UGC NET June-2019 CS Paper-2
Question 1 |
How many are there to place 8 indistinguishable balls into four distinguishable bins?
70 | |
165 | |
8 C 4 | |
8 P 4T |
Question 1 Explanation:
This is precisely the problem we saw to solve the r-combination with repetition:
= C(8+4-1,8)
= 11 C 8
= 11! / (8!(11-8)!)
= 165
= C(8+4-1,8)
= 11 C 8
= 11! / (8!(11-8)!)
= 165
Question 2 |
Match List-I with List-II:
List-I List-II
(Software process Models) (Software System)
(a) Waterfall model (i) e-business that starts with only the basic functionality and then moves on to more advanced
features.
(b) Incremental development (ii) An inventory control system for a supermarket to be developed in a highway
(c) Prototyping (iii) A virtual reality system for simulating vehicle navigation in a highway.
(d) RAD (iv) Automate the manual system for student record maintenance in a school
Choose the correct option from those given below:
List-I List-II
(Software process Models) (Software System)
(a) Waterfall model (i) e-business that starts with only the basic functionality and then moves on to more advanced
features.
(b) Incremental development (ii) An inventory control system for a supermarket to be developed in a highway
(c) Prototyping (iii) A virtual reality system for simulating vehicle navigation in a highway.
(d) RAD (iv) Automate the manual system for student record maintenance in a school
Choose the correct option from those given below:
(a)-(ii),(b)-(iv),(c)-(i),(d)-(iii) | |
(a)-(i),(b)-(iii),(c)-(iv),(d)-(ii) | |
(a)-(iii),(b)-(ii),(c)-(iv),(d)-(i) | |
(a)-(iv),(b)-(i),(c)-(iii),(d)-(ii) |
Question 2 Explanation:
Waterfall model→ Automate the manual system for student record maintenance in a school
Incremental development→ e-business that starts with only the basic functionality and then moves on to more advanced features.
Prototyping→ A virtual reality system for simulating vehicle navigation in a highway.
RAD→ An inventory control system for a supermarket to be developed in a highway
Incremental development→ e-business that starts with only the basic functionality and then moves on to more advanced features.
Prototyping→ A virtual reality system for simulating vehicle navigation in a highway.
RAD→ An inventory control system for a supermarket to be developed in a highway
Question 3 |
A computer has six tapes drives with n processes competing for them. Each process may need two drives. What is the maximum value of n for the system to be deadlock free?
5 | |
4 | |
3 | |
6 |
Question 3 Explanation:
Each process needs 2 drives. So for deadlock just give each process one drive. So total 6 process can be given 1 drive each and can cause deadlock. So to break deadlock just reduce 1 process.
So maximum no. of process for the system to be deadlock free is 5.
So maximum no. of process for the system to be deadlock free is 5.
Question 4 |
In the context of 3D computer graphics, which of the following statements is/are TRUE?
P: Orthographics transformations keep parallel lines parallel
Q: Orthographic transformations are affine transformations
Select the correct answer from the options given below:
P: Orthographics transformations keep parallel lines parallel
Q: Orthographic transformations are affine transformations
Select the correct answer from the options given below:
Both P and Q | |
Neither P and Q | |
Only P | |
Only Q |
Question 5 |
Which of the following statements are DMl statements?
