs, s→q', p→q)
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A) | |
Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is NOT the correct explanation of (A) | |
(A) is true but (R) is false | |
(A) is false but (R) is true |
Question 20 |
Assume that f(n) and g(n) are asymptotically positive. Which of the following is correct?
f(n)=O(g(n)) and g(n)=O(h(n))⇨ f(n)=ω(h(n)) | |
f(n)=Ω(g(n)) and g(n)=Ω(h(n))⇨ f(n)=O(h(n)) | |
f(n)=o(g(n)) and g(n)=o(h(n))⇨ f(n)=o(h(n)) | |
f(n)=ω(g(n)) and g(n)=ω(h(n))⇨ f(n)=Ω(h(n)) |
Question 21 |
Which one is a connectionless transport-layer protocol that belongs to the Internet protocol family?
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) | |
User Datagram Protocol (UDP) | |
Routing Protocol (RP) | |
Datagram Control Protocol (DCP) |
Question 22 |
Consider an error free 64 kbps satellite channel used to send 512-byte data frame in one direction with very short acknowledgements coming back the other way. What is the maximum throughput for window size of 15?
32 kbps | |
48 kbps | |
64 kbps | |
70 kbps |
Question 22 Explanation:
Sliding window will send specified number of frames, wait for one ack for that set of frames
Given, 512 bytes x 8 bits/B = 4096 bits per frame
Transmission time to send one frame= 4096/64000 bps = 64 msec
Propagation time = 270msec
Round trip delay = (2*Propagation time)=540 msec
Transmission time + Round trip delay =604 msec
The maximum throughput is possible when Window size = [1+ 2Tpropagation/Ttransmission]
= (1+2*270/64)=9.43~10
= Window size =15
-The window size will give throughput as maximum bandwidth available that is 64 Kbps
Given, 512 bytes x 8 bits/B = 4096 bits per frame
Transmission time to send one frame= 4096/64000 bps = 64 msec
Propagation time = 270msec
Round trip delay = (2*Propagation time)=540 msec
Transmission time + Round trip delay =604 msec
The maximum throughput is possible when Window size = [1+ 2Tpropagation/Ttransmission]
= (1+2*270/64)=9.43~10
= Window size =15
-The window size will give throughput as maximum bandwidth available that is 64 Kbps
Question 23 |
How many rotations are required during the construction of an AVL tree if the following elements are to be added in the given sequence?
35, 50, 40, 25, 30, 60, 78, 20, 28
35, 50, 40, 25, 30, 60, 78, 20, 28
2 left rotations, 2 right rotations | |
2 left rotations, 3 right rotations | |
3 left rotations, 2 right rotations | |
3 left rotations, 1 right rotations |
Question 24 |
Of the following, which is NOT a logical error?
Using the '=', instead of '==' to determine if two values are equal | |
Divide by zero | |
Failing to initialize counter and total variables before the body of loop. | |
Using commas instead of two required semicolon in a for loop header |
Question 25 |
Let ε=0.0005. and Let Rε be the relation {(x,y)εR2:|x-y|<ε}, Rε could be interpretated as the relation approximately equal. Rε is
(A) Reflexive
(B) Symmetric
(C) Transitive
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(A) Reflexive
(B) Symmetric
(C) Transitive
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(A) and (B) only true | |
(B) and (C) only true | |
(A) and (C) only true | |
(A), (B) and (C) true |
There are 25 questions to complete.