(a) Update [tablename]
Set [ columnname] = VALUE
(b) Delete [tablename]
(c) Select * from [tablename]
(a) Update [tablename]
Set [ columnname] = VALUE
(b) Delete [tablename]
(c) Select * from [tablename]
(a) and (b) | |
(a) and (d) | |
(a), (b) and (c) | |
(b) and (c) |
Question 5 Explanation:
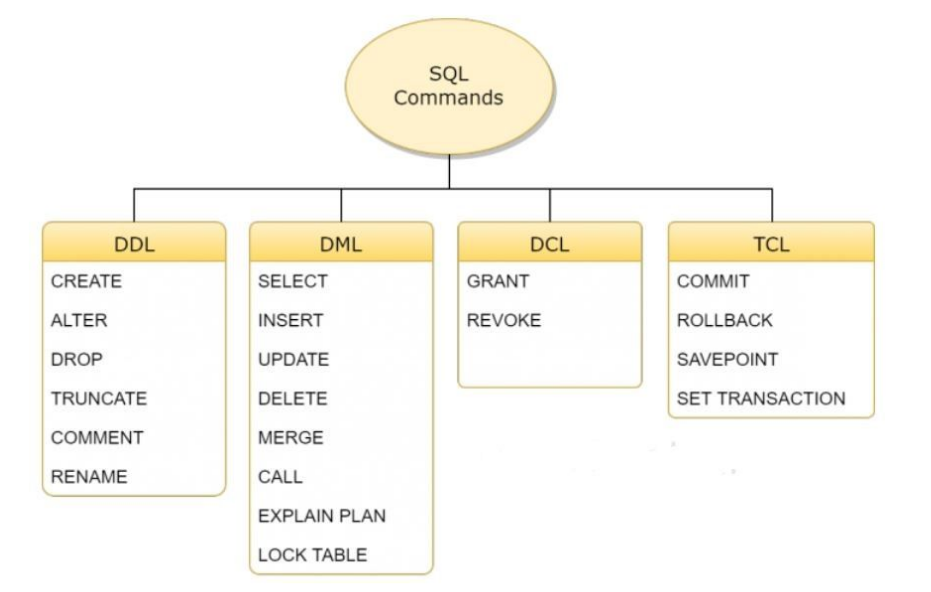
Question 6 |
What percentage(%) of the IPv4, IP address space do all class C addresses consume?
12.5% | |
25% | |
37.5% | |
50% |
Question 6 Explanation:
Total possible IP numbers numbers of all classes 0 to 255.
Class-A: 0 to 127. It means 50%
Class-B: 128 to 191. It means 25%
Class-C: 192 to 223. It means 12.5 %
Class-D: 224 to 239. It means 6.25%
Class-E: 240 to 255. It means 6.25%
Class-A: 0 to 127. It means 50%
Class-B: 128 to 191. It means 25%
Class-C: 192 to 223. It means 12.5 %
Class-D: 224 to 239. It means 6.25%
Class-E: 240 to 255. It means 6.25%
Question 7 |
Which of the following key constraints is required for functioning of foreign key in the context of relational database?
Unique key | |
Primary key | |
candidate key | |
Check key |
Question 7 Explanation:
Foreign key is a key whose values depends on the primary key of a relation. So for the functioning of a foreign key in the context of relational database we need a primary key.
Question 8 |
Software Reuse is
The process of analysing software with the objective of recovering its design and specification | |
The process of existing software artifacts and knowledge to build new software | |
Concerned with reimplementing legacy system to make them more maintainable | |
The process of analysing software to create a representation of a higher level of abstraction and breaking software down into its parts to see how it works |
Question 8 Explanation:
Software Reuse is the process of existing software artifacts and knowledge to build new software.
Question 9 |
Which of the following is principal conjunctive normal form for [(pVq) ∧ ~p → ~q]?
pV~q | |
pVq | |
~p Vq | |
~p V ~q |
Question 9 Explanation:
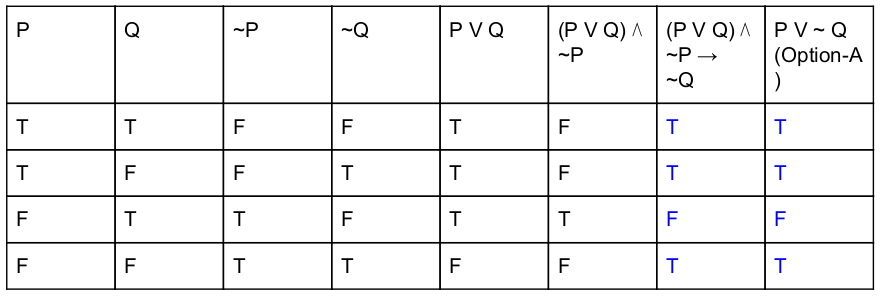
Question 10 |
Match List-I with List-II
List-I List-II
(a) p → q (i) ¬(q → ¬p)
(b) p v q (ii) p ∧ ¬q
(c) p ∧ q (iii) ¬p → q
(d) ¬(p → q) (iv) ¬p v q
Choose the correct option from those given below:
List-I List-II
(a) p → q (i) ¬(q → ¬p)
(b) p v q (ii) p ∧ ¬q
(c) p ∧ q (iii) ¬p → q
(d) ¬(p → q) (iv) ¬p v q
Choose the correct option from those given below:
(a)-(ii);(b)-(iii);(c)-(i);(d)-(iv) | |
(a)-(ii);(b)-(i);(c)-(iii);(d)-(iv) | |
(a)-(iv);(b)-(i);(c)-(iii);(d)-(ii) | |
(a)-(iv);(b)-(iii);(c)-(i);(d)-(ii) |
Question 10 Explanation:
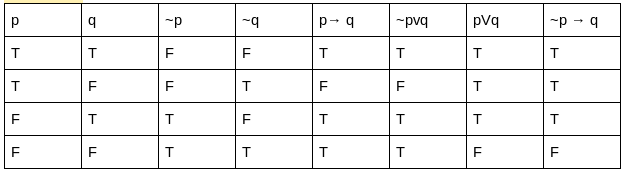
Question 11 |
Consider the following methods:
M 1 : mean of maximum
M 2 : Centre of area
M 3 : Height method
Which of the following is/are defuzzification method(s)?
M 1 : mean of maximum
M 2 : Centre of area
M 3 : Height method
Which of the following is/are defuzzification method(s)?
Only M 1 | |
Only M 1 and M 2 | |
Only M 2and M 3 | |
M 1 , M 2 and M 3 |
Question 11 Explanation:
Defuzzication Methods:
Following defuzzication methods are known to calculate crisp output
→ Maxima Methods
1.Height method
2.First of maxima (FoM)
3.Last of maxima (LoM)
4.Mean of maxima(MoM)
→ Centroid methods:
1. Center of gravity method (CoG)
2. Center of sum method (CoS)
3. Center of area method (CoA)
→ Weighted average method
1.Height method
2.First of maxima (FoM)
3.Last of maxima (LoM)
4.Mean of maxima(MoM)
→ Centroid methods:
1. Center of gravity method (CoG)
2. Center of sum method (CoS)
3. Center of area method (CoA)
→ Weighted average method
Question 12 |
Replacing the expression 4*2.14 by 8.56 is known as
Constant folding | |
Induction variable | |
Strength reduction | |
Code reduction |
Question 12 Explanation:
Take variable i=4*2.14
We are simply folding the value into 8.56 because to avoid multiplication costly operation.
We are simply folding the value into 8.56 because to avoid multiplication costly operation.
Question 13 |
A fuzzy conjunction operator denoted as t(x,y) and fuzzy disjunction operator denoted as s(x,Y) form dual pair if they satisfy the condition:
t(x,y)= 1-s(x,y) | |
t(x,y)=s(1-x,1-y) | |
t(x,y)=1-s(1-x,1-y) | |
t(x,y)=s(1+x,1+y) |
Question 13 Explanation:

Question 14 |
Which data structure is used by the compiler for managing variables and their attributes?
Binary tree | |
link list | |
Symbol table | |
Parse table |
Question 14 Explanation:
Symbol tables are data structures that are used by compilers to hold information about source-program constructs. The information is collected incrementally by the analysis phases of
a compiler and used by the synthesis phases to generate the target code. Entries in the symbol table contains information about an identifier such as its character string (or lexeme) , its type,its position in storage, and any other relevant information.
Question 15 |
Which type of addressing mode, less number of memory references are required?
Immediate | |
Implied | |
register | |
indexed | |
None of the above |
Question 15 Explanation:
Excluded for evaluation
Question 16 |
How many different Boolean functions of degree n are there?
22n | |
(22)2 | |
22n-1 | |
2n |
Question 16 Explanation:
There are 2 n different n-tuples of 0s and 1s.
A Boolean function is an assignment of 0 or 1 to each of these 2 n different n-tuples.
Therefore, there are 2 2^n different Boolean functions.
Example: How many different Boolean functions of degree 4 are there?
Solution: 16

A Boolean function is an assignment of 0 or 1 to each of these 2 n different n-tuples.
Therefore, there are 2 2^n different Boolean functions.
Example: How many different Boolean functions of degree 4 are there?
Solution: 16
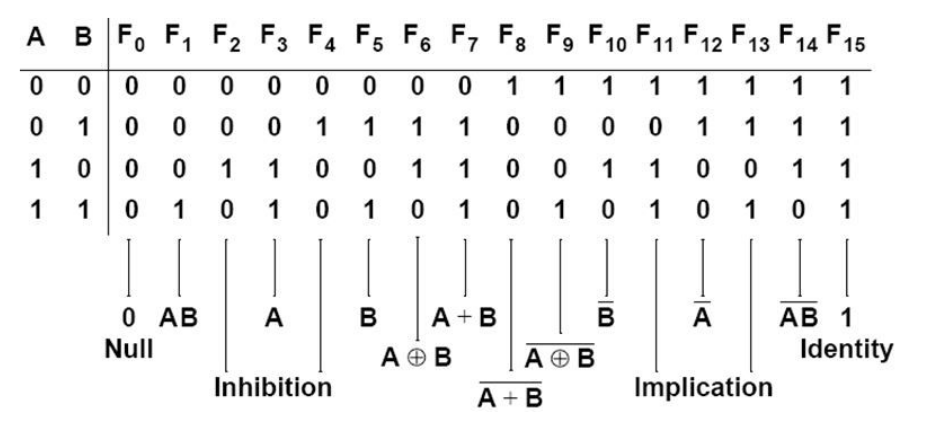
Question 17 |
Consider the equation (146) b + (313) b-2 = (246) 8 . Which of the following is the value of b?
8 | |
7 | |
10 | |
16 |
Question 17 Explanation:
(146)7+(317)7-2=(246)8
Substitute 7 in b,
(146)7+(317)7-2=(246)8
(146)7+(317)5=(246)8
(146)7=1*72+4*71+6*70
=49+28+6
=83
(317)5=3*52+1*51+7*50
=75+5+7
= 87
(246)8=2*82+4*81+6*80
=128+32+6
= 166
∴ (146)7+(317)5=(246)8
=83+87
=166
166=166
LHS = RHS equal only if b is 7.
Substitute 7 in b,
(146)7+(317)7-2=(246)8
(146)7+(317)5=(246)8
(146)7=1*72+4*71+6*70
=49+28+6
=83
(317)5=3*52+1*51+7*50
=75+5+7
= 87
(246)8=2*82+4*81+6*80
=128+32+6
= 166
∴ (146)7+(317)5=(246)8
=83+87
=166
166=166
LHS = RHS equal only if b is 7.
Question 18 |
Match List-I with List-II
List-I List-II
(a) Disk (i) Thread
(b) CPU (ii) Signal
(c) Memory (iii) File System
(d) Interrupt (iv) Virtual address
Choose the correct option from those given below:
List-I List-II
(a) Disk (i) Thread
(b) CPU (ii) Signal
(c) Memory (iii) File System
(d) Interrupt (iv) Virtual address
Choose the correct option from those given below:
(a)-(i); (b)-(ii); (c)-(iii); (d)-(iv) | |
(a)-(iii); (b)-(i); (c)-(iv); (d)-(ii) | |
(a)-(ii); (b)-(i); (c)-(iv); (d)-(iii) | |
(a)-(ii); (b)-(iv); (c)-(iii);(d)-(i) |
Question 18 Explanation:
Disk--> File system
CPU → Thread
memory → Virtual address space
Interrupt → Signal
CPU → Thread
memory → Virtual address space
Interrupt → Signal
Question 19 |
In the TCP/IP model, encryption and decryption are functions of ____ layer
data link | |
network | |
Transport | |
Application |
Question 19 Explanation:
encryption and decryption are functions of presentation layer in the OSI reference model. Here, they were given TCP/IP model. It combines Session, presentation and Application layers into Application layer.
Question 20 |
Suppose that a connected planar graph has six vertices, each of degrees four. Into how many regions is the plane divided by a planar representation of this graph?
6 | |
8 | |
12 | |
10 |
Question 20 Explanation:
We apply Euler’s formula where r = e−v + 2.
Since each vertex has degree 4, the sum of the degrees is 24.
By the handshaking theorem, 2e = 24 .
so, e = 12.
r = 12−6 + 2
r = 8
Thus we have 8 regions in this planar graph.
Since each vertex has degree 4, the sum of the degrees is 24.
By the handshaking theorem, 2e = 24 .
so, e = 12.
r = 12−6 + 2
r = 8
Thus we have 8 regions in this planar graph.
Question 21 |
Consider a disk system with 100 cylinders. The requests to access the cylinders occur in the following sequence:
4,34,10,7,19,73,2,15,6,20
Assuming that the head is current at cylinder 50, what is the time taken to satisfy all requests if it takes 1ms to move from the cylinder to adjacent one and the shortest seek time first policy is used?
4,34,10,7,19,73,2,15,6,20
Assuming that the head is current at cylinder 50, what is the time taken to satisfy all requests if it takes 1ms to move from the cylinder to adjacent one and the shortest seek time first policy is used?
357 ms | |
238 ms | |
276 ms | |
119 ms |
Question 21 Explanation:
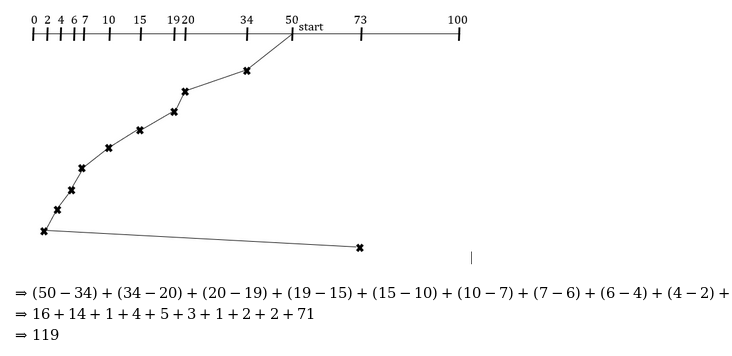
Question 22 |
Which of the following problems is/are decidable problem(s) (recursively enumerable) on a Turing machine M?
(a) G is a CFG with L(G)=∅
(b) There exist two TMs M1 and M2 such that L(M) ⊆{L(M1)UL(M2)}= language of all TMs
(c) M is a TM that accepts w using a most 2|w| cells of tape
(a) G is a CFG with L(G)=∅
(b) There exist two TMs M1 and M2 such that L(M) ⊆{L(M1)UL(M2)}= language of all TMs
(c) M is a TM that accepts w using a most 2|w| cells of tape
(a) and (b) only | |
(a) only | |
(a), (b) and (c) | |
(c) only |
Question 22 Explanation:
(a): L(G)=∅ is a emptiness problem and emptiness problem for context free languages is decidable.
(b): Recursive: The reason is we can assume L(M2)=∑* and hence any TM (M1) will be definitely subset of L(M2). So we only need to see that M1 is a valid Turing machine and no need to check whether it is subset of L(M2) as it is obviously subset of L(M2)=∑*. Checking validity of Turing machine is always a halting process, hence it is recursive.
(c): L={(M,w)|M is a TM that accepts w using at most 2|w| squares of its tape}.
Recursive: Let m be he number of states in M, and k be the size of the alphabet that M uses, and r=|w|. If M uses at most 2r squares of its tape, then there are at most Alpha=mK2r 2r configurations(why?). If M runs on w for more than α steps, and does not use more than 2r squares of its tape, then M must be in the one configuration at least twice(pigeonhole principle), in which case M would enter an infinite loop on input w. Based on this, we design a machine M* that decides L that works as follows:
M* runs M on w for at most α+1 steps.
If M accepts w which steps with using at most 2r squares, M* halts and accepts.
If M rejects w within α steps with using at most 2r squares, M* halts and rejects.
If M goes beyond 2r squares, M* halts and rejects.
If M does not halt and does not go beyond 2r squares, M* rejects.
Note: To know the definition of configurations and the details, reader may refer to "Introduction to theory of computation Michael Sipser, Chapter 8 Space complexity)
(b): Recursive: The reason is we can assume L(M2)=∑* and hence any TM (M1) will be definitely subset of L(M2). So we only need to see that M1 is a valid Turing machine and no need to check whether it is subset of L(M2) as it is obviously subset of L(M2)=∑*. Checking validity of Turing machine is always a halting process, hence it is recursive.
(c): L={(M,w)|M is a TM that accepts w using at most 2|w| squares of its tape}.
Recursive: Let m be he number of states in M, and k be the size of the alphabet that M uses, and r=|w|. If M uses at most 2r squares of its tape, then there are at most Alpha=mK2r 2r configurations(why?). If M runs on w for more than α steps, and does not use more than 2r squares of its tape, then M must be in the one configuration at least twice(pigeonhole principle), in which case M would enter an infinite loop on input w. Based on this, we design a machine M* that decides L that works as follows:
M* runs M on w for at most α+1 steps.
If M accepts w which steps with using at most 2r squares, M* halts and accepts.
If M rejects w within α steps with using at most 2r squares, M* halts and rejects.
If M goes beyond 2r squares, M* halts and rejects.
If M does not halt and does not go beyond 2r squares, M* rejects.
Note: To know the definition of configurations and the details, reader may refer to "Introduction to theory of computation Michael Sipser, Chapter 8 Space complexity)
Question 23 |
Consider Euler's Φ function given by
Φ(n)=nπp|n(1-(1/p))
Where p runs over all the primes dividing n. What is the value of Φ(45)?
Φ(n)=nπp|n(1-(1/p))
Where p runs over all the primes dividing n. What is the value of Φ(45)?
3 | |
12 | |
6 | |
24 |
Question 23 Explanation:
Φ(45) → Φ(9*5)
→ Φ(32 * 5)
→ Φ(32) * Φ(5)
→ Φ(32 - 3,(2-1)) * (5-1)
= 24
Remember Formula:
If p is prime then Φ(p) = (p-1)
and if p is not prime and it's in prime power k from then Φ(pk) = pk - p(k-1)
→ Φ(32 * 5)
→ Φ(32) * Φ(5)
→ Φ(32 - 3,(2-1)) * (5-1)
= 24
Remember Formula:
If p is prime then Φ(p) = (p-1)
and if p is not prime and it's in prime power k from then Φ(pk) = pk - p(k-1)
Question 24 |
Consider double hashing of the form
h(k,i)=(h 1 (k)+ih 2 (k)) mod m
Where h 1 (k)=k mod m
h 2 (k)=1+(k mod n)
Where n=m-1and m=701
for k=123456, what is the difference between first and second probes in terms of slots?
h(k,i)=(h 1 (k)+ih 2 (k)) mod m
Where h 1 (k)=k mod m
h 2 (k)=1+(k mod n)
Where n=m-1and m=701
for k=123456, what is the difference between first and second probes in terms of slots?
255 | |
256 | |
257 | |
258 |
Question 24 Explanation:
Given h(k,i)=h1(k)+ih2(k)
where h1(k)=k mod m
h2(k)=1+k mod n
where n=m-1 and m=701. For k=123456
h1(k)=123456 mod 701
h1(k)=80
h2(k)=1+(123456 mod 700)
h2(k)=1+256=257
1st probe: i=1
h(k,i)=h1(k)+ih2(k)
h(k,1)=h1(k)+ih2(k)
h(k,1)=80+257=337
h(k,1)=337
2nd probe: i=2
h(k,2)=80+2257
h(k,2)=80+514
h(k,2)=594
∴ Difference h(k,2)-h(k,1)
594-337
257
where h1(k)=k mod m
h2(k)=1+k mod n
where n=m-1 and m=701. For k=123456
h1(k)=123456 mod 701
h1(k)=80
h2(k)=1+(123456 mod 700)
h2(k)=1+256=257
1st probe: i=1
h(k,i)=h1(k)+ih2(k)
h(k,1)=h1(k)+ih2(k)
h(k,1)=80+257=337
h(k,1)=337
2nd probe: i=2
h(k,2)=80+2257
h(k,2)=80+514
h(k,2)=594
∴ Difference h(k,2)-h(k,1)
594-337
257
There are 24 questions to complete.
